The tetrapartite synapse_ Extracellular matrix remodeling
... with the catalytic Zn2þ. When this interaction is broken, Zn2þ ...
... with the catalytic Zn2þ. When this interaction is broken, Zn2þ ...
AP150 PATHWAYS ASSIGNMENT
... An action potential begins on a ___UPPER MOTOR_ neurons that leaves the __FRONTAL__ lobe of the brain and passes through the ____CEREBRAL PENDUNCLES__ of the midbrain and then the __PYRAMIDS__ of the medulla oblongata where it then decussates and travels down a __ANTERIOR OR LATTERAL __ column to th ...
... An action potential begins on a ___UPPER MOTOR_ neurons that leaves the __FRONTAL__ lobe of the brain and passes through the ____CEREBRAL PENDUNCLES__ of the midbrain and then the __PYRAMIDS__ of the medulla oblongata where it then decussates and travels down a __ANTERIOR OR LATTERAL __ column to th ...
Organization of acetylcholine-containing structures in the cranial
... precise information on their spatial location in relation to the cholinergic motoneurons in the rat (Ichikawa and Hirata, 1990) and monkey (Ichikawa and Shimizu, 1998). Our experiment revealed internuclear differences between the ChAT-positive bouton-like structures and motoneurons of the particular ...
... precise information on their spatial location in relation to the cholinergic motoneurons in the rat (Ichikawa and Hirata, 1990) and monkey (Ichikawa and Shimizu, 1998). Our experiment revealed internuclear differences between the ChAT-positive bouton-like structures and motoneurons of the particular ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 16.1 Scanning electron micrograph of a
... ventral midline. The axons cross the midline at the floor plate; upon exiting the floor plate, they make a sharp right-angle turn and project in a rostral (anterior) direction. A long-range gradient of Netrin-1 protein (green dots) and a shorter-range gradient of Slit protein (red dots) are shown. R ...
... ventral midline. The axons cross the midline at the floor plate; upon exiting the floor plate, they make a sharp right-angle turn and project in a rostral (anterior) direction. A long-range gradient of Netrin-1 protein (green dots) and a shorter-range gradient of Slit protein (red dots) are shown. R ...
Role of Nitric Oxide on Dopamine Release and Morphine
... potential failures (Klyachko et al., 2001). These mechanisms may explain how NO modulates DA in NA. However, IbTx known as a BK channel blocker, does not inhibit frequency-dependent effects of SIN-1 (NO donor) on DA release in NA. Several studies reported that NO-mediated DA release was independent ...
... potential failures (Klyachko et al., 2001). These mechanisms may explain how NO modulates DA in NA. However, IbTx known as a BK channel blocker, does not inhibit frequency-dependent effects of SIN-1 (NO donor) on DA release in NA. Several studies reported that NO-mediated DA release was independent ...
Ch18 Lecture
... transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another. •The space between the two neurons is called a synapse. •The presynaptic neuron releases the neurotransmitter. •The postsynaptic neuron contains the receptors that bind the neurotransmitter. ...
... transmits nerve impulses from one neuron to another. •The space between the two neurons is called a synapse. •The presynaptic neuron releases the neurotransmitter. •The postsynaptic neuron contains the receptors that bind the neurotransmitter. ...
Chapter 3
... olfactory receptors produce generator potentials – when large enough, it generates a nerve impulse in a firstorder neuron • Receptor potential – vision, hearing, equilibrium and taste receptors produce receptor potentials – receptor cells release neurotransmitter molecules on firstorder neurons prod ...
... olfactory receptors produce generator potentials – when large enough, it generates a nerve impulse in a firstorder neuron • Receptor potential – vision, hearing, equilibrium and taste receptors produce receptor potentials – receptor cells release neurotransmitter molecules on firstorder neurons prod ...
plexus injury after spinal cord implantation of avulsed ventral roots
... surface.' 6 Reinnervation of the implanted ventral root was achieved after an initial growth of new axons in the CNS.6 By the use of intracellular recording in the spinal cord and staining with horseradish peroxidase it was found that alpha and probably also gamma motor neurons were able to reinnerv ...
... surface.' 6 Reinnervation of the implanted ventral root was achieved after an initial growth of new axons in the CNS.6 By the use of intracellular recording in the spinal cord and staining with horseradish peroxidase it was found that alpha and probably also gamma motor neurons were able to reinnerv ...
Cranial Nerves
... involved in movement of the eye, and propriception. It works with nerve III and IV. The next cranial nerve is Cranial Nerve VII, the facial nerve. Like its name states, it is involved in facial expressions, taste and secretion of saliva and tears. It is a mixed nerve. Cranial nerve VIII is the vesti ...
... involved in movement of the eye, and propriception. It works with nerve III and IV. The next cranial nerve is Cranial Nerve VII, the facial nerve. Like its name states, it is involved in facial expressions, taste and secretion of saliva and tears. It is a mixed nerve. Cranial nerve VIII is the vesti ...
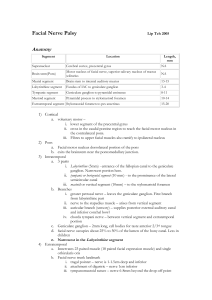
Facial Nerve Palsy
... settings indicates complete nerve degeneration. ii. Uses Hilger nerve stimulator iii. Subjective measure iv. Abnormal test if 3-3.5mA difference between sides b. Maximal stimulation test (MST) i. Similar to NET but uses maximal stimulation -Current is set at 5mA ii. The observed strength of the musc ...
... settings indicates complete nerve degeneration. ii. Uses Hilger nerve stimulator iii. Subjective measure iv. Abnormal test if 3-3.5mA difference between sides b. Maximal stimulation test (MST) i. Similar to NET but uses maximal stimulation -Current is set at 5mA ii. The observed strength of the musc ...
Combined Nerve Palsy - Alpha Hand Surgery Centre
... • Trying to restore motion to all joints results in weakness an secondary deformity • Better to achieve a few well supported actions • Tailor to patient’s needs • Consider joint fusion to provide stability ...
... • Trying to restore motion to all joints results in weakness an secondary deformity • Better to achieve a few well supported actions • Tailor to patient’s needs • Consider joint fusion to provide stability ...
video slide - Buena Park High School
... – Electrical current flows directly from one cell to another via a gap junction ...
... – Electrical current flows directly from one cell to another via a gap junction ...
Median Nerve Conduction Velocity
... Velocity of nerve conduction was first measured in the mid-nineteenth century and in the 1940’s new technology permitted routine use of nerve conduction tests to diagnose certain neuromuscular disorders. Today, neurologists frequently assess conduction velocities of both sensory and motor nerves. A ...
... Velocity of nerve conduction was first measured in the mid-nineteenth century and in the 1940’s new technology permitted routine use of nerve conduction tests to diagnose certain neuromuscular disorders. Today, neurologists frequently assess conduction velocities of both sensory and motor nerves. A ...
characterisation of dopamine neurons of the murine ventral
... grateful for my supervisor Elena Vashchinkina, for her watchful eye on the literature and never-ending patience to offer her wisdom despite the differences in our projects. I sincerely hope we stay in touch. I would also like to acknowledge all the wonderful members of the Pharmacology department, f ...
... grateful for my supervisor Elena Vashchinkina, for her watchful eye on the literature and never-ending patience to offer her wisdom despite the differences in our projects. I sincerely hope we stay in touch. I would also like to acknowledge all the wonderful members of the Pharmacology department, f ...
Chapter 15 - Houston Community College Learning Web
... • Carry sensations of fast pain, or prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or a deep cut • Sensations reach the CNS quickly and often trigger somatic reflexes ...
... • Carry sensations of fast pain, or prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or a deep cut • Sensations reach the CNS quickly and often trigger somatic reflexes ...
Skeletal System
... Like sensory neurons serving somatic structures (skeletal muscles and skin) The cell bodies of visceral sensory neurons are located in the sensory ganglia of associated cranial nerves or in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord ...
... Like sensory neurons serving somatic structures (skeletal muscles and skin) The cell bodies of visceral sensory neurons are located in the sensory ganglia of associated cranial nerves or in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord ...
AMPA Receptor Calcium Permeability, GluR2
... various models to be more susceptible to AMPA receptormediated injury than other spinal neurons. It has been hypothesized that this selective vulnerability of motoneurons is caused by the expression of highly Ca 21-permeable AMPA receptors and a complete or relative lack of the AMPA receptor subunit ...
... various models to be more susceptible to AMPA receptormediated injury than other spinal neurons. It has been hypothesized that this selective vulnerability of motoneurons is caused by the expression of highly Ca 21-permeable AMPA receptors and a complete or relative lack of the AMPA receptor subunit ...
Grip Strength:
... • “….Anterior and middle deltoid activity decreased by 2% MVE, while posterior deltoid, infraspinatus and trapezius activity increased by 2% MVE and biceps brachii activity increased by 6% MVE.” Antony NT, Keir PJ. Effects of Posture, Movement and Hand Load on Shoulder Muscle Activity. Journal ...
... • “….Anterior and middle deltoid activity decreased by 2% MVE, while posterior deltoid, infraspinatus and trapezius activity increased by 2% MVE and biceps brachii activity increased by 6% MVE.” Antony NT, Keir PJ. Effects of Posture, Movement and Hand Load on Shoulder Muscle Activity. Journal ...
Glutamate Receptors Form Hot Spots on Apical Dendrites of
... from the somata of layer V pyramidal neurons in neocortical slices, the recording chamber was perfused with solution containing 1 mM caged glutamate (Wieboldt et al. 1994). With apparatus developed for infrared-guided laser photostimulation (Fig. 1, A and B), we were able to visually direct a 1-m s ...
... from the somata of layer V pyramidal neurons in neocortical slices, the recording chamber was perfused with solution containing 1 mM caged glutamate (Wieboldt et al. 1994). With apparatus developed for infrared-guided laser photostimulation (Fig. 1, A and B), we were able to visually direct a 1-m s ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.