Structure of the central nervous system of a juvenile acoel
... neuropile, and axon bundles were segmented, after which they could be displayed as a 3D digital model. Note that, given the relatively large gaps between adjacent sections, counts of individual cells (in particular sensory receptors) are not particularly accurate, given that the size of the ciliated ...
... neuropile, and axon bundles were segmented, after which they could be displayed as a 3D digital model. Note that, given the relatively large gaps between adjacent sections, counts of individual cells (in particular sensory receptors) are not particularly accurate, given that the size of the ciliated ...
Document
... • Semicircular Canals - sense of equilibrium • Cochlea - sense or hearing • Organ of Corti - contains hearing receptors, hair cells detect vibrations • Pathway: Nerve cells --> interpreted by the temporal lobe of the cerebrum ...
... • Semicircular Canals - sense of equilibrium • Cochlea - sense or hearing • Organ of Corti - contains hearing receptors, hair cells detect vibrations • Pathway: Nerve cells --> interpreted by the temporal lobe of the cerebrum ...
a study of axonal protein trafficking in neuronal networks via the
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
an appraisal of the mechanism of action of
... longed and continuous pressure due to trickling of medicated liquid over forehead causes tranquility of mind and reduces stress by modulating the nerve progression/stimulation5. When nerve endings of autonomic nervous system are stimulated, they produce chemical substances like Acetylcholine which e ...
... longed and continuous pressure due to trickling of medicated liquid over forehead causes tranquility of mind and reduces stress by modulating the nerve progression/stimulation5. When nerve endings of autonomic nervous system are stimulated, they produce chemical substances like Acetylcholine which e ...
RULE 099.37 OCCUPATIONAL CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
... Median minus ulnar palmar latency abnormal > 0.3 msecs. 2. Median motor latency (wrist to APB at 8 cm.) Abnormal latency > 4.5 msecs. Median minus ulnar motor distal latency abnormal > 1.8 msecs. 3. Median sensory distal latency (wrist to digit at 14 cm.) Abnormal latency > 3.5 msecs. 4. Fourth digi ...
... Median minus ulnar palmar latency abnormal > 0.3 msecs. 2. Median motor latency (wrist to APB at 8 cm.) Abnormal latency > 4.5 msecs. Median minus ulnar motor distal latency abnormal > 1.8 msecs. 3. Median sensory distal latency (wrist to digit at 14 cm.) Abnormal latency > 3.5 msecs. 4. Fourth digi ...
Object Recognition and Learning using the BioRC Biomimetic Real
... This requires 104 synapse circuits and about 104 2-input adder circuits, to sum the inputs. We need one axon hillock to perform the thresholding/spiking function. ...
... This requires 104 synapse circuits and about 104 2-input adder circuits, to sum the inputs. We need one axon hillock to perform the thresholding/spiking function. ...
What Is the Nervous System?
... Central Nervous System • The nervous system consists of two major divisions—the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system includes all the other part ...
... Central Nervous System • The nervous system consists of two major divisions—the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system includes all the other part ...
What Is the Nervous System?
... Central Nervous System • The nervous system consists of two major divisions—the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system includes all the other part ...
... Central Nervous System • The nervous system consists of two major divisions—the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system is the control center of the body. It includes the brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system includes all the other part ...
Section 11.3
... • Nervous system infections are rare because its tissues are well protected. • Meningitis (men in JY tis) causes inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. • The most serious form of meningitis can be prevented with a vaccine. • A bite from an infected animal can transmit r ...
... • Nervous system infections are rare because its tissues are well protected. • Meningitis (men in JY tis) causes inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. • The most serious form of meningitis can be prevented with a vaccine. • A bite from an infected animal can transmit r ...
12 Steps to Muscle Contraction
... 1. A nerve impulse travels to the neuromuscular junction on a muscle cell. The neuromuscular junction is the point where the axons of the nerve meet with the muscle cell. 2. Ach is released from the axon to receptors located on the sarcolemma 3. The binding Ach causes depolarization of the sarcolemm ...
... 1. A nerve impulse travels to the neuromuscular junction on a muscle cell. The neuromuscular junction is the point where the axons of the nerve meet with the muscle cell. 2. Ach is released from the axon to receptors located on the sarcolemma 3. The binding Ach causes depolarization of the sarcolemm ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... Beta: Present when nervous system is active & person is engaged in awake mental activity. Delta: Present in awake infants and sleeping adults, indicative of brain damage in awake adults. Theta: Present in children & adults during emotional stress, may be a sign of brain disorder. ...
... Beta: Present when nervous system is active & person is engaged in awake mental activity. Delta: Present in awake infants and sleeping adults, indicative of brain damage in awake adults. Theta: Present in children & adults during emotional stress, may be a sign of brain disorder. ...
Chapter 14 Autonomic nervous system
... 1. Modality is the property by which one sensation is distinguished from another. 2. In general, a given sensory neuron carries only one modality. C. Components of Sensation 1. For a sensation to arise, four events must occur. 2. These are stimulation, transduction, conduction, and translation. a. A ...
... 1. Modality is the property by which one sensation is distinguished from another. 2. In general, a given sensory neuron carries only one modality. C. Components of Sensation 1. For a sensation to arise, four events must occur. 2. These are stimulation, transduction, conduction, and translation. a. A ...
The Reflex Arc
... C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, s ...
... C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, s ...
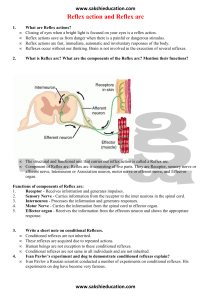
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this. Conditional reflexes are not same in all individuals and n ...
... bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this. Conditional reflexes are not same in all individuals and n ...
Online Textbook Worksheets
... _____ 2. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. _____ 3. The peripheral nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. _____ 4. The myelin sheath is similar to the plastic that encases an electrical cord. _____ 5. The somatic nervous system con ...
... _____ 2. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. _____ 3. The peripheral nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. _____ 4. The myelin sheath is similar to the plastic that encases an electrical cord. _____ 5. The somatic nervous system con ...
Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation of normalization in the visual cortex is thought to involve inhibitory neurons t ...
... which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation of normalization in the visual cortex is thought to involve inhibitory neurons t ...
File
... nervous system, myelin, synapse, axon. 1. high alert 2. transmits impulses away from cell body 3. fatty insulating material 4. gap between neurons ...
... nervous system, myelin, synapse, axon. 1. high alert 2. transmits impulses away from cell body 3. fatty insulating material 4. gap between neurons ...
5-Autonomic Nervous System
... of T 1- L2 (OR L3) segments of spinal cord (Thoracolumbar outflow) (Outflow means the passage of impulses outwardly from the central nervous system.) o As their preganglionic neurons are short, their ganglia are located near the CNS (spinal cord). ...
... of T 1- L2 (OR L3) segments of spinal cord (Thoracolumbar outflow) (Outflow means the passage of impulses outwardly from the central nervous system.) o As their preganglionic neurons are short, their ganglia are located near the CNS (spinal cord). ...
Nervous System PPT
... of the CNS in order to create a response to the stimulus through chemical synapse activity. White Matter: It contains nerve fibers. Many of these nerve fibers (axons) are surrounded by a type of fat called myelin. The myelin gives the white matter it's color. Myelin acts as an insulator. It plays an ...
... of the CNS in order to create a response to the stimulus through chemical synapse activity. White Matter: It contains nerve fibers. Many of these nerve fibers (axons) are surrounded by a type of fat called myelin. The myelin gives the white matter it's color. Myelin acts as an insulator. It plays an ...
Nervous System - Fuller Anatomy
... Anesthetics are often injected into the epidural space. The drug should only affect spinal nerves in the area of the injection. Result is an epidural block-temporary sensory loss or motor paralysis (depending on anesthetic) used to control pain during childbirth. ...
... Anesthetics are often injected into the epidural space. The drug should only affect spinal nerves in the area of the injection. Result is an epidural block-temporary sensory loss or motor paralysis (depending on anesthetic) used to control pain during childbirth. ...
315midterm - Rocky Mountain College
...Give the two types of anxiety and what each refers
Which type of person is a seeker of stimulus the
extravert or introvert? What’s the explanation for this
according to Eysenck’s theory?
Draw and describe the Inverted U Theory. Explain at
least two considerations in the
application of th ...
...
Chapter 21 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Reflexes are simple, stereotyped and repeatable motor actions (example: movements) brought about by a specific sensory stimulus. The reflex is involuntary but may involve the use of voluntary (skeletal) muscle and nerves. ...
... Reflexes are simple, stereotyped and repeatable motor actions (example: movements) brought about by a specific sensory stimulus. The reflex is involuntary but may involve the use of voluntary (skeletal) muscle and nerves. ...
22. ANS.Neuroscience
... • Composed of two plexuses of nerve cells and fibers located in the wall of gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus to the anal canal • Submucous or Meisner’s plexus lies in the submucosa, is mainly concerned with the control of the glands in the ...
... • Composed of two plexuses of nerve cells and fibers located in the wall of gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus to the anal canal • Submucous or Meisner’s plexus lies in the submucosa, is mainly concerned with the control of the glands in the ...
ANS.Neuroscience.09
... • Composed of two plexuses of nerve cells and fibers located in the wall of gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus to the anal canal • Submucous or Meisner’s plexus lies in the submucosa, is mainly concerned with the control of the glands in the ...
... • Composed of two plexuses of nerve cells and fibers located in the wall of gastrointestinal tract from the esophagus to the anal canal • Submucous or Meisner’s plexus lies in the submucosa, is mainly concerned with the control of the glands in the ...
word - marric.us
... From the individual cell to the total organism, each functioning unit is organized according to homeostasis, or how the body and its parts deal with changing demands while maintaining a constant internal environment. In 1859 noted French physiologist Claude Bernard described the difference between t ...
... From the individual cell to the total organism, each functioning unit is organized according to homeostasis, or how the body and its parts deal with changing demands while maintaining a constant internal environment. In 1859 noted French physiologist Claude Bernard described the difference between t ...