Schwann cells
... Schwann cells hold 1 – 12 small nerve fibers in grooves on its surface membrane folds once around each fiber overlapping itself along the edges mesaxon – neurilemma wrapping of unmyelinated nerve fibers ...
... Schwann cells hold 1 – 12 small nerve fibers in grooves on its surface membrane folds once around each fiber overlapping itself along the edges mesaxon – neurilemma wrapping of unmyelinated nerve fibers ...
Brain and Nervous System
... neurotransmitters, mitochondria and other cell organelles, 2. a postsynaptic ending that contains receptor sites for neurotransmitters and, 3. a synaptic cleft or space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic endings. ...
... neurotransmitters, mitochondria and other cell organelles, 2. a postsynaptic ending that contains receptor sites for neurotransmitters and, 3. a synaptic cleft or space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic endings. ...
Selective nerve root blocks - Desert Spine and Sports Physicians
... Nerve roots exit the spinal cord and form nerves that travel into the arms, legs and chest. These nerve roots may become inflamed and painful due to compression or irritation from things like herniated discs or bone spurs. A selective nerve root block involves placing a temporary anesthetic (numbing ...
... Nerve roots exit the spinal cord and form nerves that travel into the arms, legs and chest. These nerve roots may become inflamed and painful due to compression or irritation from things like herniated discs or bone spurs. A selective nerve root block involves placing a temporary anesthetic (numbing ...
Nervous System
... Intelligence, Learning, and Memory When you learn things, messages travel from one neuron to another, over and over. Then the brain creates connections (or pathways) between the neurons, so things become easier and you can do them better and better. In young children, the brain is highly adaptable. ...
... Intelligence, Learning, and Memory When you learn things, messages travel from one neuron to another, over and over. Then the brain creates connections (or pathways) between the neurons, so things become easier and you can do them better and better. In young children, the brain is highly adaptable. ...
Trigeminal nerve
... through mandibular canal in association with inferior alveolar vein and artey • This nerve anteriorly through the mandibular canal until mental foramen and then divided in to two branches : mental and incisive 4.Mylohyoid nerve : branch from inferior alveolar nerve iust before its entry into the can ...
... through mandibular canal in association with inferior alveolar vein and artey • This nerve anteriorly through the mandibular canal until mental foramen and then divided in to two branches : mental and incisive 4.Mylohyoid nerve : branch from inferior alveolar nerve iust before its entry into the can ...
solutions
... Refers to the fact that biomedical signals occur within a conductive medium, human tissue, that links electrical activity within a microscopic source to potential distributions across the body’s surface. It is important because understanding this principle helps to correctly interpret biomedical wav ...
... Refers to the fact that biomedical signals occur within a conductive medium, human tissue, that links electrical activity within a microscopic source to potential distributions across the body’s surface. It is important because understanding this principle helps to correctly interpret biomedical wav ...
Control and Coordination
... central nervous system. In response to stimuli, sensory neurons generate and propagate signals to the central nervous system which then processes and conducts signals back to the muscles and glands. It is made up of 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. ...
... central nervous system. In response to stimuli, sensory neurons generate and propagate signals to the central nervous system which then processes and conducts signals back to the muscles and glands. It is made up of 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. ...
Control and Coordination(converted)
... central nervous system. In response to stimuli, sensory neurons generate and propagate signals to the central nervous system which then processes and conducts signals back to the muscles and glands. It is made up of 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. ...
... central nervous system. In response to stimuli, sensory neurons generate and propagate signals to the central nervous system which then processes and conducts signals back to the muscles and glands. It is made up of 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. ...
chapter 48
... neuron to another and then back to its source (for example memory stored information). ...
... neuron to another and then back to its source (for example memory stored information). ...
THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL REFLEXES
... A: Receptive fields. Size and locations of the receptive fields of 15 sensory units, determined by recording from the median nerve. All of these sensory units were rapidly adapting and were most likely conducting from Meisner-corpuscles. Within each receptive fields there are many Meissner corpuscle ...
... A: Receptive fields. Size and locations of the receptive fields of 15 sensory units, determined by recording from the median nerve. All of these sensory units were rapidly adapting and were most likely conducting from Meisner-corpuscles. Within each receptive fields there are many Meissner corpuscle ...
Nervous Systems II PPT
... 3 basic function of all neurons: ◦ Receive and integrate incoming signals ◦ Conduct these signals through the cell ◦ Transmit these signals to other cells ...
... 3 basic function of all neurons: ◦ Receive and integrate incoming signals ◦ Conduct these signals through the cell ◦ Transmit these signals to other cells ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... ◦ Controls protein manufacturing ◦ Directs metabolism ◦ No role in neural signaling ...
... ◦ Controls protein manufacturing ◦ Directs metabolism ◦ No role in neural signaling ...
Epilepsy & Membrane Potentials
... Mechanical and/or biomolecules cause opening/closing of ion channels (K+, Ca2+, Na+) on receptor membrane = ...
... Mechanical and/or biomolecules cause opening/closing of ion channels (K+, Ca2+, Na+) on receptor membrane = ...
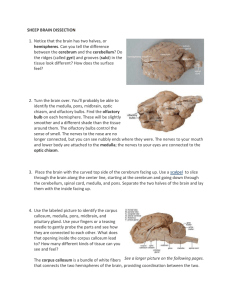
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and smell. You can find this by looking on the outside of one of the hemispheres. You will see a horizontal groove called the lateral fissure. The temporal lobe is the section of the cerebrum below this line. The frontal lobe also plays a part in smell, plus ...
... The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and smell. You can find this by looking on the outside of one of the hemispheres. You will see a horizontal groove called the lateral fissure. The temporal lobe is the section of the cerebrum below this line. The frontal lobe also plays a part in smell, plus ...
Nervous tissue Nervous system
... in the body, they can be grouped into three general categories. • Sensory neurons convey impulses from receptors to the CNS. Processes of these neurons are included in somatic afferent and visceral afferent nerve fibers. Somatic afferent fibers convey sensations of pain, temperature, touch, and pres ...
... in the body, they can be grouped into three general categories. • Sensory neurons convey impulses from receptors to the CNS. Processes of these neurons are included in somatic afferent and visceral afferent nerve fibers. Somatic afferent fibers convey sensations of pain, temperature, touch, and pres ...
nervous system physiology 7
... Autonomic postganglionic neurons can change their transmitters phenotype ! Some ANS neurons can change their transmitter phenotypes under appropriate environmental conditions, demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo – phenotypic switching/plasticity: – During development (e.g. innervation of sweat g ...
... Autonomic postganglionic neurons can change their transmitters phenotype ! Some ANS neurons can change their transmitter phenotypes under appropriate environmental conditions, demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo – phenotypic switching/plasticity: – During development (e.g. innervation of sweat g ...
MOTILITY-FLOW AND GROWTH CONE NAVIGATION ANALYSIS
... • Special image processing algorithms were adapted • Detection of very small and slowly moving spatial changes, and to inspect low contrast image features characteristic of motion and dynamics of a living cell in a long time frame. ...
... • Special image processing algorithms were adapted • Detection of very small and slowly moving spatial changes, and to inspect low contrast image features characteristic of motion and dynamics of a living cell in a long time frame. ...
Poster Session Abstract Booklet - The New York Academy of Sciences
... Ultrasound (US) technology enables non-invasive stimulation of inaccessible areas, such as deep brain tissue, and has shown promise as both a therapeutic tool and a technique to study basic neuronal mechanisms. The goal of this project is to analyze the response properties of US stimulation in perip ...
... Ultrasound (US) technology enables non-invasive stimulation of inaccessible areas, such as deep brain tissue, and has shown promise as both a therapeutic tool and a technique to study basic neuronal mechanisms. The goal of this project is to analyze the response properties of US stimulation in perip ...
Introduction to the Cervical Spine
... The spine is composed of four main areas, cervical (C1-C7), thoracic (T1-T12), lumbar (L1-L5), the sacrum, and the coccyx. Each spinal vertebra can be divided into an anterior part called the vertebral body, which provides much of the structural support (and is separated from its neighboring vertebr ...
... The spine is composed of four main areas, cervical (C1-C7), thoracic (T1-T12), lumbar (L1-L5), the sacrum, and the coccyx. Each spinal vertebra can be divided into an anterior part called the vertebral body, which provides much of the structural support (and is separated from its neighboring vertebr ...
Chapter 11 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... – In some neurons, axons are short or absent; in others, axon comprises almost entire length of cell • Some axons can be over 1 meter long ...
... – In some neurons, axons are short or absent; in others, axon comprises almost entire length of cell • Some axons can be over 1 meter long ...
Practice Exam 3 ANSWERS
... a. is propagated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels b. occurs whenever a pre-synaptic nerve fires a charge to a post synaptic nerve c. is carried out only whenever half of the neural threshold is reached d. moves bidirectionally away from the cell body 4. Saltatory conduction is made po ...
... a. is propagated by the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels b. occurs whenever a pre-synaptic nerve fires a charge to a post synaptic nerve c. is carried out only whenever half of the neural threshold is reached d. moves bidirectionally away from the cell body 4. Saltatory conduction is made po ...
Unit 1 – Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – projections of cell cytoplasm that carry signals towards the cell body Cell Body (soma) - holds all of the general parts of a cell as well as the nucleus, which is the control center Axon – extension of cytoplasm that carries signal (nerve impulse) away from dendrites and the cell ...
... Dendrites – projections of cell cytoplasm that carry signals towards the cell body Cell Body (soma) - holds all of the general parts of a cell as well as the nucleus, which is the control center Axon – extension of cytoplasm that carries signal (nerve impulse) away from dendrites and the cell ...