Nervous System
... Nervous tissue cont’d. • Neuron structure cont’d. – 3 parts of a neuron • Cell body – Contains nucleus and most organelles • Dendrites – Extensions leading toward cell body – Receive signals from other neurons – Send them to cell body • Axon – Conducts impulses away from cell body – Toward other ne ...
... Nervous tissue cont’d. • Neuron structure cont’d. – 3 parts of a neuron • Cell body – Contains nucleus and most organelles • Dendrites – Extensions leading toward cell body – Receive signals from other neurons – Send them to cell body • Axon – Conducts impulses away from cell body – Toward other ne ...
PowerPoint Chapter 29
... d. Touch, temperature, and pain 1). Touch- uses two types of mechanoreceptors (light and heavy ...
... d. Touch, temperature, and pain 1). Touch- uses two types of mechanoreceptors (light and heavy ...
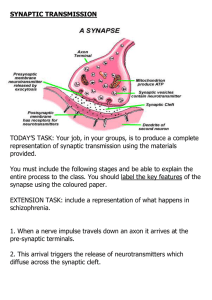
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic ...
... 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic ...
Chapter 14-Nervous Tissue
... • Bipolar have two processes from cell body • Present in olfactory epithelium of nose and retina of eye Cell body ...
... • Bipolar have two processes from cell body • Present in olfactory epithelium of nose and retina of eye Cell body ...
Understanding Glial Differentiation in Vertebrate Nervous - J
... 2002). Consistently, knockout mouse embryos that lack Neuregulin1 or the genes for its receptor showed a severe reduction of Schwann cell precursors along the spinal nerve (Jessen and Mirsky 2002). While Neuregulin1 has also been suggested to regulate migration and survival of Schwann cells (Jessen ...
... 2002). Consistently, knockout mouse embryos that lack Neuregulin1 or the genes for its receptor showed a severe reduction of Schwann cell precursors along the spinal nerve (Jessen and Mirsky 2002). While Neuregulin1 has also been suggested to regulate migration and survival of Schwann cells (Jessen ...
Brain`s Building Blocks
... chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions ◦ genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
... chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions ◦ genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
Nervous System Notes
... of interacting subsystems composed of group of cells. MS-LS1-8: Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories. ...
... of interacting subsystems composed of group of cells. MS-LS1-8: Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories. ...
File
... Chapter 2: The Biology of Mind Objectives ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, ...
... Chapter 2: The Biology of Mind Objectives ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... A disorder of the inner ear. Although the cause is unknown, it probably results from an abnormality in the fluids of the inner ear. Ménière’s disease is one of the most common causes of dizziness originating in the inner ear. In most cases only one ear is involved, but both ears may be affecte ...
... A disorder of the inner ear. Although the cause is unknown, it probably results from an abnormality in the fluids of the inner ear. Ménière’s disease is one of the most common causes of dizziness originating in the inner ear. In most cases only one ear is involved, but both ears may be affecte ...
Bilateral communication between
... Bilateral communication between musculocutaneous and median nerve the MN in the middle of the arm, whereas in type III, the lateral root fibres of the MN pass along the MCN and after some distance, leave it to form the lateral root of the MN. In type IV, the MCN fibres join the lateral root of the ...
... Bilateral communication between musculocutaneous and median nerve the MN in the middle of the arm, whereas in type III, the lateral root fibres of the MN pass along the MCN and after some distance, leave it to form the lateral root of the MN. In type IV, the MCN fibres join the lateral root of the ...
Morphological Identification of Cell Death in Dorsal Root Ganglion
... peripheral axotomy than motor neurons, probably because they depend more on neurotrophic molecules released by peripheral target organs [15]. Our study showed that direct reconnection of the proximal nerve stump with its distal stump will reduce the sensory neuronal loss from 42% to 23.7%. In the pr ...
... peripheral axotomy than motor neurons, probably because they depend more on neurotrophic molecules released by peripheral target organs [15]. Our study showed that direct reconnection of the proximal nerve stump with its distal stump will reduce the sensory neuronal loss from 42% to 23.7%. In the pr ...
Assignment 8
... 31. What is the function of the eustachian tube? If you are at high altitude and your ears are popping what should you do and why? nerve. This nerve joins the 32. The neurons from the organ of corti form the ). Impulses travel to the pons and then to the nerve to form the vestibulocochlear nerve (n ...
... 31. What is the function of the eustachian tube? If you are at high altitude and your ears are popping what should you do and why? nerve. This nerve joins the 32. The neurons from the organ of corti form the ). Impulses travel to the pons and then to the nerve to form the vestibulocochlear nerve (n ...
The Nervous System 35-2
... Sensory neurons – carry impulses from the sense organ s to the spinal cord Motor neurons – carry impulses from the brain and the spinal cord to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them ...
... Sensory neurons – carry impulses from the sense organ s to the spinal cord Motor neurons – carry impulses from the brain and the spinal cord to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... -Binds to receptors on ligand-gated channels in the muscle cell, producing an EPSP. -excitatory to vertebrate skeletal muscles -excitatory or inhibitory at other sites. ex)heart muscles-> inhibitory -certain bacteria produce a toxin that specifically inhibits presynaptic release of acetylcholine; to ...
... -Binds to receptors on ligand-gated channels in the muscle cell, producing an EPSP. -excitatory to vertebrate skeletal muscles -excitatory or inhibitory at other sites. ex)heart muscles-> inhibitory -certain bacteria produce a toxin that specifically inhibits presynaptic release of acetylcholine; to ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Understand the structures involved in controlling limbic and autonomic functions. ...
... Understand the structures involved in controlling limbic and autonomic functions. ...
Chapter 2
... Form a non-continuous tube of insulation along axon Bare, non-myelinated portions called Nodes of Ranvier In CNS only (Schwann cells form myelin in PNS) ...
... Form a non-continuous tube of insulation along axon Bare, non-myelinated portions called Nodes of Ranvier In CNS only (Schwann cells form myelin in PNS) ...
Neuron_glia interaction
... Clear neurotransmitters (glutamate and GABA): Astrocytes have distal processes rich in transporters that remove excess neurotransmitters (especially glutamate) If Glutamate is not removed: Diffuses into the ECS. Presynaptic bind and inhibition of its own release. Influence other synapses - “Intersyn ...
... Clear neurotransmitters (glutamate and GABA): Astrocytes have distal processes rich in transporters that remove excess neurotransmitters (especially glutamate) If Glutamate is not removed: Diffuses into the ECS. Presynaptic bind and inhibition of its own release. Influence other synapses - “Intersyn ...
Document
... • Most nerves are mixtures of afferent and efferent fibers and somatic and autonomic (visceral) fibers • Pure sensory (afferent) or motor (efferent) nerves are rare • Types of fibers in mixed nerves: ...
... • Most nerves are mixtures of afferent and efferent fibers and somatic and autonomic (visceral) fibers • Pure sensory (afferent) or motor (efferent) nerves are rare • Types of fibers in mixed nerves: ...
Kevin
... Transmission of Nerve Impulses 6. Refractory Period • This occurs when the sodium and potassium ions are returned to their original sides. While the neuron is pumping the ions to their respective sides, it does not respond to incoming stimuli. After this is complete, the neuron is back to its polar ...
... Transmission of Nerve Impulses 6. Refractory Period • This occurs when the sodium and potassium ions are returned to their original sides. While the neuron is pumping the ions to their respective sides, it does not respond to incoming stimuli. After this is complete, the neuron is back to its polar ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
... Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
... Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
Figure 8.12
... ◦ Allows for light to pass through ◦ Repairs itself easily ◦ The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection ...
... ◦ Allows for light to pass through ◦ Repairs itself easily ◦ The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection ...
The Nervous System and Neurons
... Nervous System (PNS) Mainly nerve fibres outside the brain and spinal cord Consists of long dendrites or axons taking impulses to ...
... Nervous System (PNS) Mainly nerve fibres outside the brain and spinal cord Consists of long dendrites or axons taking impulses to ...
Nervous System
... M.S. Multiple Sclerosis Deterioration of the _____________________________________________ scar tissue on axon no impulse transmission impaired neural function loss of coordination tremor paralysis Nerve Damage due to injury If damaged neurons are covered by the thin membrane c ...
... M.S. Multiple Sclerosis Deterioration of the _____________________________________________ scar tissue on axon no impulse transmission impaired neural function loss of coordination tremor paralysis Nerve Damage due to injury If damaged neurons are covered by the thin membrane c ...