CH 14 brain cranial nerves A and P 2017
... physical and emotional body - during sleep the body releases the most HGH, memories are consolidated or purged ...
... physical and emotional body - during sleep the body releases the most HGH, memories are consolidated or purged ...
Vestibular senses
... - Auditory neurons are together in spiral ganglion and give rise to auditory nerve (part of vestibulocochlear nerve, VIII cranial nerve) which synapse on cochlear nuclei in medulla. - Don’t need to know all the connections in medulla and pons (trapezoid body, superior olivary complex, etc), but reme ...
... - Auditory neurons are together in spiral ganglion and give rise to auditory nerve (part of vestibulocochlear nerve, VIII cranial nerve) which synapse on cochlear nuclei in medulla. - Don’t need to know all the connections in medulla and pons (trapezoid body, superior olivary complex, etc), but reme ...
File - Leuzinger High School(AP)
... cues from the current situation may subconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier similar experience "I've experienced this before." ...
... cues from the current situation may subconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier similar experience "I've experienced this before." ...
Biological Perspective Studies
... Golgi defended the reticularist position, though, because he could not see with certainty that axons did not fuse to other cells. He wrote: “There is certainly to be found a very widespread network of filaments anastomosing one with the other throughout the gray matter of the brain.” ...
... Golgi defended the reticularist position, though, because he could not see with certainty that axons did not fuse to other cells. He wrote: “There is certainly to be found a very widespread network of filaments anastomosing one with the other throughout the gray matter of the brain.” ...
Memory - Walton High
... 1. Next-in-line-Effect: When you are so anxious about being next that you cannot remember what the person just before you in line says, but you can recall what other people around you say. 2. Spacing Effect: We retain information better when we rehearse over time. This is why long-term studying is b ...
... 1. Next-in-line-Effect: When you are so anxious about being next that you cannot remember what the person just before you in line says, but you can recall what other people around you say. 2. Spacing Effect: We retain information better when we rehearse over time. This is why long-term studying is b ...
Adolescent Brain
... A. Plasticity a. Speeds up conduction time – (100x) neuron - neuron b. Accelerates information processing by helping axons more quickly after firing (up to 30x faster) ...
... A. Plasticity a. Speeds up conduction time – (100x) neuron - neuron b. Accelerates information processing by helping axons more quickly after firing (up to 30x faster) ...
Machine Intelligence
... fully conscious signal) • subconscious process (stimulated by internal or external signals) Thus, while paying attention is a conscious experience, switching attention does not have to be. ...
... fully conscious signal) • subconscious process (stimulated by internal or external signals) Thus, while paying attention is a conscious experience, switching attention does not have to be. ...
Completed Notes
... During sleep the reticular activating system (RAS) can arouse you w/excitatory neurotransmitters if important stimuli sensed. (see RAS later) ...
... During sleep the reticular activating system (RAS) can arouse you w/excitatory neurotransmitters if important stimuli sensed. (see RAS later) ...
Mapping image data to stereotaxic spaces: Applications to brain
... of a particular tissue (e.g., gray matter) mapped to that location. Each voxel in the image to be transformed is mapped to some location in the stereotaxic space, through the elastic transformation. If this location does not coincide with the location of the center of a voxel, then the counters of t ...
... of a particular tissue (e.g., gray matter) mapped to that location. Each voxel in the image to be transformed is mapped to some location in the stereotaxic space, through the elastic transformation. If this location does not coincide with the location of the center of a voxel, then the counters of t ...
Nervous System Ch 10 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... • Ionic current flows through extra-cellular fluid & triggers impulse at next node ...
... • Ionic current flows through extra-cellular fluid & triggers impulse at next node ...
EMOTION: Information as Subjective Feeling
... • Better affect and arousal regulation • Better understanding of stress and distress and how it affects us • Better awareness of Self and how I function and see the world • What am I not thinking about? • Could I change the way I see myself? Others? • Is there another way to think about this? ...
... • Better affect and arousal regulation • Better understanding of stress and distress and how it affects us • Better awareness of Self and how I function and see the world • What am I not thinking about? • Could I change the way I see myself? Others? • Is there another way to think about this? ...
Overview of the Nervous System
... • Consciousness – alert and aware of person, place, time • Confusion – not able to think • Lethargy – limited speech, may/maynot be oriented to PPT • Obtundation – stimulation needed for arousal • Stupor – unresponsive except for vigorous stimuli • Coma – no vocalization or arousal ...
... • Consciousness – alert and aware of person, place, time • Confusion – not able to think • Lethargy – limited speech, may/maynot be oriented to PPT • Obtundation – stimulation needed for arousal • Stupor – unresponsive except for vigorous stimuli • Coma – no vocalization or arousal ...
Click here for Biopsychology information pack
... Synaptic transmission is the process for transmitting messages from neuron to neuron. Since neurons form a network, they somehow have to be interconnected. When a nerve signal, or impulse reaches the ends of its axon, it has travelled as an action potential, or a pulse of electricity. However, there ...
... Synaptic transmission is the process for transmitting messages from neuron to neuron. Since neurons form a network, they somehow have to be interconnected. When a nerve signal, or impulse reaches the ends of its axon, it has travelled as an action potential, or a pulse of electricity. However, there ...
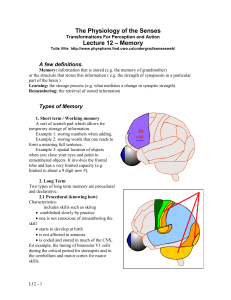
Types of Memory
... permanent changes in synaptic strength between assemblies of neurons. For example, rats raised in a rich environment have a thicker cortex with larger and more synapses. In the case of procedural memory, the changes are produced gradually by repeated exposure to the stimulus. ...
... permanent changes in synaptic strength between assemblies of neurons. For example, rats raised in a rich environment have a thicker cortex with larger and more synapses. In the case of procedural memory, the changes are produced gradually by repeated exposure to the stimulus. ...
Ch 4 V Cortexb - Texas A&M University
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
... • A blind man who damaged the occipital lobe can still navigate and walk without bumping into objects. ch 4 ...
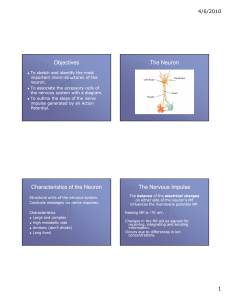
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
Type 2 - yhernandez
... b. encoding new information to replace previously learned information c. using available cues to identify information that has been previously learned d. looking at an image and retaining a detailed visual image for several minutes 91. According to network theory, memory is organized by: a. nodes, a ...
... b. encoding new information to replace previously learned information c. using available cues to identify information that has been previously learned d. looking at an image and retaining a detailed visual image for several minutes 91. According to network theory, memory is organized by: a. nodes, a ...
System Architecture of ERS/ERD
... • Occurs with flashing lights (3-5 Hz) • Have been used to monitor function during surgery for lesions involving the pituitary gland, optic nerve and chiasma. • Application: ...
... • Occurs with flashing lights (3-5 Hz) • Have been used to monitor function during surgery for lesions involving the pituitary gland, optic nerve and chiasma. • Application: ...
nervous system - Cloudfront.net
... What is the function of the nervous system? • The nervous system is made up of the structures that control actions and reactions of the body in response to stimuli in the environment. • The nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). ...
... What is the function of the nervous system? • The nervous system is made up of the structures that control actions and reactions of the body in response to stimuli in the environment. • The nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). ...