Glutamate Inhibits GABA Excitatory Activity in
... in inhibiting excitation at developing GABAergic synapses? In this paper we test the hypothesis that inhibitory actions of glutamate in developing hypothalamic neurons reduce the excitatory activity of GABA. We used the hypothalamus because of the relatively large proportion of GABAergic cells and p ...
... in inhibiting excitation at developing GABAergic synapses? In this paper we test the hypothesis that inhibitory actions of glutamate in developing hypothalamic neurons reduce the excitatory activity of GABA. We used the hypothalamus because of the relatively large proportion of GABAergic cells and p ...
Dendrite structure
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
Dendrite structure
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
... (Ostapoff et al. 1994). These descriptors are not readily applicable to stellate neurons in other areas of the brain. In some neurons, dendrites radiate in arbitrary directions from the cell body but are restricted to a planar region. This type of laminar radiation (see Table 1.2) is seen in horizon ...
PDF
... tors and enzymes involved in neurotransmission, including choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and NMDA receptors [6], may be cited as important responses to injury that are related to a regenerative strategy [5-8] in the cell body. In adults, such a physiological shift is more related to cell repair th ...
... tors and enzymes involved in neurotransmission, including choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and NMDA receptors [6], may be cited as important responses to injury that are related to a regenerative strategy [5-8] in the cell body. In adults, such a physiological shift is more related to cell repair th ...
Impact of acute inflammation on spinal motoneuron synaptic
... tors and enzymes involved in neurotransmission, including choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and NMDA receptors [6], may be cited as important responses to injury that are related to a regenerative strategy [5-8] in the cell body. In adults, such a physiological shift is more related to cell repair th ...
... tors and enzymes involved in neurotransmission, including choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) and NMDA receptors [6], may be cited as important responses to injury that are related to a regenerative strategy [5-8] in the cell body. In adults, such a physiological shift is more related to cell repair th ...
Isoforms of the human histamine H receptor
... A single gene can potentially codify for several proteins by mRNA alternative splicing. In this process, exons or introns can be excluded from precursor mRNA, thus generating different variants of mature mRNA. The end-result is the synthesis of several proteins from a same gene, with different amino ...
... A single gene can potentially codify for several proteins by mRNA alternative splicing. In this process, exons or introns can be excluded from precursor mRNA, thus generating different variants of mature mRNA. The end-result is the synthesis of several proteins from a same gene, with different amino ...
Sense Organs - mohamadtermos
... Your taste buds have receptors for different kinds of chemicals: sugar, salt, sours, and bitters. This diagram shows how a sugar molecule can enter a taste bud and bind to an ion channel in the membrane of a receptor cell. The receptor cell then sends neurotransmitters to activate the sensory neuron ...
... Your taste buds have receptors for different kinds of chemicals: sugar, salt, sours, and bitters. This diagram shows how a sugar molecule can enter a taste bud and bind to an ion channel in the membrane of a receptor cell. The receptor cell then sends neurotransmitters to activate the sensory neuron ...
Identification of Mechanoafferent Neurons in Terrestrial Snail
... examination of 263 PlVL cells in 52 preparations. The PlVL neurons were electrically silent, showing no spontaneous activity or fast synaptic potentials both in isolated brain and reduced CNS-foot preparations. The average membrane potential of the PlVL cells was 57.5 ⫾ 3.1 mV. A gentle mechanical t ...
... examination of 263 PlVL cells in 52 preparations. The PlVL neurons were electrically silent, showing no spontaneous activity or fast synaptic potentials both in isolated brain and reduced CNS-foot preparations. The average membrane potential of the PlVL cells was 57.5 ⫾ 3.1 mV. A gentle mechanical t ...
32 MaxPlanckResearch 3 | 09 Small but mighty: In mice, around ten
... potentially identify hundreds of thousands. Because small structural changes in odorant molecules alter the interaction with the receptors only gradually, the number of chemicals that can be smelled is theoretically unlimited. A receptor protein recognizes a defined part of a molecule very specifica ...
... potentially identify hundreds of thousands. Because small structural changes in odorant molecules alter the interaction with the receptors only gradually, the number of chemicals that can be smelled is theoretically unlimited. A receptor protein recognizes a defined part of a molecule very specifica ...
ELECTRODEPOSITION OF ALLOYS, 1930 TO 1940.1 By Ci
... Somato-sympathetic reflex. The average SNA response to intermittent stimulation of the tibial nerve was tested both before and after microinjection of drugs. Intermittent tibial nerve stimulation resulted in a characteristic two-peaked response in the sSNA with the latencies of 115 ⫾ 2 ms and 211 ⫾ ...
... Somato-sympathetic reflex. The average SNA response to intermittent stimulation of the tibial nerve was tested both before and after microinjection of drugs. Intermittent tibial nerve stimulation resulted in a characteristic two-peaked response in the sSNA with the latencies of 115 ⫾ 2 ms and 211 ⫾ ...
Preferential Termination of Corticorubral Axons on Spine
... Shatz, 1993; Goodman, 1996), but relatively little is known about what interactions occur within the final target. It is presumed that a cascade of complex events must take place at the target, because not only the presynaptic axons but also the postsynaptic cells must be continuously growing and re ...
... Shatz, 1993; Goodman, 1996), but relatively little is known about what interactions occur within the final target. It is presumed that a cascade of complex events must take place at the target, because not only the presynaptic axons but also the postsynaptic cells must be continuously growing and re ...
Applying Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation to the Study of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity in Neural Networks
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
Inan et al., 2006
... the development and plasticity of thalamocortical afferent clustering into a barrel pattern. We localize PKARII function to postsynaptic processes in barrel cortex and show that postsynaptic PKA targets, but not presynaptic PKA targets, have decreased phosphorylation in pkar2b knock-out (PKARII⫺/⫺ ...
... the development and plasticity of thalamocortical afferent clustering into a barrel pattern. We localize PKARII function to postsynaptic processes in barrel cortex and show that postsynaptic PKA targets, but not presynaptic PKA targets, have decreased phosphorylation in pkar2b knock-out (PKARII⫺/⫺ ...
Modulation of Responses of Feline Ventral Spinocerebellar Tract
... threshold for generating an action potential. If it was subthreshold, the intensity of the stimuli was adjusted according to whether any action potential was induced by the second stimulus. Because the EPSP after the second stimulus was superimposed on that after the first stimulus, the presence of ...
... threshold for generating an action potential. If it was subthreshold, the intensity of the stimuli was adjusted according to whether any action potential was induced by the second stimulus. Because the EPSP after the second stimulus was superimposed on that after the first stimulus, the presence of ...
Spinal Cord - Sydney University Medical Society
... Joint Receptors - these are carried via Type II fibres (~30-70m/s) o Pain / Temperature A-delta Free Nerve Endings – these Type III fibres have small amount of myelin and are associated with sharp, local pain which is typically superficial (~0.5-2m/s) C Free Nerve Endings – these Type IV fibre ...
... Joint Receptors - these are carried via Type II fibres (~30-70m/s) o Pain / Temperature A-delta Free Nerve Endings – these Type III fibres have small amount of myelin and are associated with sharp, local pain which is typically superficial (~0.5-2m/s) C Free Nerve Endings – these Type IV fibre ...
Role of Cerebral Cortex in Voluntary Movements
... turn, can alter activity in the motor cortex or brain-stem descending systems. One of the roles of the motor cortex is to transform these diverse input signals, including sensory signals, into appropriate output commands coding which muscles should contract and at what force. MOTOR CORTEX FUNCTIONS ...
... turn, can alter activity in the motor cortex or brain-stem descending systems. One of the roles of the motor cortex is to transform these diverse input signals, including sensory signals, into appropriate output commands coding which muscles should contract and at what force. MOTOR CORTEX FUNCTIONS ...
Stahl_3rd_ch19_Part2..
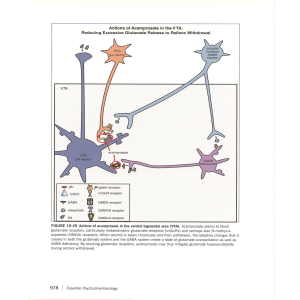
... FIGURE 19-30 Actions of opiates on reward circuits. Neurons originating in the arcuate nucleus project to both the ventral tegmental area (VTA),site of dopamine cell bodies and also where many neurotransmitters project, and the nucleus accumbens, to which dopaminergic neurons project. Opiate neurons ...
... FIGURE 19-30 Actions of opiates on reward circuits. Neurons originating in the arcuate nucleus project to both the ventral tegmental area (VTA),site of dopamine cell bodies and also where many neurotransmitters project, and the nucleus accumbens, to which dopaminergic neurons project. Opiate neurons ...
Expression of AMPA/kainate receptors during development of chick
... GluR1, GluR2/3, GluR4 and GluR6/7 was determined in the retinospheroids and in chick retinas by immunodetection using polyclonal antibodies. The changes in [Ca2+ ]i in response to 400 M kainate increased from 5 h in vitro to 3 days, and remained constant until day 14, whereas the [Ca2+ ]i in respon ...
... GluR1, GluR2/3, GluR4 and GluR6/7 was determined in the retinospheroids and in chick retinas by immunodetection using polyclonal antibodies. The changes in [Ca2+ ]i in response to 400 M kainate increased from 5 h in vitro to 3 days, and remained constant until day 14, whereas the [Ca2+ ]i in respon ...
The Organization of the Frontal Motor Cortex
... showed that F3 is electrically excitable with low-intensity currents and contains a complete body movement representation. Evoked movements mainly involved proximal and axial muscles and, typically, a combination of different joints, even at the minimal effective current intensity. Distal movements, ...
... showed that F3 is electrically excitable with low-intensity currents and contains a complete body movement representation. Evoked movements mainly involved proximal and axial muscles and, typically, a combination of different joints, even at the minimal effective current intensity. Distal movements, ...
Post-pubertal Emergence of Prefrontal Cortical Up
... D1 + NMDA-induced membrane potential oscillations could reflect activity of a local neural network impinging on the recorded neuron. Holding the membrane potential to its baseline value failed to block plateau depolarizations induced by D1--NMDA in six of six cells tested (Fig. 4a), suggesting that v ...
... D1 + NMDA-induced membrane potential oscillations could reflect activity of a local neural network impinging on the recorded neuron. Holding the membrane potential to its baseline value failed to block plateau depolarizations induced by D1--NMDA in six of six cells tested (Fig. 4a), suggesting that v ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.