How is information about touch relayed to the brain?
... • Four types of touch receptors have been identified: Pacinian corpuscles: Encapsulated (onion-like) receptors. Detect vibration. Fast-adapting (i.e., phasic, highly sensitive to change). Large receptive fields. Meissner’s corpuscles: Encapsulated receptors. Detect light touch. Fast-adapting. Sm ...
... • Four types of touch receptors have been identified: Pacinian corpuscles: Encapsulated (onion-like) receptors. Detect vibration. Fast-adapting (i.e., phasic, highly sensitive to change). Large receptive fields. Meissner’s corpuscles: Encapsulated receptors. Detect light touch. Fast-adapting. Sm ...
The Spinal Cord - Lightweight OCW University of Palestine
... 1. Neurone: is a nerve cell and its processes. 2. Nucleus: is a group of nerve cells located in the CNS. 3. Ganglia: is a group of nerve cells located out the CNS. 4. Nerve fiber: is an axon or dendrite. 5. Nerve: is a bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS. 6. Tract: is a group of nerve fibers in the CN ...
... 1. Neurone: is a nerve cell and its processes. 2. Nucleus: is a group of nerve cells located in the CNS. 3. Ganglia: is a group of nerve cells located out the CNS. 4. Nerve fiber: is an axon or dendrite. 5. Nerve: is a bundle of nerve fibers in the PNS. 6. Tract: is a group of nerve fibers in the CN ...
Friday October 19th
... (pacemakers and slow waves) What are the differences between single-unit and multi-unit smooth muscle? (location, spread of excitation) ...
... (pacemakers and slow waves) What are the differences between single-unit and multi-unit smooth muscle? (location, spread of excitation) ...
Central Sensitization
... normal input and there can also be long term potentiation (LTP) after repeated stimulation from the periphery. This is often termed a barrage and can lead to long lasting changes in nociceptor properties and increased sensitivity and excitability. This generally occurs after an acute painful event a ...
... normal input and there can also be long term potentiation (LTP) after repeated stimulation from the periphery. This is often termed a barrage and can lead to long lasting changes in nociceptor properties and increased sensitivity and excitability. This generally occurs after an acute painful event a ...
Nervous Tissue NOTES
... this happens at one location on the axon, it affects the next section, and the next section… This sends the electrical impulse (action potential) along the entire axon As the signal travels along the axon, Na+ rushes into the cell as K+ rushes out of the cell to try to repolarize the membran ...
... this happens at one location on the axon, it affects the next section, and the next section… This sends the electrical impulse (action potential) along the entire axon As the signal travels along the axon, Na+ rushes into the cell as K+ rushes out of the cell to try to repolarize the membran ...
foods of the chinese
... hair-like sensory receptors that bend under the weight of otoliths (which are small crystals of calcium carbonate) that provide the inertia needed to detect head rotation, linear acceleration, and the direction of gravitational force. Thermoception is the sense of heat and the absence of heat (cold) ...
... hair-like sensory receptors that bend under the weight of otoliths (which are small crystals of calcium carbonate) that provide the inertia needed to detect head rotation, linear acceleration, and the direction of gravitational force. Thermoception is the sense of heat and the absence of heat (cold) ...
Diapositiva 1
... brain disease for which there is no cure. Slowly and inexorably, the disease attacks nerve cells in all parts of the brain's cortex, as well as some surrounding structures, thereby impairing the person's abilities to govern emotions, recognize errors and patterns, coordinate movement, and remember. ...
... brain disease for which there is no cure. Slowly and inexorably, the disease attacks nerve cells in all parts of the brain's cortex, as well as some surrounding structures, thereby impairing the person's abilities to govern emotions, recognize errors and patterns, coordinate movement, and remember. ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology, Nervous System and Special
... Static sensation registers the gravitational pull on otoliths Dynamic sensation registers the angular or rotary motion of the fluid in the _________________________________ Mechanism of Hearing 39. Differentiate the sensation mechanism for low-pitch and high-pitch sounds. High-pitch are sensed at th ...
... Static sensation registers the gravitational pull on otoliths Dynamic sensation registers the angular or rotary motion of the fluid in the _________________________________ Mechanism of Hearing 39. Differentiate the sensation mechanism for low-pitch and high-pitch sounds. High-pitch are sensed at th ...
Chapter 44
... impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) 3. Interneurons (association neurons) provide more complex reflexes and associative functions (learning and memory) ...
... impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) 3. Interneurons (association neurons) provide more complex reflexes and associative functions (learning and memory) ...
document
... •The term apraxia will be used here to mean inability to follow a motor command that is not due to a primary motor deficit or a language impairment. It is apparently caused by a deficit in higher-order planning or conceptualization of the motor task. You can test for apraxia by asking the patient to ...
... •The term apraxia will be used here to mean inability to follow a motor command that is not due to a primary motor deficit or a language impairment. It is apparently caused by a deficit in higher-order planning or conceptualization of the motor task. You can test for apraxia by asking the patient to ...
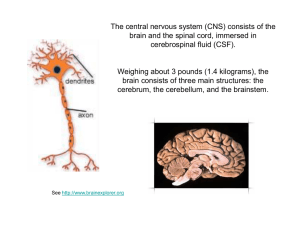
The human brain - "G. Galilei" – Pescara
... Brain : the part of the central nervous system enclosed in the cranium of humans and other vertebrates, consisting of a soft, convoluted mass of grey and white matter and serving to control and coordinate the mental and physical actions. Brainstem : is the posterior part of the brain which includes ...
... Brain : the part of the central nervous system enclosed in the cranium of humans and other vertebrates, consisting of a soft, convoluted mass of grey and white matter and serving to control and coordinate the mental and physical actions. Brainstem : is the posterior part of the brain which includes ...
9d. Know the functions of the nervous system and the role of
... The __________________ ________________ controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses throughout the body. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord. Motor neurons carry im ...
... The __________________ ________________ controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses throughout the body. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord. Motor neurons carry im ...
09. Assessment of Neurologic System
... Anatomy and Physiology: Brain Consists of cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum and brainstem Gray matter (cell bodies) and white matter ...
... Anatomy and Physiology: Brain Consists of cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum and brainstem Gray matter (cell bodies) and white matter ...
chapter 13 peripheral nervous system
... The muscle spindle Muscle spindle becomes slack and no tension is mainAPs are fired. It is tained and it can unable to signal further still signal changes length changes. in length. ...
... The muscle spindle Muscle spindle becomes slack and no tension is mainAPs are fired. It is tained and it can unable to signal further still signal changes length changes. in length. ...
The Nervous system - Locust Trace Veterinary Assistant Program
... – Provide complex pathways present in the brain and spinal cord. ■ Motor Neurons-deliver the signal from the CNS to the muscle or gland stimulated for a response. ...
... – Provide complex pathways present in the brain and spinal cord. ■ Motor Neurons-deliver the signal from the CNS to the muscle or gland stimulated for a response. ...
consciousness
... matter.’ It covers the nuclei deep within the cerebral hemisphere known as the ‘white matter’. ...
... matter.’ It covers the nuclei deep within the cerebral hemisphere known as the ‘white matter’. ...
needle emg examination of the foot
... electrodiagnostic medicine (EDX) consultants. There are several reasons for this. One is that several published articles have reported the common occurrence of prolonged insertional activity in the intrinsic foot muscles of normal subjects.7,8,27 These findings were refuted by Dumitru et al in a lat ...
... electrodiagnostic medicine (EDX) consultants. There are several reasons for this. One is that several published articles have reported the common occurrence of prolonged insertional activity in the intrinsic foot muscles of normal subjects.7,8,27 These findings were refuted by Dumitru et al in a lat ...
Advanced Biology\AB U14 Nervous System
... can result in pain or paralysis. Probably the best known nerve is the sciatic nerve. It is the largest nerve. It exits between lumbar vertebrae, travels behind the hips and down the back of the leg. When giving IM injections, nurses aim for the upper, outer quadrant of the buttocks to avoid hitting ...
... can result in pain or paralysis. Probably the best known nerve is the sciatic nerve. It is the largest nerve. It exits between lumbar vertebrae, travels behind the hips and down the back of the leg. When giving IM injections, nurses aim for the upper, outer quadrant of the buttocks to avoid hitting ...
Slide 1
... same message is sent • Message sent in all neurons is the same All or nothing Law – an impulse is only generated if the stimulus is at or above the threshold. ...
... same message is sent • Message sent in all neurons is the same All or nothing Law – an impulse is only generated if the stimulus is at or above the threshold. ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.