MTC42: control of smooth muscle 11/10/07
... o Sympathetic – arising from the spinal cord (thoraco-lumbar) o Parasympathetic – arising from the brain stem (cranio-sacral) o Enteric – surrounding the gastrointestinal tract Cell bodies of ANS preganglionic neurons are found in the brain stem and spinal cord (within the CNS) and send axons (now p ...
... o Sympathetic – arising from the spinal cord (thoraco-lumbar) o Parasympathetic – arising from the brain stem (cranio-sacral) o Enteric – surrounding the gastrointestinal tract Cell bodies of ANS preganglionic neurons are found in the brain stem and spinal cord (within the CNS) and send axons (now p ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... 5. The neural components of the eye are the retina and optic nerve. The retina absorbs light, partially processes the visual information, and encodes the stimulus in action potentials conducted via the optic nerve to the brain. The sharpest vision occurs in a region of retina called the fovea centra ...
... 5. The neural components of the eye are the retina and optic nerve. The retina absorbs light, partially processes the visual information, and encodes the stimulus in action potentials conducted via the optic nerve to the brain. The sharpest vision occurs in a region of retina called the fovea centra ...
distribution of leucine-3h during axoplasmic
... was analyzed by comparing the localization of silver grains with the areas comprised by the cellular components (Ross and Benditt, 1965) . The center of a circle enclosing the silver grains was used to designate the structure beneath the grain . Areas were determined by applying a transparent screen ...
... was analyzed by comparing the localization of silver grains with the areas comprised by the cellular components (Ross and Benditt, 1965) . The center of a circle enclosing the silver grains was used to designate the structure beneath the grain . Areas were determined by applying a transparent screen ...
The Facts About Nerve Agents (General Information)
... What are nerve agents? Nerve agents are chemicals that affect the nervous system. The health effects are similar to those produced by some pesticides. The main nerve agents are the chemicals sarin (GB), soman (GD), tabun (GA) and VX. These agents are man-made and have been manufactured for use in ch ...
... What are nerve agents? Nerve agents are chemicals that affect the nervous system. The health effects are similar to those produced by some pesticides. The main nerve agents are the chemicals sarin (GB), soman (GD), tabun (GA) and VX. These agents are man-made and have been manufactured for use in ch ...
Somatosensory system
... Dorsal root ganglia - spinal nerve - limb and trunk Trigeminal ganglia - cranial nerve - head and face ...
... Dorsal root ganglia - spinal nerve - limb and trunk Trigeminal ganglia - cranial nerve - head and face ...
The Brain, Biology, and Behavior
... A highly magnified view of the synapse shown in Fig. 3.1. Neurotransmitters are stored in tiny sacs called synaptic vesicles. When a nerve impulse arrives at an axon terminal, the vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters. These transmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap to affect ...
... A highly magnified view of the synapse shown in Fig. 3.1. Neurotransmitters are stored in tiny sacs called synaptic vesicles. When a nerve impulse arrives at an axon terminal, the vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters. These transmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap to affect ...
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
... Hairy skin also contains hair follicle mechanoreceptors, in which a nerve ending is wrapped around the base of a hair so that movement of the hair stimulates the nerve ending. Animals' whiskers are specialized variations of hair follicle receptors. The whiskers are an extremely important source of s ...
... Hairy skin also contains hair follicle mechanoreceptors, in which a nerve ending is wrapped around the base of a hair so that movement of the hair stimulates the nerve ending. Animals' whiskers are specialized variations of hair follicle receptors. The whiskers are an extremely important source of s ...
The Hypothalamus and Human Nervous System: A Primer
... I reported in – “Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: An Introduction” - that multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is a real physiological disorder with an unknown origin. However, numerous theories have been proposed leaving one wondering where to start in their search for the root cause of MCS. I also pr ...
... I reported in – “Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: An Introduction” - that multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is a real physiological disorder with an unknown origin. However, numerous theories have been proposed leaving one wondering where to start in their search for the root cause of MCS. I also pr ...
SENSORY SYSTEMS (Windows to the World
... Ampullary organ sensitive to low freq. fields (0.1-20 Hz) - 0.005 uV/cm gradient - what a flounders makes at 30 cm. Detect 1.5 V battery across 1500 Km of saltwater. Gymnotidae & Mormyridae, weakly active electric fish Tuberous organ sensitive to high freq. fields (50social signals. Can pulse field ...
... Ampullary organ sensitive to low freq. fields (0.1-20 Hz) - 0.005 uV/cm gradient - what a flounders makes at 30 cm. Detect 1.5 V battery across 1500 Km of saltwater. Gymnotidae & Mormyridae, weakly active electric fish Tuberous organ sensitive to high freq. fields (50social signals. Can pulse field ...
Nervous Notes File
... When Things Go Wrong: Disruptions in Homeostasis 3. Spinal Cord Injuries Due to a blow or fracture that dislocates the ...
... When Things Go Wrong: Disruptions in Homeostasis 3. Spinal Cord Injuries Due to a blow or fracture that dislocates the ...
The Nanostructure of the Nervous System and the Impact
... There are many different types and sub-types of cells in the CNS, each a highly specialized terminal phenotype cell designed to carry out a specific function. In general, there are two main classes of cells in the nervous system: neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the fundamental functional (i.e. ...
... There are many different types and sub-types of cells in the CNS, each a highly specialized terminal phenotype cell designed to carry out a specific function. In general, there are two main classes of cells in the nervous system: neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the fundamental functional (i.e. ...
Nervous System
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
Nervous System
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
... and make synapses all over the body with other neurons, muscles and glands • communicate through action potentials • allows for short response times to changes in homeostasis – Neuroglia • guide developing neurons to make synapses • provide a supportive scaffolding for developed neurons ...
638965471899MyersMod_LG_03
... 3. Describe how nerve cells communicate, and discuss the impact of neurotransmitters and drugs on human behavior. When electrical impulses reach the axon terminal, they stimulate the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters that cross the junction between neurons called the synapse. A ...
... 3. Describe how nerve cells communicate, and discuss the impact of neurotransmitters and drugs on human behavior. When electrical impulses reach the axon terminal, they stimulate the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters that cross the junction between neurons called the synapse. A ...
06 trauma
... • The rapid movement of the brain that occurs in trauma can tear the bridging veins that extend from the cerebral hemispheres through the subarachnoid and subdural space to empty into dural sinuses • These vessels are particularly prone to tearing, and their disruption leads to bleeding into the sub ...
... • The rapid movement of the brain that occurs in trauma can tear the bridging veins that extend from the cerebral hemispheres through the subarachnoid and subdural space to empty into dural sinuses • These vessels are particularly prone to tearing, and their disruption leads to bleeding into the sub ...
Anatomical and molecular analyses used to
... the work done by the team in the same journal issue and further describes a type of biomedical device called a neural dust implant that is being used in electroceutical treatment of damaged nerves. The autonomic nervous system controls bodily functions that are not consciously directed such as diges ...
... the work done by the team in the same journal issue and further describes a type of biomedical device called a neural dust implant that is being used in electroceutical treatment of damaged nerves. The autonomic nervous system controls bodily functions that are not consciously directed such as diges ...
Opioids General - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Opioid receptors are part of a large superfamily of membrane-bound receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Oth ...
... Opioid receptors are part of a large superfamily of membrane-bound receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Oth ...
Receptor Cells
... muscles that change the thickness of the lens change how the light is bent thereby focusing the image ...
... muscles that change the thickness of the lens change how the light is bent thereby focusing the image ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... The Peripheral Nervous System What we already know… the PNS is/has – Nervous structures outside the brain and spinal cord – Nerves allow the CNS to receive information and take action – Functional components of the PNS • Afferent (Sensory) – Has somatic and visceral components » Each with a gener ...
... The Peripheral Nervous System What we already know… the PNS is/has – Nervous structures outside the brain and spinal cord – Nerves allow the CNS to receive information and take action – Functional components of the PNS • Afferent (Sensory) – Has somatic and visceral components » Each with a gener ...
The Cellular Level of Organization
... Temperature - the greater the temperature the faster the transmission – Localized cooling can block impulse conduction; therefore pain can be reduced by application of ice ...
... Temperature - the greater the temperature the faster the transmission – Localized cooling can block impulse conduction; therefore pain can be reduced by application of ice ...
Hypothalamus
... profoundly affect autonomic function, more recent investigation have demonstrated that many of these effects are due to the involvement of descending and ascending pathways of the cerebral cortex or the basal forebrain passing through the hypothalamus. ...
... profoundly affect autonomic function, more recent investigation have demonstrated that many of these effects are due to the involvement of descending and ascending pathways of the cerebral cortex or the basal forebrain passing through the hypothalamus. ...
Chapter 33 - CanonMacZoology
... • Gastrodermis- inner layer • Mesoglea- between epidermis & gastrodermis • Gastrovascular cavity- single opening or mouth • Tentacles- flexible extensions ...
... • Gastrodermis- inner layer • Mesoglea- between epidermis & gastrodermis • Gastrovascular cavity- single opening or mouth • Tentacles- flexible extensions ...
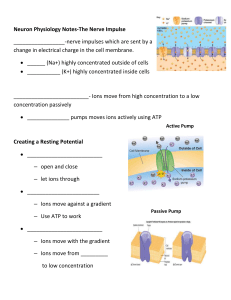
Neuron Physiology Notes
... Neuron Physiology Notes-The Nerve Impulse _________________-nerve impulses which are sent by a change in electrical charge in the cell membrane. ______ (Na+) highly concentrated outside of cells ___________ (K+) highly concentrated inside cells ...
... Neuron Physiology Notes-The Nerve Impulse _________________-nerve impulses which are sent by a change in electrical charge in the cell membrane. ______ (Na+) highly concentrated outside of cells ___________ (K+) highly concentrated inside cells ...
Objectives included for the test File
... State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron. State that nerve impulses are conducted from receptors to t ...
... State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. Draw and label a diagram of the structure of a motor neuron. State that nerve impulses are conducted from receptors to t ...