Precision Current Source is Software
... A digital potentiometer (U1) in conjunction with a precision op amp (U2) sets current through the pass transistor (ISET), and a shunt regulator (U3) provides a constant reference voltage across the digital pot. By operating in its linear region, the transistor controls load current in response to th ...
... A digital potentiometer (U1) in conjunction with a precision op amp (U2) sets current through the pass transistor (ISET), and a shunt regulator (U3) provides a constant reference voltage across the digital pot. By operating in its linear region, the transistor controls load current in response to th ...
circuits and current review
... TEST REVIEW PHYSICS For the test over current and circuits you should know: 1. What two things are needed for charge to flow between two points? 2. What is actually flowing in a current carrying wire? 3. What is an ampere? 4. The resistance of a wire depends on what three factors? 5. Which has more ...
... TEST REVIEW PHYSICS For the test over current and circuits you should know: 1. What two things are needed for charge to flow between two points? 2. What is actually flowing in a current carrying wire? 3. What is an ampere? 4. The resistance of a wire depends on what three factors? 5. Which has more ...
Twenty Questions - Kelso High School
... 17. Calculate the number of electrons that pass through a wire carrying a current of 2 A for 5 s. Qelectron = 1.6x10-19 C ...
... 17. Calculate the number of electrons that pass through a wire carrying a current of 2 A for 5 s. Qelectron = 1.6x10-19 C ...
Electric Circuits
... Although a little confusing (and more than a little irritating) we need to recall that electric potential is defined in terms of moving positive charge. And the direction of an electric field is defined as the direction that a positive charge will move in that field. ...
... Although a little confusing (and more than a little irritating) we need to recall that electric potential is defined in terms of moving positive charge. And the direction of an electric field is defined as the direction that a positive charge will move in that field. ...
Electric Circuits
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
KIRCHOFF`S VOLTAGE LAW: EXAMPLE 1
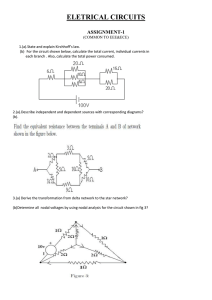
... GIVEN: Consider the circuit shown, where R1=20Ω R2=40Ω V1=20V REQUIRED: (a) The current through R1. (b) The current through R2. (c) The current leaving the voltage source. SOLUTION: (a) First, we identify the loops in the circuit. As shown below, we can choose any two of the three loops. ...
... GIVEN: Consider the circuit shown, where R1=20Ω R2=40Ω V1=20V REQUIRED: (a) The current through R1. (b) The current through R2. (c) The current leaving the voltage source. SOLUTION: (a) First, we identify the loops in the circuit. As shown below, we can choose any two of the three loops. ...
Voltage Current (electric) Resistance (electric) direct current
... a device designed to introduce resistance into an electric circuit. ...
... a device designed to introduce resistance into an electric circuit. ...
Logic
... To install, locate 2 HP of space in your Eurorack case and confirm the positive 12 volts and negative 12 volts sides of the power distribution lines. Plug the connector into the power distribution board of your case, keeping in mind that the red band corresponds to negative 12 volts. In most systems ...
... To install, locate 2 HP of space in your Eurorack case and confirm the positive 12 volts and negative 12 volts sides of the power distribution lines. Plug the connector into the power distribution board of your case, keeping in mind that the red band corresponds to negative 12 volts. In most systems ...
sot-23 bipolar transistors transistor(npn)
... changes. Rectron Inc or anyone on its behalf assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies. Data sheet specifications and its information contained are intended to provide a product description only. "Typical" parameters which may be included on RECTRON data sheets and/ or sp ...
... changes. Rectron Inc or anyone on its behalf assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies. Data sheet specifications and its information contained are intended to provide a product description only. "Typical" parameters which may be included on RECTRON data sheets and/ or sp ...
Digital Examination - Philadelphia University Jordan
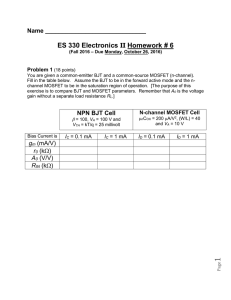
... 3- If the voltage across the capacitor is constant that means the current through the capacitor is: Constant. Maximum. Zero. 4- Bipolar transistor operated in saturation region when the base –collector junction is: Reverse biased. Forward biased. Not biased. 5- Faster turn on of the tran ...
... 3- If the voltage across the capacitor is constant that means the current through the capacitor is: Constant. Maximum. Zero. 4- Bipolar transistor operated in saturation region when the base –collector junction is: Reverse biased. Forward biased. Not biased. 5- Faster turn on of the tran ...
4.3 Notes - Seymour ISD
... Voltage (potential difference)- the ability to accelerate an electric charge between two points in an electric field. Measured in VOLTS ...
... Voltage (potential difference)- the ability to accelerate an electric charge between two points in an electric field. Measured in VOLTS ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.