Release of Acetylcholine: Signal at nerve terminal causes CA2+
... acetykcholinesterase or from the circulation. It is taken up into neurone by a high affinity, Na+- dependant, ATP requiring process. It is co-transported with Na+, and ATP is required to “pump” Na+ cations out of the neurones. This is a rate-limiting step for acetylcholine by: choline acetyl trans ...
... acetykcholinesterase or from the circulation. It is taken up into neurone by a high affinity, Na+- dependant, ATP requiring process. It is co-transported with Na+, and ATP is required to “pump” Na+ cations out of the neurones. This is a rate-limiting step for acetylcholine by: choline acetyl trans ...
KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and
... Neurons have specialised functions and vary in shape and size depending on where they are located and on their specific function. Some neurons specialise in transmitting (sending) information from sensory receptors, sensory organs, tendons or muscles to the CNS. Other neurons specialise in sending i ...
... Neurons have specialised functions and vary in shape and size depending on where they are located and on their specific function. Some neurons specialise in transmitting (sending) information from sensory receptors, sensory organs, tendons or muscles to the CNS. Other neurons specialise in sending i ...
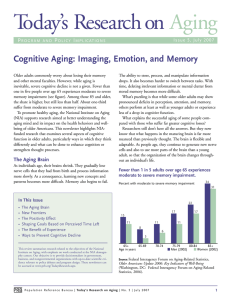
Cognitive Aging: Imaging, Emotion, and Memory
... speed of processing—reported less difficulty with daily living activities five years after the training, compared with those in the control group. Participants were tested on activities including everyday problemsolving; the ability to reason and identify information in medication labels; using the ...
... speed of processing—reported less difficulty with daily living activities five years after the training, compared with those in the control group. Participants were tested on activities including everyday problemsolving; the ability to reason and identify information in medication labels; using the ...
Self harm and Eating Disorders - King Edward VI College
... How to refer for medical advice and support • All medical referrals for students 16 or over need to be made to via the student’s GP •The GP will decide whether to offer support via the practice or refer onto adult mental health services •The Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services also transfer ...
... How to refer for medical advice and support • All medical referrals for students 16 or over need to be made to via the student’s GP •The GP will decide whether to offer support via the practice or refer onto adult mental health services •The Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services also transfer ...
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
... • The neurons send electrochemical messages to the brain so that people can respond to stimuli • Neurotransmission: – The method by which messages are sent between the synapses of the neurons ...
... • The neurons send electrochemical messages to the brain so that people can respond to stimuli • Neurotransmission: – The method by which messages are sent between the synapses of the neurons ...
Date
... C) chunking. D) automatic processing. 10. The tendency to immediately recall the first and last items in a list better than the middle items is known as the ________ effect. A) serial position B) misinformation C) imagination D) spacing 11. The day after Kirsten was introduced to 13 people at a busi ...
... C) chunking. D) automatic processing. 10. The tendency to immediately recall the first and last items in a list better than the middle items is known as the ________ effect. A) serial position B) misinformation C) imagination D) spacing 11. The day after Kirsten was introduced to 13 people at a busi ...
Learning Objectives
... 26. Compare the structures and functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 27. Distinguish between the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. 28. Describe the embryonic development of the vertebrate brain. 29. Describe the structures ...
... 26. Compare the structures and functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 27. Distinguish between the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. 28. Describe the embryonic development of the vertebrate brain. 29. Describe the structures ...
Learning and memory Learning and memory are closely
... neurotransmitters diffuse across the spaces between cells, attaching themselves to neighboring cells. Each brain cell can form thousands of links like this, giving a typical brain about 100 trillion synapses. The parts of the brain cells that receive these electric impulses are called dendrites, fea ...
... neurotransmitters diffuse across the spaces between cells, attaching themselves to neighboring cells. Each brain cell can form thousands of links like this, giving a typical brain about 100 trillion synapses. The parts of the brain cells that receive these electric impulses are called dendrites, fea ...
Introduction to Psychology
... that at one end of the cell body is a long, fibrous strand of tissue. He immediately recognizes this is an axon that is responsible for a. carrying signals away from the cell body b. receiving signals from other cells and carrying them toward the cell body c. determining the speed at which an action ...
... that at one end of the cell body is a long, fibrous strand of tissue. He immediately recognizes this is an axon that is responsible for a. carrying signals away from the cell body b. receiving signals from other cells and carrying them toward the cell body c. determining the speed at which an action ...
Nervous system - Nayland College
... of the tissue matter. This tissue is made up of nerve fibers which are responsible for sending communication signals within and between the Central Nervous System (CNS), and the nerves supplying the rest of the body. Neurons and white tissue are most likely to be attacked in MS. During periods of MS ...
... of the tissue matter. This tissue is made up of nerve fibers which are responsible for sending communication signals within and between the Central Nervous System (CNS), and the nerves supplying the rest of the body. Neurons and white tissue are most likely to be attacked in MS. During periods of MS ...
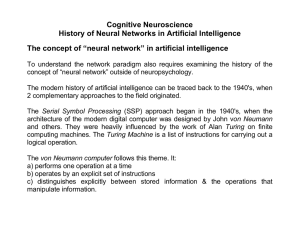
Cognitive Neuroscience History of Neural Networks in Artificial
... It was realized that, although Minsky & Papert were exactly correct in their analysis of the one-layer perceptron, their analysis did not extend to multi-layer networks or to systems with feedback loops. The PDP approach has gained a wide following since the early 1980's. Many neuroscientists believ ...
... It was realized that, although Minsky & Papert were exactly correct in their analysis of the one-layer perceptron, their analysis did not extend to multi-layer networks or to systems with feedback loops. The PDP approach has gained a wide following since the early 1980's. Many neuroscientists believ ...
Plants and Pollinators
... Function of the Spinal Cord • Expressway for signals between brain and peripheral nerves • Sensory and motor neurons make direct reflex connections in the spinal cord • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain ...
... Function of the Spinal Cord • Expressway for signals between brain and peripheral nerves • Sensory and motor neurons make direct reflex connections in the spinal cord • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain ...
Confocal microscopy with a volume holographic filter
... and improved aberration performance: Objectivelens aberrations are phase conjugated out during the hologram reconstruction process, and collector-lens aberrations (which increase the collected spot size) are irrelevant in the absence of a pinhole. The volume holographic confocal microscope is shown ...
... and improved aberration performance: Objectivelens aberrations are phase conjugated out during the hologram reconstruction process, and collector-lens aberrations (which increase the collected spot size) are irrelevant in the absence of a pinhole. The volume holographic confocal microscope is shown ...
Part I - QIBA Wiki
... 2) The development of an amyloid specific physical brain phantom whose design would be modeled directly from the final version of the Brain DRO using porous high density polyethylene. John Sunderland led this effort, and a separate report will be provided for this component. ...
... 2) The development of an amyloid specific physical brain phantom whose design would be modeled directly from the final version of the Brain DRO using porous high density polyethylene. John Sunderland led this effort, and a separate report will be provided for this component. ...
The Nervous System and the Brain
... your hand detects the pain and instantly fires off a message to your spinal cord. When the message reaches your spinal cord it connects with an interneuron that in turn activates a motor neuron. The motor neuron sends a message to cells in your arm muscles that are capable of muscle movement. Muscle ...
... your hand detects the pain and instantly fires off a message to your spinal cord. When the message reaches your spinal cord it connects with an interneuron that in turn activates a motor neuron. The motor neuron sends a message to cells in your arm muscles that are capable of muscle movement. Muscle ...
Encoding - Harding Charter Preparatory High School
... attributing to the wrong source an event that we experienced, heard about, read about, or imagined (misattribution) ...
... attributing to the wrong source an event that we experienced, heard about, read about, or imagined (misattribution) ...
Week7
... • Components of a neuron: cell body, dendrites, axon, synaptic terminals. • The electrical potential across the cell membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. • Originating in the cell body, this spike travels down the axon and causes chemical neurotransmitters to be released at synaptic te ...
... • Components of a neuron: cell body, dendrites, axon, synaptic terminals. • The electrical potential across the cell membrane exhibits spikes called action potentials. • Originating in the cell body, this spike travels down the axon and causes chemical neurotransmitters to be released at synaptic te ...
Final Research Paper - sites@gsu
... Memories are interesting, they can bring on positive and negative emotion, they help us get through life by learning what to do and more importantly what not to do. Researchers have been studying memory for a long time, some believe that memory is easily distorted and therefore unreliable, others be ...
... Memories are interesting, they can bring on positive and negative emotion, they help us get through life by learning what to do and more importantly what not to do. Researchers have been studying memory for a long time, some believe that memory is easily distorted and therefore unreliable, others be ...
Chapter 12
... other that each synapse on others • Converging circuit -- input from many fibers on one neuron (respiratory center) • Reverberating circuits – neurons stimulate each other in linear sequence but one cell restimulates the first cell to start the process all over ...
... other that each synapse on others • Converging circuit -- input from many fibers on one neuron (respiratory center) • Reverberating circuits – neurons stimulate each other in linear sequence but one cell restimulates the first cell to start the process all over ...
Nervous System Study Guide 1
... 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ...
... 8. It seems like a stranger is following you as you walk to your car in the parking lot. Your heart starts beating faster. Write out the pathway that the nervous system has taken during this experience. ...
How the Special Needs Brain Learns
... personal meaning to the student This relevancy is especially important for students with special needs, as they may have trouble focusing for very long ...
... personal meaning to the student This relevancy is especially important for students with special needs, as they may have trouble focusing for very long ...