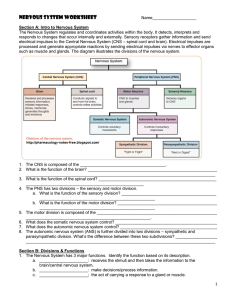
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 7, Part 2 Notes: The Nervous
... 6. Along the length of the axon are Schwann cells made of an insulating material called myelin sheath. The spaces between Schwann cells on the axon are called Nodes of Ranvier. The Schwann cells increase the speed of the nerve signal because the signal jumps from one Node of Ranvier to the next in a ...
... 6. Along the length of the axon are Schwann cells made of an insulating material called myelin sheath. The spaces between Schwann cells on the axon are called Nodes of Ranvier. The Schwann cells increase the speed of the nerve signal because the signal jumps from one Node of Ranvier to the next in a ...
Level 3 Pharmaceutical Science
... Impulses need to move from one neuron to another. The journey of an impulse from the finger crosses 3 junctions before reaching the brain. These junctions are called synapses. A synapse is a gap between two neurons. In an electrical circuit you might expect a gap to result in a failure of the circui ...
... Impulses need to move from one neuron to another. The journey of an impulse from the finger crosses 3 junctions before reaching the brain. These junctions are called synapses. A synapse is a gap between two neurons. In an electrical circuit you might expect a gap to result in a failure of the circui ...
PDF
... cleidomastoid muscles, is located at the dorsomedial edge of the ventral horn at the level of C1 to C3, and the lateral column, which innervates the trapezius and cleido-occipital muscles, is located in the dorsolateral part of the ventral horn at the level of C2 to C6 (Matesz and Szekely 1983; Kram ...
... cleidomastoid muscles, is located at the dorsomedial edge of the ventral horn at the level of C1 to C3, and the lateral column, which innervates the trapezius and cleido-occipital muscles, is located in the dorsolateral part of the ventral horn at the level of C2 to C6 (Matesz and Szekely 1983; Kram ...
Figure 2.25
... The Blood-Brain Barrier • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through ...
... The Blood-Brain Barrier • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through ...
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... ‘high alert’. It’s important in forming memories. (Exercise increases the release of norepinephrine and stress decreases it.) Glutamate – an excitatory neurotransmitter which plays a role in memory. (Excessive amounts of glutamate due to a stroke or brain damage will kill neurons. ALS results from ...
... ‘high alert’. It’s important in forming memories. (Exercise increases the release of norepinephrine and stress decreases it.) Glutamate – an excitatory neurotransmitter which plays a role in memory. (Excessive amounts of glutamate due to a stroke or brain damage will kill neurons. ALS results from ...
Neurons - MrsMcFadin
... nerves and supporting cells) collects information about the body’s external and internal environment. • Also delivers instruction from brain to the appropriate part of the body. ...
... nerves and supporting cells) collects information about the body’s external and internal environment. • Also delivers instruction from brain to the appropriate part of the body. ...
in the name of god faraji.z.md
... pain, or has assessment of the grade of instability changed? How does a manual muscle test compare with yesterday? Has either active or passive range of motion changed? Does accessory movement appear to be limited? Can the patient perform a specific functional test better today than yesterda ...
... pain, or has assessment of the grade of instability changed? How does a manual muscle test compare with yesterday? Has either active or passive range of motion changed? Does accessory movement appear to be limited? Can the patient perform a specific functional test better today than yesterda ...
Summary Sodium pump.
... and the Node goes quickly from negative to positive (action potential) to positive again, and the next Node gets affected. • This jumping action is both fast and efficient (uses less energy) and is known as Saltatory conductance ...
... and the Node goes quickly from negative to positive (action potential) to positive again, and the next Node gets affected. • This jumping action is both fast and efficient (uses less energy) and is known as Saltatory conductance ...
Chapter 14 ()
... most cranial nerves contain the axons of both sensory and motor neurons the cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in sensory organs in cranial sensory ganglia near the brain (comparable to dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves) the cell bodies of motor neurons are located in gray matter (nuc ...
... most cranial nerves contain the axons of both sensory and motor neurons the cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in sensory organs in cranial sensory ganglia near the brain (comparable to dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves) the cell bodies of motor neurons are located in gray matter (nuc ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... they carry signals away from the CNS. C. A motor neuron of the spinal cord illustrates general neuron structure. (pp. 444–447) (Fig. 12.4) 1. The control center is the soma, also called the neurosoma, cell body, or perikaryon. a. It contains a single, centrally located nucleus with a large nucleolus ...
... they carry signals away from the CNS. C. A motor neuron of the spinal cord illustrates general neuron structure. (pp. 444–447) (Fig. 12.4) 1. The control center is the soma, also called the neurosoma, cell body, or perikaryon. a. It contains a single, centrally located nucleus with a large nucleolus ...
29 - IWS2.collin.edu
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Axon collaterals Telodendria Axonal terminal or synaptic knobs ...
... Long axons are called nerve fibers Usually there is only one unbranched axon per neuron Axon collaterals Telodendria Axonal terminal or synaptic knobs ...
Anatomy Physiology Final Exam Review
... d. Cl80. _________________ are neuroglia found in the peripheral nervous system. a. Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Microglia, and ependyma b. Microglia and Schwann cells c. Schwann and satellite cells d. Satellite, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and ependyma cells 81. Which of the following cells are ...
... d. Cl80. _________________ are neuroglia found in the peripheral nervous system. a. Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Microglia, and ependyma b. Microglia and Schwann cells c. Schwann and satellite cells d. Satellite, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and ependyma cells 81. Which of the following cells are ...
The Human Body Systems - Mr. Swan
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) o The Brain & Spinal Cord ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) o The Brain & Spinal Cord ...
Eye, Ear, Sensation & Perception
... Interpret this Sensory Information… I’m going to Fl --- for spring break. “Daylight savings time ends tomorrow, and so people should remember to change ...
... Interpret this Sensory Information… I’m going to Fl --- for spring break. “Daylight savings time ends tomorrow, and so people should remember to change ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Take up and release ions in order to control environment around neurons Involved in synapse formation in developing neural tissue Produce molecules necessary for neuronal growth ...
... Take up and release ions in order to control environment around neurons Involved in synapse formation in developing neural tissue Produce molecules necessary for neuronal growth ...
lecture 20
... – 1. chemical – two neurons separated by a synaptic cleft • requires the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron and the binding of this neurotransmitter by the postsynaptic neuron • majority of chemical synapses formed between end bulb and dendrites • some can form ...
... – 1. chemical – two neurons separated by a synaptic cleft • requires the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron and the binding of this neurotransmitter by the postsynaptic neuron • majority of chemical synapses formed between end bulb and dendrites • some can form ...
Chapter 49 and 50 Presentations-Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... in the nervous system. The membrane potential can change from its resting value when the membrane’s permeability to a particular ion changes—due to the opening/closing of ion channels. Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl- all play major roles in nerve signal ...
... in the nervous system. The membrane potential can change from its resting value when the membrane’s permeability to a particular ion changes—due to the opening/closing of ion channels. Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl- all play major roles in nerve signal ...
Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
... V2 by two sensory roots. Since the ganglion is parasympathetic, there are preganglionic neurons feeding into it from the facial nerve (greater petrosal branch) that synapse at this point then continue onward as postganglionic neurons. ...
... V2 by two sensory roots. Since the ganglion is parasympathetic, there are preganglionic neurons feeding into it from the facial nerve (greater petrosal branch) that synapse at this point then continue onward as postganglionic neurons. ...
NIH Public Access
... neurons do not upregulate growth-associated genes to the same extent as do PNS neurons. Consequently, their ability to regenerate is limited even in the absence of inhibitors. Increasing the intrinsic growth capacity of neurons allows modest axon regeneration within the CNS (Bomze et al. 2001; Neuma ...
... neurons do not upregulate growth-associated genes to the same extent as do PNS neurons. Consequently, their ability to regenerate is limited even in the absence of inhibitors. Increasing the intrinsic growth capacity of neurons allows modest axon regeneration within the CNS (Bomze et al. 2001; Neuma ...
muscle strength testing gradation chart
... 3. Herniations at lumbar disk levels do not usually affect the nerve exiting directly at that level because of the angle and position of exit of these nerves as they exit directly beneath the pedicle they essentially escape injury by the HNP. The nerve level that is usually affected is one level low ...
... 3. Herniations at lumbar disk levels do not usually affect the nerve exiting directly at that level because of the angle and position of exit of these nerves as they exit directly beneath the pedicle they essentially escape injury by the HNP. The nerve level that is usually affected is one level low ...
Journal Paper 1 - Information Services and Technology
... an influx of calcium into glial cells could be a sign that they had been stimulated. Based on that notion, investigators devised a laboratory method called calcium imaging to see whether glial cells known as terminal Schwann cells— which surround synapses where nerves meet muscle cells—were sensitiv ...
... an influx of calcium into glial cells could be a sign that they had been stimulated. Based on that notion, investigators devised a laboratory method called calcium imaging to see whether glial cells known as terminal Schwann cells— which surround synapses where nerves meet muscle cells—were sensitiv ...
The NEURON
... -guide the regrowth of PNS axons: arrange themselves in a series of cylinders that serves as a guide for sprouts of regenerating axons -If one of these sprouts encounters a cylinder the sprout will grow through the tube at the rate of 3-4 mm per day ...
... -guide the regrowth of PNS axons: arrange themselves in a series of cylinders that serves as a guide for sprouts of regenerating axons -If one of these sprouts encounters a cylinder the sprout will grow through the tube at the rate of 3-4 mm per day ...
C13 Spinal Cord / Spinal Nerves / Somatic Reflexes / MC3 What are
... What is a “stretch reflex”? What role does the cerebellum play in a “strethch reflex”? Note: outline the “path” between a muscle spindle and the change in muscle tension. What is a muscle spindle? Function? How are muscle spindles “concentrated” in different skeletal muslces? ...
... What is a “stretch reflex”? What role does the cerebellum play in a “strethch reflex”? Note: outline the “path” between a muscle spindle and the change in muscle tension. What is a muscle spindle? Function? How are muscle spindles “concentrated” in different skeletal muslces? ...
B6 – Brain and Mind Go to the BBC Bitesize website from the school
... Where are light receptor cells found in the eye? ____________________________________ What type of response is caused by simple reflexes? ________________________________ What is the benefit of simple reflex responses? ____________________________________ What is the disadvantage of only using refle ...
... Where are light receptor cells found in the eye? ____________________________________ What type of response is caused by simple reflexes? ________________________________ What is the benefit of simple reflex responses? ____________________________________ What is the disadvantage of only using refle ...