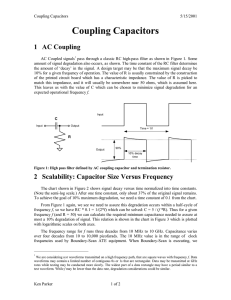
Coupling Capacitors (Updated 5-15
... of the printed circuit board which has a characteristic impedance. The value of R is picked to match this impedance, and it will usually be somewhere near 50 ohms, which is assumed here. This leaves us with the value of C which can be chosen to minimize signal degradation for an expected operational ...
... of the printed circuit board which has a characteristic impedance. The value of R is picked to match this impedance, and it will usually be somewhere near 50 ohms, which is assumed here. This leaves us with the value of C which can be chosen to minimize signal degradation for an expected operational ...
Slide 1
... switching pulse width and frequency to stabilize the output. SW Transformer : Step down the voltage with a high frequency transformer. ...
... switching pulse width and frequency to stabilize the output. SW Transformer : Step down the voltage with a high frequency transformer. ...
Key_P1 - Weber State University
... with time-delay (time delay t=phase ϕ/(360*frequency f)). Linear phase indicates that there is going to be same time delay for all the frequencies, since t will be the same. This allows for all the harmonics to be delayed by the same amount 360 f which is important for processing an input ...
... with time-delay (time delay t=phase ϕ/(360*frequency f)). Linear phase indicates that there is going to be same time delay for all the frequencies, since t will be the same. This allows for all the harmonics to be delayed by the same amount 360 f which is important for processing an input ...
B1501
... Hydrophone and Filter Amplifier Battery Powered / Chargevoltage 24Volt Batteries and Controlbuttons inside box Low Pass Filter for anti-aliasing filtering 2.nd order filter 12dB/oct. -6dB @ frequency High Pass Filter for filtering off low-freq. seawaves. 1.st order filter 6dB/oct. -3dB @ frequency U ...
... Hydrophone and Filter Amplifier Battery Powered / Chargevoltage 24Volt Batteries and Controlbuttons inside box Low Pass Filter for anti-aliasing filtering 2.nd order filter 12dB/oct. -6dB @ frequency High Pass Filter for filtering off low-freq. seawaves. 1.st order filter 6dB/oct. -3dB @ frequency U ...
Pamukkale Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilimleri Dergisi
... principle [7]. Afterward studies that were lead to SRD filters, the quadratic law of MOS in strong inversion region and saturation region and the voltage translinear principle were used [8]-[12]. Companding filters were studied by a number of researchers, because these filters have the advantages of ...
... principle [7]. Afterward studies that were lead to SRD filters, the quadratic law of MOS in strong inversion region and saturation region and the voltage translinear principle were used [8]-[12]. Companding filters were studied by a number of researchers, because these filters have the advantages of ...
High pass filter
... Let‘s construct the gain-frequency characteristic of the RC high-pass filter. Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency to the input of the circuit. If the frequency becomes lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. No DC current can pass through the capacitor because ther ...
... Let‘s construct the gain-frequency characteristic of the RC high-pass filter. Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency to the input of the circuit. If the frequency becomes lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. No DC current can pass through the capacitor because ther ...
components - Purdue Physics
... Therefore, the two time constants set the minimum resonance frequency, but f r can be increased by making R3 smaller than R1 . The band-pass (B) is defined as the frequency interval between the high and low break-frequencies (i.e., the frequencies at which gain is decreased by 30%). B(Hz) = 2 R2C ...
... Therefore, the two time constants set the minimum resonance frequency, but f r can be increased by making R3 smaller than R1 . The band-pass (B) is defined as the frequency interval between the high and low break-frequencies (i.e., the frequencies at which gain is decreased by 30%). B(Hz) = 2 R2C ...
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 13: Active Filters
... 8) Homework Assume that the open-loop gain is sufficiently large that terms with A−1 can be neglected. Calculate the approximate resonance frequency f r . Use this approximation to calculate f r including the A−1 terms. Calculate the gain at resonance ( Gr ) and the band-width (B). 9) Homework Set u ...
... 8) Homework Assume that the open-loop gain is sufficiently large that terms with A−1 can be neglected. Calculate the approximate resonance frequency f r . Use this approximation to calculate f r including the A−1 terms. Calculate the gain at resonance ( Gr ) and the band-width (B). 9) Homework Set u ...
Chapter 14
... • Resonance here occurs when the imaginary part of the admittance is zero. • This results in the same resonant frequency as in the series circuit. ...
... • Resonance here occurs when the imaginary part of the admittance is zero. • This results in the same resonant frequency as in the series circuit. ...
The two problems below replace Diefenderfer & Holton, Chapter 3, Problem 24: D&H problem 324 as stated has a typo. There should be an absolute value bracket around the right
... side, and a "j" in front of the CR2 term. Here is the actual problem that you should solve, the first part is the typocorrected DH, and the second part is additional: 1. Derive the following transfer function expression for the circuit of Figure E: vo vs ...
... side, and a "j" in front of the CR2 term. Here is the actual problem that you should solve, the first part is the typocorrected DH, and the second part is additional: 1. Derive the following transfer function expression for the circuit of Figure E: vo vs ...
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course Presentation
... C. The difference between the repeater’s transmit and receive frequencies D. The maximum frequency deviation permitted on the repeater’s input signal ...
... C. The difference between the repeater’s transmit and receive frequencies D. The maximum frequency deviation permitted on the repeater’s input signal ...
Document
... – Identify the source sinusoid and note the frequency – Convert the source(s) to complex/phasor form (you can ignore the ωt component at this point) – Represent each circuit element by it's AC impedance. Impedances add like resistors. – Solve the resulting phasor circuit using standard circuit solvi ...
... – Identify the source sinusoid and note the frequency – Convert the source(s) to complex/phasor form (you can ignore the ωt component at this point) – Represent each circuit element by it's AC impedance. Impedances add like resistors. – Solve the resulting phasor circuit using standard circuit solvi ...
A Systematic Design of Electronically Tunable Ladder Filters Employing DO-OTAs
... of RLC ladder filter using only DO-OTAs and grounded capacitors that lead to simple structure, easy to design and suitable for IC fabrication. A fifth-order Chebyshev low-pass filter and a sixth-order Chebyshev band-pass filter which retain a minimum requirement of passive elements and have an advan ...
... of RLC ladder filter using only DO-OTAs and grounded capacitors that lead to simple structure, easy to design and suitable for IC fabrication. A fifth-order Chebyshev low-pass filter and a sixth-order Chebyshev band-pass filter which retain a minimum requirement of passive elements and have an advan ...
1.5V Square-Root Domain Band-Pass Filter With Stacking Technique
... saturation region to implement the square-root domain filters. In this paper, a square-root domain filter scheme based on the MOSFET square law to implement the band-pass and is proposed. The aims are to establish an adjustable Q architecture and to increase the operation frequency. The presented ci ...
... saturation region to implement the square-root domain filters. In this paper, a square-root domain filter scheme based on the MOSFET square law to implement the band-pass and is proposed. The aims are to establish an adjustable Q architecture and to increase the operation frequency. The presented ci ...
Lecture 5: RC Filters. Series Resonance and
... That is, Q is the ratio of the resonant frequency divided by the 3dB frequency bandwidth. A series RLC circuit is used as the RF Filter in the NorCal 40A. (See Fig. 1.13 and the circuit on the front flap.) You’ll start the construction of this filter in Prob. 8. Recall that in a superhet receiver, t ...
... That is, Q is the ratio of the resonant frequency divided by the 3dB frequency bandwidth. A series RLC circuit is used as the RF Filter in the NorCal 40A. (See Fig. 1.13 and the circuit on the front flap.) You’ll start the construction of this filter in Prob. 8. Recall that in a superhet receiver, t ...
DL25667670
... multi-layer technology can be used as a reduced size bandpass filter [6], [7]. However, conventionally the electrical length has been recommended by 45º or less for efficient coupling [8]. Nowadays SAW filters are widely used in the mobile communication market. But they are still not compatible with ...
... multi-layer technology can be used as a reduced size bandpass filter [6], [7]. However, conventionally the electrical length has been recommended by 45º or less for efficient coupling [8]. Nowadays SAW filters are widely used in the mobile communication market. But they are still not compatible with ...
EMC Filters
... statements about the suitability of our products for a particular customer application. As a rule, EPCOS is either unfamiliar with individual customer applications or less familiar with them than the customers themselves. For these reasons, it is always ultimately incumbent on the customer to check ...
... statements about the suitability of our products for a particular customer application. As a rule, EPCOS is either unfamiliar with individual customer applications or less familiar with them than the customers themselves. For these reasons, it is always ultimately incumbent on the customer to check ...
Op Amp article - New Electronics
... a dual filter based on the LTC6601. Three versions enable cutoff frequencies ranging from 6.5MHz to 25MHz. These dual channel filters have guaranteed gain and phase matching specifications. They are designed to be drop in, small form factor solutions with minimum external components. The LT6604 fami ...
... a dual filter based on the LTC6601. Three versions enable cutoff frequencies ranging from 6.5MHz to 25MHz. These dual channel filters have guaranteed gain and phase matching specifications. They are designed to be drop in, small form factor solutions with minimum external components. The LT6604 fami ...
TEP High-pass and low-pass filters with Cobra3 TEP High
... Set-up and procedure Connect the Function Generator Module to the Cobra3 unit and set up the equipment according to Fig. 1. Connect the Cobra3 unit to your computer to port COM1, COM2 or to USB port (for USB computer port use USB to RS232 Converter 14602.10). Connect both Cobra3 and Function Generat ...
... Set-up and procedure Connect the Function Generator Module to the Cobra3 unit and set up the equipment according to Fig. 1. Connect the Cobra3 unit to your computer to port COM1, COM2 or to USB port (for USB computer port use USB to RS232 Converter 14602.10). Connect both Cobra3 and Function Generat ...
COURSE NUMBER: E E 352 Design of a Low
... This may be attributable in part to implementing resistor values slightly below the calculated resistances. In general for filters of this type, greater resistance translates to poles at lower frequencies. Moreover, the potentiometer inserted as a volume control placed limits on the gain achievable ...
... This may be attributable in part to implementing resistor values slightly below the calculated resistances. In general for filters of this type, greater resistance translates to poles at lower frequencies. Moreover, the potentiometer inserted as a volume control placed limits on the gain achievable ...
141 EBI100C Electrical Bio-Impedance Amplifier The EBI100C
... The EBI100C records the parameters associated with cardiac output measurements, thoracic impedance changes as a function of respiration or any kind of biological impedance monitoring. The EBI100C incorporates a precision high frequency current source, which injects a very small (100µA) current throu ...
... The EBI100C records the parameters associated with cardiac output measurements, thoracic impedance changes as a function of respiration or any kind of biological impedance monitoring. The EBI100C incorporates a precision high frequency current source, which injects a very small (100µA) current throu ...
Distributed element filter
A distributed element filter is an electronic filter in which capacitance, inductance and resistance (the elements of the circuit) are not localised in discrete capacitors, inductors and resistors as they are in conventional filters. Its purpose is to allow a range of signal frequencies to pass, but to block others. Conventional filters are constructed from inductors and capacitors, and the circuits so built are described by the lumped element model, which considers each element to be ""lumped together"" at one place. That model is conceptually simple, but it becomes increasingly unreliable as the frequency of the signal increases, or equivalently as the wavelength decreases. The distributed element model applies at all frequencies, and is used in transmission line theory; many distributed element components are made of short lengths of transmission line. In the distributed view of circuits, the elements are distributed along the length of conductors and are inextricably mixed together. The filter design is usually concerned only with inductance and capacitance, but because of this mixing of elements they cannot be treated as separate ""lumped"" capacitors and inductors. There is no precise frequency above which distributed element filters must be used but they are especially associated with the microwave band (wavelength less than one metre).Distributed element filters are used in many of the same applications as lumped element filters, such as selectivity of radio channel, bandlimiting of noise and multiplexing of many signals into one channel. Distributed element filters may be constructed to have any of the bandforms possible with lumped elements (low-pass, band-pass, etc.) with the exception of high-pass, which is usually only approximated. All filter classes used in lumped element designs (Butterworth, Chebyshev, etc.) can be implemented using a distributed element approach.There are many component forms used to construct distributed element filters, but all have the common property of causing a discontinuity on the transmission line. These discontinuities present a reactive impedance to a wavefront travelling down the line, and these reactances can be chosen by design to serve as approximations for lumped inductors, capacitors or resonators, as required by the filter.The development of distributed element filters was spurred on by the military need for radar and electronic counter measures during World War II. Lumped element analogue filters had long before been developed but these new military systems operated at microwave frequencies and new filter designs were required. When the war ended, the technology found applications in the microwave links used by telephone companies and other organisations with large fixed-communication networks, such as television broadcasters. Nowadays the technology can be found in several mass-produced consumer items, such as the converters (figure 1 shows an example) used with satellite television dishes.