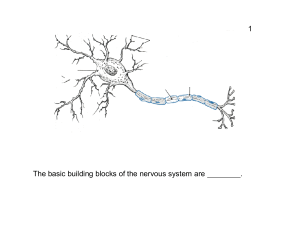
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... two sensory systems. For instance, when he smells a rose, he recognizes the odor but he cannot visualize the flower without actually looking at it. The part of Matthew's brain that was damaged is probably the A. amygdala. B. hippocampus. C. reticular formation. D. hypothalamus. Which of the followin ...
... two sensory systems. For instance, when he smells a rose, he recognizes the odor but he cannot visualize the flower without actually looking at it. The part of Matthew's brain that was damaged is probably the A. amygdala. B. hippocampus. C. reticular formation. D. hypothalamus. Which of the followin ...
Getting to Know: Nervous
... called the axon. Neurons vary in size, but some have axons that stretch for more than one meter in the body! The nerve cells do not touch each other but are separated by spaces called synapses. ...
... called the axon. Neurons vary in size, but some have axons that stretch for more than one meter in the body! The nerve cells do not touch each other but are separated by spaces called synapses. ...
Chapter 10 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... them to the cell body • Axon – conducts impulses away from the nerve cell • Terminal end fibers – lead the nervous impulse away from the axon and toward the synapse. ...
... them to the cell body • Axon – conducts impulses away from the nerve cell • Terminal end fibers – lead the nervous impulse away from the axon and toward the synapse. ...
Chp 9: NERVOUS TISSUE
... of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain ______________________________: dendrites and one axon fused together forming a continuous process that emerges from cell body; begin in embryo as bipolar neurons; most function as sensory receptors for touch, pressure, pain, or thermal stimuli. Cell ...
... of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain ______________________________: dendrites and one axon fused together forming a continuous process that emerges from cell body; begin in embryo as bipolar neurons; most function as sensory receptors for touch, pressure, pain, or thermal stimuli. Cell ...
Coordination and Regulation Check 4 (Solutions)
... 2. Write the functions of each of the four signaling molecules listed in Q1. Neurotransmitters: Compounds produced and released at the ends of axons, such as acetylcholine. They bind to specific receptors on target cell to initiate a response in that cell. Animal hormones: Transported through bloods ...
... 2. Write the functions of each of the four signaling molecules listed in Q1. Neurotransmitters: Compounds produced and released at the ends of axons, such as acetylcholine. They bind to specific receptors on target cell to initiate a response in that cell. Animal hormones: Transported through bloods ...
PowerPoint
... • As a result, Na+ ions diffuse through the membrane into the cell. • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
... • As a result, Na+ ions diffuse through the membrane into the cell. • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
glial cells - Steven-J
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
... Neurons are nerve cells that transmit nerve signals to and from the brain at up to 200 mph. The neuron consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a projection called an axon, which conduct the nerve signal. At the other end of the axon, the axon terminals trans ...
chapter 44 lecture slides
... – Two parts of the temporal lobes, the hippocampus and the amygdala, are involved in both short-term memory and its consolidation into long-term memory ...
... – Two parts of the temporal lobes, the hippocampus and the amygdala, are involved in both short-term memory and its consolidation into long-term memory ...
chapter 44 lecture slides
... – Two parts of the temporal lobes, the hippocampus and the amygdala, are involved in both short-term memory and its consolidation into long-term memory ...
... – Two parts of the temporal lobes, the hippocampus and the amygdala, are involved in both short-term memory and its consolidation into long-term memory ...
molecular mechanisms of axonal regeneration in the central
... the number on the intact side provides an index of neurodegeneration that can be used to test various strategies to improve neuron survival following axotomy. This model was used to demonstrate that transplanting tissue grafts of fetal neural tissue into the lesion site protected many of the Clarke’ ...
... the number on the intact side provides an index of neurodegeneration that can be used to test various strategies to improve neuron survival following axotomy. This model was used to demonstrate that transplanting tissue grafts of fetal neural tissue into the lesion site protected many of the Clarke’ ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the structure identified in question 16. ...
... D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the structure identified in question 16. ...
Reaching for the brain: stimulating neural activity as the big leap in
... increasing electrical activity of retinal ganglion cells to enhance regrowth of their axons. This builds upon a large body of evidence—both from preclinical work and clinical trials—for its success in peripheral nerve regeneration, where electrical stimulation is a well-known treatment to promote ne ...
... increasing electrical activity of retinal ganglion cells to enhance regrowth of their axons. This builds upon a large body of evidence—both from preclinical work and clinical trials—for its success in peripheral nerve regeneration, where electrical stimulation is a well-known treatment to promote ne ...
14.1-NervousMusculo-Skeletal-System
... The myelin sheath is a protein-rich gel that coats the arms of neurons (the dendrites and axons), creating electrical insulation. Describe the ‘gap’ between neurons. What is it called? How does a signal pass through this ‘gap’? The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an el ...
... The myelin sheath is a protein-rich gel that coats the arms of neurons (the dendrites and axons), creating electrical insulation. Describe the ‘gap’ between neurons. What is it called? How does a signal pass through this ‘gap’? The gap between the neurons is called the synapse. This is where an el ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... There is a town where 5% of all the people living there have unlisted phone numbers. If you selected 100 names at random from the town’s phone directory, on average, how many of these people would have unlisted phone numbers? ...
... There is a town where 5% of all the people living there have unlisted phone numbers. If you selected 100 names at random from the town’s phone directory, on average, how many of these people would have unlisted phone numbers? ...
S1 Table.
... transient in Oct6 mutants, while arrest is prominent in Krox20 mutant Depends on continued axonal contact Oct6 is strongly down-regulated after the pick of myelination GFAP is a glial-specific member of the intermediate filament family Appears in relatively late stage in Schwann cell development, do ...
... transient in Oct6 mutants, while arrest is prominent in Krox20 mutant Depends on continued axonal contact Oct6 is strongly down-regulated after the pick of myelination GFAP is a glial-specific member of the intermediate filament family Appears in relatively late stage in Schwann cell development, do ...
File
... Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior _________ muscles and relay sensory impulses from skin of the ...
... Craniosacral division: the _____________ nervous system, in which nerves originate in the brain stem or sacral region of the spinal cord Dorsal ramus: the division of __________ spinal nerves that transmit motor impulses to the posterior _________ muscles and relay sensory impulses from skin of the ...
biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite
... Terms and Topics: Nervous and Endocrine Systems biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite agonists axon antagonists myelin sheath blood-brain barrier cell body nervous system central nervous system terminal branches of axon synapse (synaptic gap) peripheral nervous system neural i ...
... Terms and Topics: Nervous and Endocrine Systems biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite agonists axon antagonists myelin sheath blood-brain barrier cell body nervous system central nervous system terminal branches of axon synapse (synaptic gap) peripheral nervous system neural i ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... 1. At rest – Na+/K+ pump moving ions – potassium gates open 2. Stimulation – potassium gates close – sodium gates open 3. The flood of sodium into the cytoplasm ...
... 1. At rest – Na+/K+ pump moving ions – potassium gates open 2. Stimulation – potassium gates close – sodium gates open 3. The flood of sodium into the cytoplasm ...
Neurons Short Version
... Unipolar neurons has one extension from the cell body. Bipolar neurons have two extensions from the cell body. Multipolar neurons ( which are the most common) and usually the one referred to has many dendrites and usually one axon. ...
... Unipolar neurons has one extension from the cell body. Bipolar neurons have two extensions from the cell body. Multipolar neurons ( which are the most common) and usually the one referred to has many dendrites and usually one axon. ...