* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lab 1 - filters
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Analogue filter wikipedia , lookup
Linear filter wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
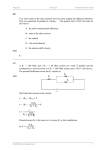
WLS 501 NAME: lab 01 Winter 2011 Student Number: Introduction to low pass and high pass filters Objective: To study the characteristics of passive low pass filters and passive high pass filters. Equipment and components required: Signal generator Capacitors with different range of values Resistors with range of values Connecting cables Oscilloscope and connecting leads a) Low Pass Filter with cut-off frequency of 30 KHz Draw RC circuit to show low pass filter Select an appropriate capacitor value between 1 nF and 20 nF Value of Capacitor Selected: Calculate the Value of Resistor required so that cut-off frequency for the low pass filter is 30 KHz Use the formula: fc = 1/(2RC) Calculated value of the Resistor: Select the closest value of the resistor (make sure that the calculated value is practical value like 300 Ohms or 1 KOhms or 10 KOhms etc.: Connect the RC Low Pass Filter Circuit Turn the Signal Generator On and set the frequency to 1000 Hz. Set the peak-to-peak voltage as 1 Volt. For all values of WLS 501 NAME: lab 01 Winter 2011 Student Number: frequencies given below, make sure that the voltage is kept at 1 Volt peak-to-peak. Fill in the following table: Frequency 1000 Hz 10000 Hz 20000 Hz 22000 Hz 23000 Hz 24000 Hz 25000 Hz 26000 Hz 28000 Hz 29000 Hz 29200 Hz 29400 Hz 29600 Hz 29800 Hz 30000 Hz 31000 Hz 32000 Hz 33000 Hz b) Vin Vout Vout/Vin dB RC High Pass Filter with cut-off frequency of 1 KHz Draw RC circuit to represent high pass filter Select an appropriate capacitor value between 1 nF and 20 nF Value of Capacitor Selected: WLS 501 NAME: lab 01 Winter 2011 Student Number: Calculate the value of Resistor so that cut-off frequency for the high pass filter is 1 KHz Use the formula: fc = 1/(2RC) Calculated value of the Resistor: Select the resistor having closest practical value: Connect the RC High Pass Filter Circuit Turn on the Signal Generator and set the frequency to 100 Hz. Set the peak-to-peak voltage as 1 Volt. For all values of frequencies given below, make sure that the voltage is kept at 1 Volt peak-to-peak. Fill in the following table: Frequency 50 Hz 100 Hz 200 Hz 300 Hz 400 Hz 500 Hz 600 Hz 700 Hz 800 Hz 900 Hz 950 Hz 960 Hz 970 Hz 980 Hz 990 Hz 1000 Hz 1100 Hz 1200 Hz Vin Vout Vout/Vin dB WLS 501 NAME: lab 01 Winter 2011 Student Number: