Population vectors and motor cortex: neural coding or
... of secreted signaling proteins, and are known to be involved in early developmental patterning. Several are also expressed in the brain, and the presence of WNT-7a in cerebellar granule cells during the period of synaptogenesis prompted the authors to examine a possible role in this process. Hall et ...
... of secreted signaling proteins, and are known to be involved in early developmental patterning. Several are also expressed in the brain, and the presence of WNT-7a in cerebellar granule cells during the period of synaptogenesis prompted the authors to examine a possible role in this process. Hall et ...
Nonpharmacologic Interventions in Pain Management
... Most common source is patients using “dietary supplements” ...
... Most common source is patients using “dietary supplements” ...
The Nervous System
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
Comparison of Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions
... The two primary types of visceral receptors, mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors, are distributed throughout the body. Mechanoreceptors sense pressure, stretch, or tension. Slow-adapting mechanoreceptors sense fullness in the bowel, bladder, and stomach. Fast-adapting mechanoreceptors sense the move ...
... The two primary types of visceral receptors, mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors, are distributed throughout the body. Mechanoreceptors sense pressure, stretch, or tension. Slow-adapting mechanoreceptors sense fullness in the bowel, bladder, and stomach. Fast-adapting mechanoreceptors sense the move ...
Done by : Noor Bjant.hala Dr: loai zghol
... Thermoreceptors are a combination of ( Warm receptors and cold receptors) , we feel the temperature due to the activation and combination of these receptors , at high temperatures the warm receptor will be activated and at low temperatures the cold receptors will be activated. ...
... Thermoreceptors are a combination of ( Warm receptors and cold receptors) , we feel the temperature due to the activation and combination of these receptors , at high temperatures the warm receptor will be activated and at low temperatures the cold receptors will be activated. ...
The Muscular System
... Ability of a muscle to respond to stimuli Ability of a muscle to shorten in length Ability to stretch and return to original position Ability to extend in length Ability to transmit nerve impulses ...
... Ability of a muscle to respond to stimuli Ability of a muscle to shorten in length Ability to stretch and return to original position Ability to extend in length Ability to transmit nerve impulses ...
Nerve Tissue
... importance for our ability to control movements that has led to the realization that Parkinson's disease is caused by a lack of dopamine in certain parts of the ...
... importance for our ability to control movements that has led to the realization that Parkinson's disease is caused by a lack of dopamine in certain parts of the ...
Skeletal System
... motor activities Nearly spinal nerves and many cranial nerves contain both somatic and autonomic fibers Most of the body’s adaptations to changing internal and external conditions involve both skeletal activity and enhanced response of visceral organs ...
... motor activities Nearly spinal nerves and many cranial nerves contain both somatic and autonomic fibers Most of the body’s adaptations to changing internal and external conditions involve both skeletal activity and enhanced response of visceral organs ...
A Study on Various Sites of Supranuclear Facial Nerve
... state of India. International Journal of Biomedical and Advance Research 4(9): 661-665. ...
... state of India. International Journal of Biomedical and Advance Research 4(9): 661-665. ...
TRIGEMINAL NEURLAGIA
... description of TGN. The patient was the Countess of Northumberland, wife of British Ambassador to the French Court. • Nicolas Andre : called the clinical entity ‘Tic douloureaux’ in 1756 describing 5 patients who suffered from a : ‘cruel and obscure illness which causes in the face some violent moti ...
... description of TGN. The patient was the Countess of Northumberland, wife of British Ambassador to the French Court. • Nicolas Andre : called the clinical entity ‘Tic douloureaux’ in 1756 describing 5 patients who suffered from a : ‘cruel and obscure illness which causes in the face some violent moti ...
Program-overview - vita-life
... P 21 Capillarisation Increases the arterial circulation in the muscles and develops the capillaries, especially in the area of the fast muscle fibers. Ideal addition to anaerobic endurance training. Regulates circulation in the area of maintaining general health. Improves the blood flow in the vein ...
... P 21 Capillarisation Increases the arterial circulation in the muscles and develops the capillaries, especially in the area of the fast muscle fibers. Ideal addition to anaerobic endurance training. Regulates circulation in the area of maintaining general health. Improves the blood flow in the vein ...
gustatory and olfactory senses
... Sensory receptors are transducers; they convert stimuli into electric signals. In most cases, they do not directly generate action potentials. Instead, sensory receptors generate receptor potentials, which vary in intensity with the intensity of the stimulus. These changes in membrane potential are ...
... Sensory receptors are transducers; they convert stimuli into electric signals. In most cases, they do not directly generate action potentials. Instead, sensory receptors generate receptor potentials, which vary in intensity with the intensity of the stimulus. These changes in membrane potential are ...
7th sci Nervous System and Brain ppt nervous system and
... Nervous System • Sensory: gathers info around the body; examples – light, oxygen levels, body temperature ...
... Nervous System • Sensory: gathers info around the body; examples – light, oxygen levels, body temperature ...
The Special Senses
... • Specialized nerve receptors are located in the dermal layers of the skin which are sensitive to pressure associated with touch, heat, cold, and pain. These are specially modified sensory neurons called receptors. There are also receptors in muscle tissue which detect stretching, force of contracti ...
... • Specialized nerve receptors are located in the dermal layers of the skin which are sensitive to pressure associated with touch, heat, cold, and pain. These are specially modified sensory neurons called receptors. There are also receptors in muscle tissue which detect stretching, force of contracti ...
Chapter 12
... University of South Carolina Norman J. Arnold School of Public Health Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders University of South Carolina ...
... University of South Carolina Norman J. Arnold School of Public Health Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders University of South Carolina ...
The Nonvisual Sensory Systems
... if pathways other than pain are sufficiently active, they close the “gates” for pain messages Modification of pain messages Opiates-decrease substance P activity ...
... if pathways other than pain are sufficiently active, they close the “gates” for pain messages Modification of pain messages Opiates-decrease substance P activity ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... by the corpus callosum. Other fissures separate each hemisphere into four lobes – each controls different actions: 1. frontal lobe – voluntary muscle movement and speech 2. parietal lobe – touch, pain, temperature 3. temporal lobe (or auditory) – interpreting sounds 4. occipital lobe (or visual) – i ...
... by the corpus callosum. Other fissures separate each hemisphere into four lobes – each controls different actions: 1. frontal lobe – voluntary muscle movement and speech 2. parietal lobe – touch, pain, temperature 3. temporal lobe (or auditory) – interpreting sounds 4. occipital lobe (or visual) – i ...
Perceptrons
... one direction • There is only one type of transmitter per synapse • The transmitter allows an electrical message to be turned into a chemical message and back into an electrical message. ...
... one direction • There is only one type of transmitter per synapse • The transmitter allows an electrical message to be turned into a chemical message and back into an electrical message. ...
Slide ()
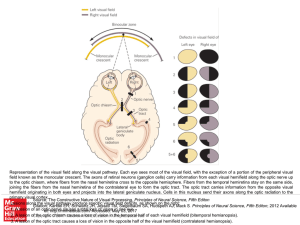
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Slide ()
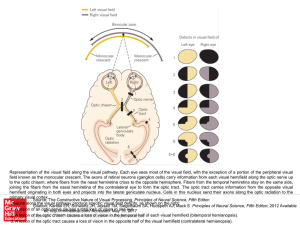
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Steps of Evaluation
... duramater and dural sheaths around nerve roots) or a contractile unit (muscle with its tendons and attachments). Additional tests are used to verify problems as identifying the anatomic structure and state of pathology so that the appropriate therapeutic exercise program can be designed. ...
... duramater and dural sheaths around nerve roots) or a contractile unit (muscle with its tendons and attachments). Additional tests are used to verify problems as identifying the anatomic structure and state of pathology so that the appropriate therapeutic exercise program can be designed. ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.