Cellular localization of RNA expression in central and peripheral
... research fields, studying the structural and functional organization and the development of the central and peripheral nervous system from the molecular and cellular level to the systems level. One challenge in the neuroscience field is the numerous cell types in the central nervous system (CNS), ma ...
... research fields, studying the structural and functional organization and the development of the central and peripheral nervous system from the molecular and cellular level to the systems level. One challenge in the neuroscience field is the numerous cell types in the central nervous system (CNS), ma ...
Nervous System Development Inner Cell Mass of Blastocyst Inner
... • In other cases the neural tube may not be exposed to the surface (“closed NTD”), but the spinal vertebrae and skin surrounding the spine may not be completely normal. ...
... • In other cases the neural tube may not be exposed to the surface (“closed NTD”), but the spinal vertebrae and skin surrounding the spine may not be completely normal. ...
Unit Two
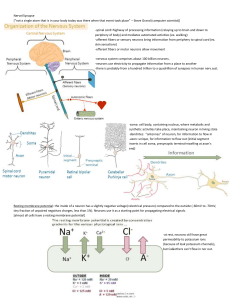
... impulses. In order for the nervous system to properly function, there must be a space between each neuron. This space is called a synapse. Synapse: The gap that exists between individual nerve cells. What can happen if the Myelin Sheath is destroyed? Multiple Sclerosis (erratic and uncontrolled beha ...
... impulses. In order for the nervous system to properly function, there must be a space between each neuron. This space is called a synapse. Synapse: The gap that exists between individual nerve cells. What can happen if the Myelin Sheath is destroyed? Multiple Sclerosis (erratic and uncontrolled beha ...
Photo Album
... A and B: Narrow spine necks (asterisks) emanate from the main dendritic shaft (D). The spine heads (S) contain filamentous material. Some large spines contain cisterns of a spine apparatus (sa, B). Asymmetric excitatory synapses are characterized by thickened postsynaptic densities (arrows A, B). A ...
... A and B: Narrow spine necks (asterisks) emanate from the main dendritic shaft (D). The spine heads (S) contain filamentous material. Some large spines contain cisterns of a spine apparatus (sa, B). Asymmetric excitatory synapses are characterized by thickened postsynaptic densities (arrows A, B). A ...
44 Nociceptive sensation. Somatic sensory analyzer
... Pain input to the spinal cord: -Projecting neurons in lamina I receive A-delta and C fibers info. -Neurons in lamina II receive input from C fibers and relay it to other laminae. -Projecting neurons in lamina V (wide-dynamic range neurons) receive A-delta, C and A-beta (low threshold mechanoceptor ...
... Pain input to the spinal cord: -Projecting neurons in lamina I receive A-delta and C fibers info. -Neurons in lamina II receive input from C fibers and relay it to other laminae. -Projecting neurons in lamina V (wide-dynamic range neurons) receive A-delta, C and A-beta (low threshold mechanoceptor ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -efferent fibers or motor neurons allow movement -nervous system comprises about 100 billion neurons. -neurons use electricity to propagate information from a place to another -there is probably from a hundred trillion to a quadrillion of synapses in human nerv.syst. ...
... -efferent fibers or motor neurons allow movement -nervous system comprises about 100 billion neurons. -neurons use electricity to propagate information from a place to another -there is probably from a hundred trillion to a quadrillion of synapses in human nerv.syst. ...
PDF
... During nervous system development, navigating axons ‘decide’ whether or not to cross the midline. Various factors that influence axon guidance and midline crossing have been identified but it remains unclear if any one transcription factor can drive the complete midline crossing transcriptional prog ...
... During nervous system development, navigating axons ‘decide’ whether or not to cross the midline. Various factors that influence axon guidance and midline crossing have been identified but it remains unclear if any one transcription factor can drive the complete midline crossing transcriptional prog ...
Anatomy back forum 2010
... b. Skin to fascia to fat to supraspinous ligament to interspinous ligament to epidural space to epidural fat to dura mater to arachnoid mater then STOP! 15. Examination of a patient reveals fecal incontinence after suffering a vertebral compression fracture that affect the sacral spinal cord. What v ...
... b. Skin to fascia to fat to supraspinous ligament to interspinous ligament to epidural space to epidural fat to dura mater to arachnoid mater then STOP! 15. Examination of a patient reveals fecal incontinence after suffering a vertebral compression fracture that affect the sacral spinal cord. What v ...
Cranial Nerves: Assessment of Functions
... Second, examine the pupils. Are they both the same size? Are they round or oval? Are they in the center of the eye facing forward, or are they deviated to the side? Normally the pupils should be round, equal in size (about 2-3 mm in diameter), and in the center of the eye. Unequal pupils (anisocoria ...
... Second, examine the pupils. Are they both the same size? Are they round or oval? Are they in the center of the eye facing forward, or are they deviated to the side? Normally the pupils should be round, equal in size (about 2-3 mm in diameter), and in the center of the eye. Unequal pupils (anisocoria ...
RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology (CDB)
... November 22, 2016– Olfaction or sense of smell, while not critical for life, can greatly influence the quality of life. The olfactory system is capable of detecting and discriminating a wide range of airborne odor molecules in the air; odorants inspired into the nasal cavity contact odorant receptor ...
... November 22, 2016– Olfaction or sense of smell, while not critical for life, can greatly influence the quality of life. The olfactory system is capable of detecting and discriminating a wide range of airborne odor molecules in the air; odorants inspired into the nasal cavity contact odorant receptor ...
Summary of Results and Discussion
... Stoeckli, personal communication). Thus, NgR-Nogo-A interaction probably takes place in the mossy fiber-CA3 pyramidal neuron synapse. Based on the hypothesis that NgR and Nogo-A downregulation is advantageous for neurons when plasticity is required, we propose two models (illustrated in figure 1.5.) ...
... Stoeckli, personal communication). Thus, NgR-Nogo-A interaction probably takes place in the mossy fiber-CA3 pyramidal neuron synapse. Based on the hypothesis that NgR and Nogo-A downregulation is advantageous for neurons when plasticity is required, we propose two models (illustrated in figure 1.5.) ...
O-Nervous System I
... Tract – a bundle of axons ins the CNS. Ganglion – a cluster of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Nucleus – gray matter in CNS with common function. ...
... Tract – a bundle of axons ins the CNS. Ganglion – a cluster of nerve cell bodies in PNS. Nucleus – gray matter in CNS with common function. ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... 25. Compare the major functional areas (sensory and motor) of the cerebral cortex in terms of location and function (a diagram may help here). 26. Explain what is meant by an association area of the cerebral cortex and name a few association traits. 27. Name the term referring to the measurement of ...
... 25. Compare the major functional areas (sensory and motor) of the cerebral cortex in terms of location and function (a diagram may help here). 26. Explain what is meant by an association area of the cerebral cortex and name a few association traits. 27. Name the term referring to the measurement of ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 35.1 Functional organization of the CNS control of breathing. Circuitry centered within the medulla oblongata of the brainstem (blue oval) generates an oscillating inspiratory–expiratory rhythm. Neurons within the oscillator circuit generate rhythmic respiratory motor output without requirin ...
... FIGURE 35.1 Functional organization of the CNS control of breathing. Circuitry centered within the medulla oblongata of the brainstem (blue oval) generates an oscillating inspiratory–expiratory rhythm. Neurons within the oscillator circuit generate rhythmic respiratory motor output without requirin ...
L7-Brainstem Student..
... • Trochlear nerve (CN IV) nucleus which also controls movements of some eye muscles . • Red Nucleus: gives out Sends Rubrospinal tract which is inhibitory to spinal Gamma Efferents neurons ( & stretch reflex /muscle tone ) • Substantia Nigra: Collection of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbr ...
... • Trochlear nerve (CN IV) nucleus which also controls movements of some eye muscles . • Red Nucleus: gives out Sends Rubrospinal tract which is inhibitory to spinal Gamma Efferents neurons ( & stretch reflex /muscle tone ) • Substantia Nigra: Collection of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbr ...
Chapter 18: Senses - Johnston Community College
... aorta respond to the pH of the blood and communicate with the medulla oblongata to change breathing rate. For example, when blood pH drops, these chemoreceptors signal the medulla respiratory center that triggers breathing rate to increase; expiration of CO2 raises the pH of the blood to normal. Tas ...
... aorta respond to the pH of the blood and communicate with the medulla oblongata to change breathing rate. For example, when blood pH drops, these chemoreceptors signal the medulla respiratory center that triggers breathing rate to increase; expiration of CO2 raises the pH of the blood to normal. Tas ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... amyloidosis and Reynaud‟s syndrome are also sometimes associated with the carpal tunnel syndrome. 7 Estimation and assessment of Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies establishes diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy. Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies are usually carried out to (i) evaluate the ...
... amyloidosis and Reynaud‟s syndrome are also sometimes associated with the carpal tunnel syndrome. 7 Estimation and assessment of Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies establishes diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy. Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) studies are usually carried out to (i) evaluate the ...
7-Physiology of brain stem2016-09-25 05:204.2 MB
... Facial grimacing on firm pressure over the supra ...
... Facial grimacing on firm pressure over the supra ...
Nervous System Reading from SparkNotes
... Neurons cannot directly pass an action potential from one to the next because of the synapses between them. Instead, neurons communicate across the synaptic clefts by the means of chemical signals known as neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the synapse, it causes the release of vesi ...
... Neurons cannot directly pass an action potential from one to the next because of the synapses between them. Instead, neurons communicate across the synaptic clefts by the means of chemical signals known as neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the synapse, it causes the release of vesi ...
Know Your Neurons: How to Classify Different Types of Neurons in
... Do these basic classes account for all types of neurons? Well, just about every neuron in the human nervous system should fall into one these broad categories—but these categories do not capture the true diversity of the nervous system. Not even close. If you really want to catalogue neurons in thei ...
... Do these basic classes account for all types of neurons? Well, just about every neuron in the human nervous system should fall into one these broad categories—but these categories do not capture the true diversity of the nervous system. Not even close. If you really want to catalogue neurons in thei ...
Nerve activates contraction
... •Axon terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters •Axon terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap •Synaptic cleft—gap between adjacent neurons •Synapse—junction between nerves ...
... •Axon terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters •Axon terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap •Synaptic cleft—gap between adjacent neurons •Synapse—junction between nerves ...
PDF
... During development, sensory neurons form neural circuits with motoneurons. Although the anatomical details of these circuits are well described, less is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory neuron development, Hiroh ...
... During development, sensory neurons form neural circuits with motoneurons. Although the anatomical details of these circuits are well described, less is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory neuron development, Hiroh ...
Visual organ
... Has ciliary processes and the ciliary muscles The ciliary processes are irregular epithelium covered connective tissue outgrowth of the ciliary body that extends toward the lens ...
... Has ciliary processes and the ciliary muscles The ciliary processes are irregular epithelium covered connective tissue outgrowth of the ciliary body that extends toward the lens ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially ...
... – Interconnected neurons that fire together or sequentially ...
chapter3Weiten
... to Neural Networks One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons Requires integration of signals ...
... to Neural Networks One neuron, signals from thousands of other neurons Requires integration of signals ...