The Nervous System - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... • Depolarization activates neuron to transmit an action potential (nerve impulse) ▫ All-or-none response ▫ Impulse conducts down entire axon ...
... • Depolarization activates neuron to transmit an action potential (nerve impulse) ▫ All-or-none response ▫ Impulse conducts down entire axon ...
The Reflex Arc
... A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
... A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
Sample Questions for Evaluation #1 – General
... c) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a( ...
... c) observable relationship between specific independent and dependent variables. d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a( ...
Action Potential
... “K+ channels that primarily allow K+ in cells only under specific conditions…” -serve a very specific function, maintaining the membrane at rest. ...
... “K+ channels that primarily allow K+ in cells only under specific conditions…” -serve a very specific function, maintaining the membrane at rest. ...
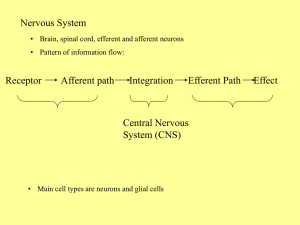
Nervous System:
... How does a sensation (such as touch) change into an electrical impulse for brain to understand? ...
... How does a sensation (such as touch) change into an electrical impulse for brain to understand? ...
Chapter Outline
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
... • Local disturbances in membrane potential – occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance – depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradients • Na+ diffuses f ...
Control of Movement
... Sensory neuron ---> alpha motor neurons monosynaptic excitation disynaptic inhibition ~ ...
... Sensory neuron ---> alpha motor neurons monosynaptic excitation disynaptic inhibition ~ ...
brainy tests - WordPress.com
... The spinal cord affects other neurons by releasing a neurotransmitter that binds to chemical receptors. False ...
... The spinal cord affects other neurons by releasing a neurotransmitter that binds to chemical receptors. False ...
AP Biology Semester 1 Review Topics
... function(s) of the hypothalamus Structure of neuron Nerve characteristics o Characteristics of axons o synapse (effect of practice) o mylenation (process, composition) Helmholtz Theory o nerve impulse o salutatory conduction CNS vs PNS (components) Parasympathetic vs. Sympathetic (see chart) compo ...
... function(s) of the hypothalamus Structure of neuron Nerve characteristics o Characteristics of axons o synapse (effect of practice) o mylenation (process, composition) Helmholtz Theory o nerve impulse o salutatory conduction CNS vs PNS (components) Parasympathetic vs. Sympathetic (see chart) compo ...
Ch 4: Synaptic Transmission
... When the threshold of excitation is hit, the voltage-activated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes in The Na+ influx causes the membrane potential to spike to +50mV This triggers the voltage-gated K+ channels to open & K+ flows out After 1ms, Na+ channels close End of rising phase ...
... When the threshold of excitation is hit, the voltage-activated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes in The Na+ influx causes the membrane potential to spike to +50mV This triggers the voltage-gated K+ channels to open & K+ flows out After 1ms, Na+ channels close End of rising phase ...
Muscle Structure
... A motor neuron and the muscle it innervates is called a motor unit; when stimulated all the muscle fibres of a motor unit contract together The sarcoplasm is the interior structure of the muscle fibre. The sarcoplasm contains contractile components which consists of protein filaments; other prot ...
... A motor neuron and the muscle it innervates is called a motor unit; when stimulated all the muscle fibres of a motor unit contract together The sarcoplasm is the interior structure of the muscle fibre. The sarcoplasm contains contractile components which consists of protein filaments; other prot ...
Chapter 2
... Basic law of axonal conduction: All-or-none law, i.e. action potential, once started, is always finished to the end of the axon Rate law – variations in the intensity of the stimulus or other info being transmitted in an axon are represented by variations in the rate at which that axon fires Saltato ...
... Basic law of axonal conduction: All-or-none law, i.e. action potential, once started, is always finished to the end of the axon Rate law – variations in the intensity of the stimulus or other info being transmitted in an axon are represented by variations in the rate at which that axon fires Saltato ...
Final Exam Practice Problems
... attracted as the Netrin will have an attractive force (since unc-5 isn’t expressed) and Slit will have no effect. In the third case, the neuron will be attracted as the Slit/Robo interaction will cause a strong repulsion that outweighs the Netrin attraction. 8. How does Agrin induce mAChR clustering ...
... attracted as the Netrin will have an attractive force (since unc-5 isn’t expressed) and Slit will have no effect. In the third case, the neuron will be attracted as the Slit/Robo interaction will cause a strong repulsion that outweighs the Netrin attraction. 8. How does Agrin induce mAChR clustering ...
The Zombie Diaries
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
Outline: Muscular System
... neural stimulation: takes place at the __________________________. o ...
... neural stimulation: takes place at the __________________________. o ...
Motor
... neuronal pools: 1) α (alpha) motor neurons, which innervate extrafusal muscle fibers - the striated muscle fibers that generate the forces needed for movement. 2) small γ (gamma) motor neurons innervate specialized muscle fibers that are actually sensory receptors called muscle spindles. The muscle ...
... neuronal pools: 1) α (alpha) motor neurons, which innervate extrafusal muscle fibers - the striated muscle fibers that generate the forces needed for movement. 2) small γ (gamma) motor neurons innervate specialized muscle fibers that are actually sensory receptors called muscle spindles. The muscle ...
Lecture Outline ()
... • Neuron doctrine -- nerve pathway is not a continuous “wire” but a series of separate cells • Neuronal communication is based on mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – ...
... • Neuron doctrine -- nerve pathway is not a continuous “wire” but a series of separate cells • Neuronal communication is based on mechanisms for producing electrical potentials & currents – electrical potential - difference in concentration of charged particles between different parts of the cell – ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.