here
... sheaths allow nerve impulses to transmit more quickly along the axon. Sensory neurons – carry nerve impulses (e.g. vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with ...
... sheaths allow nerve impulses to transmit more quickly along the axon. Sensory neurons – carry nerve impulses (e.g. vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with ...
6. Brain Lateralization
... Next, with the aid of a computer, this energy is converted into three-dimensional pictures. A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems. In case of brain study, we follow the same procedure and study the function of ...
... Next, with the aid of a computer, this energy is converted into three-dimensional pictures. A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems. In case of brain study, we follow the same procedure and study the function of ...
02Biology of the brain
... to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lobe damage? A. B. C. D. ...
... to his frontal lobe. She is perplexed by his behavior. Which of the following would you tell her is “normal behavior” for a person with frontal lobe damage? A. B. C. D. ...
Morphological Basis of Learning and Memory: Vertebrates
...
...
At least three other synapse features appear to be sensitive to experience. First, small discontinuities in the postsynaptic density, termed perforations, have been found to increase in number following complex environment exposure and to decrease in affected synapses subsequent to sensory ...
Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... Aggression; Serial killers low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
... Aggression; Serial killers low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
Information Processing
... of information, sometimes described as 7 + /- 2. it is called working memory because it is where new information is temporarily placed while it is mentally processed. STM maintain information for a limited time, until the learner has adequate resources to process the information, or until the inform ...
... of information, sometimes described as 7 + /- 2. it is called working memory because it is where new information is temporarily placed while it is mentally processed. STM maintain information for a limited time, until the learner has adequate resources to process the information, or until the inform ...
Alzheimer`s Disease and its Effects on the Central Nervous System
... Alzheimer’s Disease and its Effects on the Central Nervous System Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person’s memory and his ability to learn, make judgments, communicate, and carry out daily activities as well as eventually bringing about his or her ...
... Alzheimer’s Disease and its Effects on the Central Nervous System Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person’s memory and his ability to learn, make judgments, communicate, and carry out daily activities as well as eventually bringing about his or her ...
Biological Impact
... • For convenience sake, each hemisphere of the brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions.. • The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cortex that carries the ...
... • For convenience sake, each hemisphere of the brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions.. • The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cortex that carries the ...
The Nervous System
... object with your hand. The impulse is sent to the spinal cord immediately. The spinal cord responds by sending impulses to your arm muscles to cause you to quickly pull ...
... object with your hand. The impulse is sent to the spinal cord immediately. The spinal cord responds by sending impulses to your arm muscles to cause you to quickly pull ...
This Week at Elida - Elida Local Schools
... In addition, greater inter connectedness among various regions of the brain allows for better communication between parts associated with different functions. For example, connections between regions of the brain responsible for logical reasoning become better connected with those responsible for ex ...
... In addition, greater inter connectedness among various regions of the brain allows for better communication between parts associated with different functions. For example, connections between regions of the brain responsible for logical reasoning become better connected with those responsible for ex ...
Morphological Basis of Learning and Memory: Vertebrates
... Greenough (1972) followed up these findings, reporting that visual cortical neurons of rats reared in enriched environments had larger dendritic fields than did those of cage housed controls. Dendrites of neurons receive the bulk of the synaptic input (see Figure 1), so the implication was that new ...
... Greenough (1972) followed up these findings, reporting that visual cortical neurons of rats reared in enriched environments had larger dendritic fields than did those of cage housed controls. Dendrites of neurons receive the bulk of the synaptic input (see Figure 1), so the implication was that new ...
Memory - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... – Garven et al. (1998) looked at techniques used in McMartin PreSchool Case and found that they greatly increased false allegations from 15% to 80% (Big statement: Other Kids said this happened) – In 2000 Garven, Wood, and Malpass did a similar study using positive reinforcers to reporting false all ...
... – Garven et al. (1998) looked at techniques used in McMartin PreSchool Case and found that they greatly increased false allegations from 15% to 80% (Big statement: Other Kids said this happened) – In 2000 Garven, Wood, and Malpass did a similar study using positive reinforcers to reporting false all ...
Chapter 3
... amphetamines Smoking Dopamine Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
... amphetamines Smoking Dopamine Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
Chapter 2
... amphetamines Smoking Dopamine Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
... amphetamines Smoking Dopamine Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
Love Is The Most Powerful Healing Force In The World
... fired in the frontal lobe of a monkey when it grabbed a peanut. The curious thing was that, in another monkey who was watching the first monkey grab the peanut, the same cluster of cells fired. The cells seemed to reflect the actions of the other monkey almost like a mirror reflects one’s image. As ...
... fired in the frontal lobe of a monkey when it grabbed a peanut. The curious thing was that, in another monkey who was watching the first monkey grab the peanut, the same cluster of cells fired. The cells seemed to reflect the actions of the other monkey almost like a mirror reflects one’s image. As ...
2 CHAPTER The Biology of Behavior Chapter Preview Our nervous
... synaptic gap between neurons and pass on excitatory or inhibitory messages. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic nervous system, which directs voluntary movements and reflexes, and the autonomic nervous system, which ...
... synaptic gap between neurons and pass on excitatory or inhibitory messages. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic nervous system, which directs voluntary movements and reflexes, and the autonomic nervous system, which ...
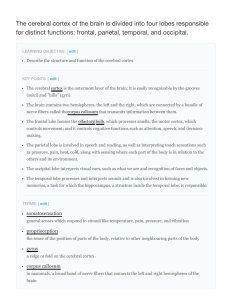
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... patients' left visual fields, they may be unable to verbally name the object (and may claim not to have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and is unable to signal to the speech center, which generally is found i ...
... patients' left visual fields, they may be unable to verbally name the object (and may claim not to have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and is unable to signal to the speech center, which generally is found i ...
Memory
... windows while counting phonologically) on a certain task, but we can’t use one tool twice at the same time (counting number of words in the sentence because numbers and words are verbal labels). ...
... windows while counting phonologically) on a certain task, but we can’t use one tool twice at the same time (counting number of words in the sentence because numbers and words are verbal labels). ...
Functional Neural Anatomy
... Species-differences involve differences in “smoothness” and differences in the amount of cortex relative to the body, which is related to species-typical diets (e.g., fruit-eating bats have relatively bigger brains than insect-eating bats; carnivores have relatively bigger brains than herbivores) an ...
... Species-differences involve differences in “smoothness” and differences in the amount of cortex relative to the body, which is related to species-typical diets (e.g., fruit-eating bats have relatively bigger brains than insect-eating bats; carnivores have relatively bigger brains than herbivores) an ...