Topics for Exam #1
... Charge/Time = Current DC Current --- Constant, do not change with time Voltage – Joule/Coulomb Resistance and Conductance Resistivity Determine resistance of a piece of material Resistors Standard Values Tolerance Color Coding ...
... Charge/Time = Current DC Current --- Constant, do not change with time Voltage – Joule/Coulomb Resistance and Conductance Resistivity Determine resistance of a piece of material Resistors Standard Values Tolerance Color Coding ...
Make your own relay Tips - Dionics-USA
... Military performance is required. The SSRs with the required high-power electrical performance either may not be available at all in a single package, or may be prohibitively expensive. In general, this traces to a combination of the high cost for the technology in packaging and the relatively low v ...
... Military performance is required. The SSRs with the required high-power electrical performance either may not be available at all in a single package, or may be prohibitively expensive. In general, this traces to a combination of the high cost for the technology in packaging and the relatively low v ...
File
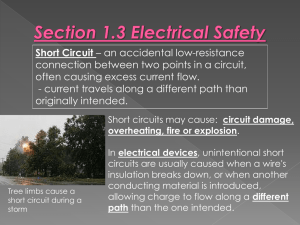
... connection between two points in a circuit, often causing excess current flow. - current travels along a different path than originally intended. Short circuits may cause: circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. ...
... connection between two points in a circuit, often causing excess current flow. - current travels along a different path than originally intended. Short circuits may cause: circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. ...
DS9503 ESD Protection Diode with Resistors
... DS9502, the DS9503 includes two 5Ω isolation resistors on chip. Although 5Ω are negligible during communication, they represent a high impedance relative to the conducting diode during an ESD event. Thus, the diode absorbs the energy while the resistors further isolate and protect the circuit at the ...
... DS9502, the DS9503 includes two 5Ω isolation resistors on chip. Although 5Ω are negligible during communication, they represent a high impedance relative to the conducting diode during an ESD event. Thus, the diode absorbs the energy while the resistors further isolate and protect the circuit at the ...
Measurement Lab
... There are many possible sources of error and here is only a small list of some: The wires have some resistance which we assume non-existent for this experiment, will affect slightly the measurement of the current. The resistors are not their stated Ohms because it has degraded. The VOM was inc ...
... There are many possible sources of error and here is only a small list of some: The wires have some resistance which we assume non-existent for this experiment, will affect slightly the measurement of the current. The resistors are not their stated Ohms because it has degraded. The VOM was inc ...
Electromotive Force
... total of the potential rises is equal to the potential drops. The current through a resistor is in the direction of a potential drop since the resistor dissipates energy. The + sign to on the left of each resistor means that side is a higher potential than the right side of the resistor which has th ...
... total of the potential rises is equal to the potential drops. The current through a resistor is in the direction of a potential drop since the resistor dissipates energy. The + sign to on the left of each resistor means that side is a higher potential than the right side of the resistor which has th ...
13 - Kambing UI
... not be less than 40.000uF, (a golden rule of around 2000uF/A), but we recommend up to 50.000uF. This capacity can be built up by several smaller capacitors in parallel. The base of this design is a simple 12V regulator (7812). The output voltage can be brought to desired value (here 13.8V) by two ex ...
... not be less than 40.000uF, (a golden rule of around 2000uF/A), but we recommend up to 50.000uF. This capacity can be built up by several smaller capacitors in parallel. The base of this design is a simple 12V regulator (7812). The output voltage can be brought to desired value (here 13.8V) by two ex ...
Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit
... Initially, we assume that the signal frequency is sufficiently low so that any capacitance at the gate terminal can be neglected. The input to the gate thus appears as an open circuit, or an infinite resistance. Eq. 6.14 relates the small-signal drain current to the small-signal input voltage and Eq ...
... Initially, we assume that the signal frequency is sufficiently low so that any capacitance at the gate terminal can be neglected. The input to the gate thus appears as an open circuit, or an infinite resistance. Eq. 6.14 relates the small-signal drain current to the small-signal input voltage and Eq ...
Laboratory 1. Introduction: laboratory thematic
... between a pair of closely-spaced conductors (called 'plates'). When voltage is applied to the capacitor, electric charges of equal magnitude, but opposite polarity, build up on each plate. Capacitors are used in electrical circuits as energy-storage devices. They can also be used to differentiate be ...
... between a pair of closely-spaced conductors (called 'plates'). When voltage is applied to the capacitor, electric charges of equal magnitude, but opposite polarity, build up on each plate. Capacitors are used in electrical circuits as energy-storage devices. They can also be used to differentiate be ...
3.0 Principles of Electrical Engineering.docx
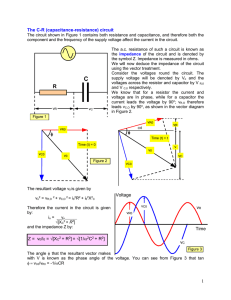
... Alternating current (AC) is bi-directional, meaning that the flow of charge changes direction periodically5. As shown in Figure 2, the magnitude and direction of the current are not constant. From period t0 to t1 the current is positive and the flow in the circuit is clockwise. From period t1 to t2 ...
... Alternating current (AC) is bi-directional, meaning that the flow of charge changes direction periodically5. As shown in Figure 2, the magnitude and direction of the current are not constant. From period t0 to t1 the current is positive and the flow in the circuit is clockwise. From period t1 to t2 ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.