In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent
... a. Calculate the voltage vR and the current iR and express in phasor notation when Zmatch = (0 + j0). Since Zmatch is equal to 0 and the other component in the branch is a resistor, the current and voltage must be in phase (i.e., the phase angle of vR must equal iR ...
... a. Calculate the voltage vR and the current iR and express in phasor notation when Zmatch = (0 + j0). Since Zmatch is equal to 0 and the other component in the branch is a resistor, the current and voltage must be in phase (i.e., the phase angle of vR must equal iR ...
Resistors in Series and Parallel
... using a voltmeter and the current in a circuit using a ammeter. We need to connect these two devices in different ways. ...
... using a voltmeter and the current in a circuit using a ammeter. We need to connect these two devices in different ways. ...
Methodology PRINT
... microphones, transistors, LM386 and ADC0831. An Omni-directional Electret Condenser Microphone Cartridge was used. This type of microphone is used in everyday appliances such as telephones, tape recorders, and hearing aids. This microphone has a maximum voltage of 12 and a standard voltage of 4.5. T ...
... microphones, transistors, LM386 and ADC0831. An Omni-directional Electret Condenser Microphone Cartridge was used. This type of microphone is used in everyday appliances such as telephones, tape recorders, and hearing aids. This microphone has a maximum voltage of 12 and a standard voltage of 4.5. T ...
Ch 5 Homework - ECM
... 25. A(n) ____ is a machine, device, or system that changes DC voltage into AC voltage and can be designed to produce variable frequency. ...
... 25. A(n) ____ is a machine, device, or system that changes DC voltage into AC voltage and can be designed to produce variable frequency. ...
DC500VBC625A DC500V
... The I-t curves above are plots of the average values of measurements obtained under conditions specified by SOC. These data are for reference only and are not intended to infer any guaranteed values. ...
... The I-t curves above are plots of the average values of measurements obtained under conditions specified by SOC. These data are for reference only and are not intended to infer any guaranteed values. ...
Activity 6A
... a level below the holding current IH. There are various techniques for turning off a thyristor. In all the commutation techniques, the anode current is maintained below the holding current for a sufficiently long time, so that all the excess carriers in the four layers are swept out or recombined. ...
... a level below the holding current IH. There are various techniques for turning off a thyristor. In all the commutation techniques, the anode current is maintained below the holding current for a sufficiently long time, so that all the excess carriers in the four layers are swept out or recombined. ...
AC circuits ch 23 S2017
... The rms amplitude is the DC voltage which will deliver the same average power as the AC signal. ...
... The rms amplitude is the DC voltage which will deliver the same average power as the AC signal. ...
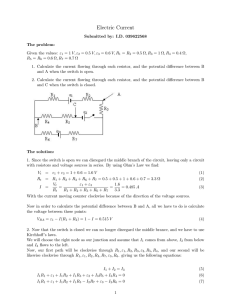
Electric Current
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
ohms_law
... After connecting the circuit as in the diagram we vary the o_______ voltage of the g_________. Then we read the voltage a________ the resistor on the v__________ and the c__________ flowing through the resistor on the a__________ and we record them in the table (next page). For each reading of these ...
... After connecting the circuit as in the diagram we vary the o_______ voltage of the g_________. Then we read the voltage a________ the resistor on the v__________ and the c__________ flowing through the resistor on the a__________ and we record them in the table (next page). For each reading of these ...
AP_Physics_B_-_Planck_s_Constant_lab
... In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectri ...
... In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectri ...
PDEV-1018 AMATEUR RADIO OPERATOR INTRODUCTION
... attract electrons Negative potential Grid used to control electron flow ...
... attract electrons Negative potential Grid used to control electron flow ...
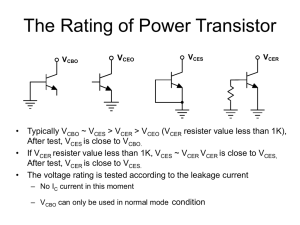
The Rating of Power Transistor
... • If customer is doubt with the rating voltage of power transistor, customer can simulation test with VCBO ,VCES , VCER , VCEO • Inside chip VCER driver sink resistor is less than 10ohm, the VCER is close to VCBO. • More and more big semi-conductor company use Vces instead of Vcbo to avoid mis-under ...
... • If customer is doubt with the rating voltage of power transistor, customer can simulation test with VCBO ,VCES , VCER , VCEO • Inside chip VCER driver sink resistor is less than 10ohm, the VCER is close to VCBO. • More and more big semi-conductor company use Vces instead of Vcbo to avoid mis-under ...
Document
... enough energy to escape the atom forming electron hole pairs. This gives a voltage across the junction. There will be no other power source in the circuit. Used in solar cell for calculators etc. Photoconductive mode (reverse biased) When light shines on it the resistance decreases as electrons are ...
... enough energy to escape the atom forming electron hole pairs. This gives a voltage across the junction. There will be no other power source in the circuit. Used in solar cell for calculators etc. Photoconductive mode (reverse biased) When light shines on it the resistance decreases as electrons are ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.