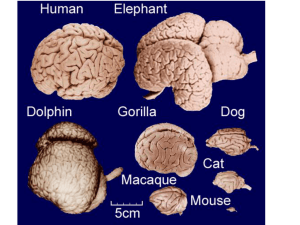
The Nervous System
... Describe how the nervous system detects signals and transmits information. ...
... Describe how the nervous system detects signals and transmits information. ...
Articles about the Brain Works
... still learning exactly how memory works, but they know that short term memory allows us to remember something for a very short time without rehearsing or practicing it. We can't remember a lot of things in short term memory though, and, like its name suggests, these memories don't last very long. Th ...
... still learning exactly how memory works, but they know that short term memory allows us to remember something for a very short time without rehearsing or practicing it. We can't remember a lot of things in short term memory though, and, like its name suggests, these memories don't last very long. Th ...
Perceptrons
... used by brain cells as messengers. They are stored in the vesicles in the nerve ending ready to be released • Receptors - these are structures on the surface of the receiving cell which have a space designed just for the transmitter (if the transmitter is a key, receptors are the lock into which the ...
... used by brain cells as messengers. They are stored in the vesicles in the nerve ending ready to be released • Receptors - these are structures on the surface of the receiving cell which have a space designed just for the transmitter (if the transmitter is a key, receptors are the lock into which the ...
Memory - Caleb Lack
... • How we store our experiences in memory depends on our interpretations and expectations of them • Schemas are organized knowledge structure or mental model that we’ve stored in memory – What happens when you go to a restaurant? ...
... • How we store our experiences in memory depends on our interpretations and expectations of them • Schemas are organized knowledge structure or mental model that we’ve stored in memory – What happens when you go to a restaurant? ...
Sensory Cortex
... A. a regulatory mechanism B. the consciousness switch of the brain C. a relay system D. a bridge between the 2 cerebral hemispheres ...
... A. a regulatory mechanism B. the consciousness switch of the brain C. a relay system D. a bridge between the 2 cerebral hemispheres ...
A neural support vector machine
... rich phenomenology of chaotic itinerancy. Simulations in several different types of artificial neural networks confirm the ubiquity of such stochastic switching. Pantic’, Torres, Kappen, and Gielen (2002) studied models of associative memories with depressible synapses and found a phase with fast os ...
... rich phenomenology of chaotic itinerancy. Simulations in several different types of artificial neural networks confirm the ubiquity of such stochastic switching. Pantic’, Torres, Kappen, and Gielen (2002) studied models of associative memories with depressible synapses and found a phase with fast os ...
Neuroscience and Behavior (The Brain)
... The cerebral cortex • There has also been a cortical area identified that specializes in receiving information from the skin senses and from the movement of body parts • Sensory cortex- the area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations • Stimulate a part of th ...
... The cerebral cortex • There has also been a cortical area identified that specializes in receiving information from the skin senses and from the movement of body parts • Sensory cortex- the area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations • Stimulate a part of th ...
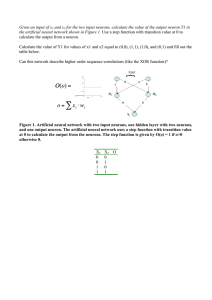
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... Now, we include the “bias” for the input to each neuron. This can be implemented as an addition input neuron to each layer that always has the value 1 (see figure 2). With this additional bias, calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out th ...
... Now, we include the “bias” for the input to each neuron. This can be implemented as an addition input neuron to each layer that always has the value 1 (see figure 2). With this additional bias, calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out th ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... • A. The corpus callosum transfers information between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function ...
... • A. The corpus callosum transfers information between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function ...
Memory
... Children’s eyewitness recall can be unreliable if leading questions are posed. However, if cognitive interviews are neutrally worded, the accuracy of their recall increases. In cases of sexual abuse, this usually suggests a lower percentage of abuse. ...
... Children’s eyewitness recall can be unreliable if leading questions are posed. However, if cognitive interviews are neutrally worded, the accuracy of their recall increases. In cases of sexual abuse, this usually suggests a lower percentage of abuse. ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
Technical Definitions
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
Memory
... 15. To improve your depth of processing, you could go through the items on the list and think about the meaning of each one. What is another way you could improve your depth of processing? a. Study in just one time and place in order to increase the probability of context-dependent memory. b. Study ...
... 15. To improve your depth of processing, you could go through the items on the list and think about the meaning of each one. What is another way you could improve your depth of processing? a. Study in just one time and place in order to increase the probability of context-dependent memory. b. Study ...
Test 3
... 1. List the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system, and describe their relationship to each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mat ...
... 1. List the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system, and describe their relationship to each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mat ...
The Special Senses and Functional Aspects of the Nervous System
... Thought- What is a thought and how is it produced? A thought is a conscious understanding in the brain of image or language or words. It is the result of billions of exchanges of neurotransmitters across billions of synapses and the conductions of millions of impulses through millions of neurons. Th ...
... Thought- What is a thought and how is it produced? A thought is a conscious understanding in the brain of image or language or words. It is the result of billions of exchanges of neurotransmitters across billions of synapses and the conductions of millions of impulses through millions of neurons. Th ...
LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
... Column & Body of the Fornix Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The pa ...
... Column & Body of the Fornix Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The pa ...
File
... the message down the axon. The axon is a single, larger “transmitter” fiber that extends from the soma. ...
... the message down the axon. The axon is a single, larger “transmitter” fiber that extends from the soma. ...
Assessing the Chaotic Nature of Neural Networks
... suggested that merely their presence in the system as represented mathematically by Equation 12 results in positive Lyapunov exponents. Perhaps a Laplacian transformation of the system can reduce the dimensionality of the system while preserving the delay aspect which is vitally important to a physi ...
... suggested that merely their presence in the system as represented mathematically by Equation 12 results in positive Lyapunov exponents. Perhaps a Laplacian transformation of the system can reduce the dimensionality of the system while preserving the delay aspect which is vitally important to a physi ...