Simple Current Limit Circuit using Transistors
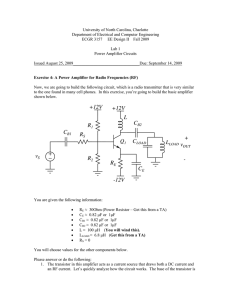
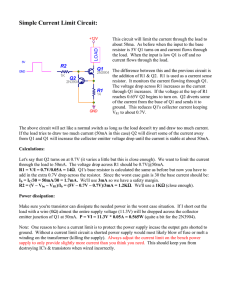
... The above circuit will act like a normal switch as long as the load doesn't try and draw too much current. If the load tries to draw too much current (50mA in this case) Q2 will divert some of the current away from Q1 and Q1 will increase the collector emitter voltage drop until the current is stabl ...
... The above circuit will act like a normal switch as long as the load doesn't try and draw too much current. If the load tries to draw too much current (50mA in this case) Q2 will divert some of the current away from Q1 and Q1 will increase the collector emitter voltage drop until the current is stabl ...
EXAM 1 A
... Problem # 2 How many feet of wire do I need to get 50 from aluminum wire with a radius of 0.5 mm? The resistivity of aluminum is 2.83 x 10-6 -cm ...
... Problem # 2 How many feet of wire do I need to get 50 from aluminum wire with a radius of 0.5 mm? The resistivity of aluminum is 2.83 x 10-6 -cm ...
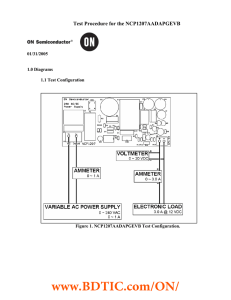
www.BDTIC.com/ON/ Test Procedure for the NCP1207AADAPGEVB 01/31/2005
... Figure 3. Gate Driver and Drain Voltage at Very Light Load ...
... Figure 3. Gate Driver and Drain Voltage at Very Light Load ...
Electricity - 7SMSscience
... to pass through (ex. metal) Insulator – substance that does not readily conduct electricity; does not allow electricity to pass through (ex. plastic) ...
... to pass through (ex. metal) Insulator – substance that does not readily conduct electricity; does not allow electricity to pass through (ex. plastic) ...
“Switch-On” Electronics - Cleveland State University
... Air conditioner: 2000 W Clock: 2 W Television: 200 W Light bulb: 100 W ...
... Air conditioner: 2000 W Clock: 2 W Television: 200 W Light bulb: 100 W ...
Homework 5 ECE 520.491 CAD VLSI Design of Digital Circuits
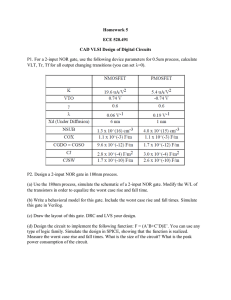
... P2. Design a 2-input NOR gate in 180nm process. (a) Use the 180nm process, simulate the schematic of a 2-input NOR gate. Modify the W/L of the transistors in order to equalize the worst case rise and fall time. (b) Write a behavioral model for this gate. Include the worst case rise and fall times. S ...
... P2. Design a 2-input NOR gate in 180nm process. (a) Use the 180nm process, simulate the schematic of a 2-input NOR gate. Modify the W/L of the transistors in order to equalize the worst case rise and fall time. (b) Write a behavioral model for this gate. Include the worst case rise and fall times. S ...
Lab Experiment III
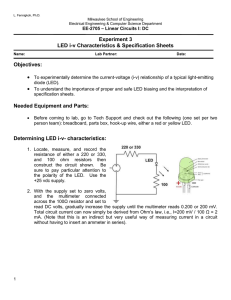
... Determining LED i-v- characteristics: 1. Locate, measure, and record the resistance of either a 220 or 330, and 100 ohm resistors then construct the circuit shown. Be sure to pay particular attention to the polarity of the LED. Use the +25 vdc supply. 2. With the supply set to zero volts, and the mu ...
... Determining LED i-v- characteristics: 1. Locate, measure, and record the resistance of either a 220 or 330, and 100 ohm resistors then construct the circuit shown. Be sure to pay particular attention to the polarity of the LED. Use the +25 vdc supply. 2. With the supply set to zero volts, and the mu ...
The unijunction transistor
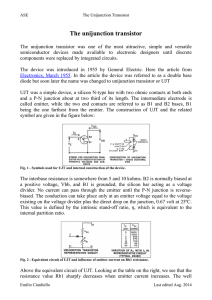
... The interbase resistance is somewhere from 5 and 10 kohms. B2 is normally biased at a positive voltage, Vbb, and B1 is grounded, the silicon bar acting as a voltage divider. No current can pass through the emitter until the P-N junction is reversebiased. The conduction can take place only at an emit ...
... The interbase resistance is somewhere from 5 and 10 kohms. B2 is normally biased at a positive voltage, Vbb, and B1 is grounded, the silicon bar acting as a voltage divider. No current can pass through the emitter until the P-N junction is reversebiased. The conduction can take place only at an emit ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.