Information - Chosen Hill School
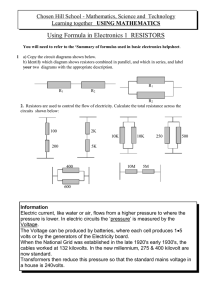
... You will need to refer to the ‘Summary of formulas used in basic electronics helpsheet. ...
... You will need to refer to the ‘Summary of formulas used in basic electronics helpsheet. ...
4 – The Power BJT 3
... Index “r” refers to the rising time (from 10 to 90% of maximum value), for example tri is the current rise time which depends upon the base current. The falling time is indexed by “f”; the parameter tfi is the current falling time, i.e. when the transistor is blocking such time corresponds to crossi ...
... Index “r” refers to the rising time (from 10 to 90% of maximum value), for example tri is the current rise time which depends upon the base current. The falling time is indexed by “f”; the parameter tfi is the current falling time, i.e. when the transistor is blocking such time corresponds to crossi ...
OHMS LAW
... 1. Assuming the resistance does not change: As voltage increases, current increases. As voltage decreases, current decreases. 2. Assuming the voltage does not change: As resistance increases, current decreases. As resistance decreases, current increases. ...
... 1. Assuming the resistance does not change: As voltage increases, current increases. As voltage decreases, current decreases. 2. Assuming the voltage does not change: As resistance increases, current decreases. As resistance decreases, current increases. ...
Transistor Switching Times Delay Time
... that the CBJ is FWD biased in saturation. – excess minority charge carriers, stored in the depletion region must be withdrawn or recombine before begins IC to fall. Fall Time – t f – the time it takes for IC to fall from 90% to 10% of its maximum. Turn-Off Time – t off = t s + t f ...
... that the CBJ is FWD biased in saturation. – excess minority charge carriers, stored in the depletion region must be withdrawn or recombine before begins IC to fall. Fall Time – t f – the time it takes for IC to fall from 90% to 10% of its maximum. Turn-Off Time – t off = t s + t f ...
ch 28 sol
... In the flashlight, the current is 0.40A and the voltage of each of two cells is 1.5 V. Find (a) the power generated by each cell, (b) the power consumed by the bulb, and (c) the energy dissipated in the bulb in 5.5 minutes of operation. (a) This is a single-loop circuit with no branch points. The 0. ...
... In the flashlight, the current is 0.40A and the voltage of each of two cells is 1.5 V. Find (a) the power generated by each cell, (b) the power consumed by the bulb, and (c) the energy dissipated in the bulb in 5.5 minutes of operation. (a) This is a single-loop circuit with no branch points. The 0. ...
Electric Safety Quiz
... 5. What is the purpose of the round prong on a three-prong plug? a) It carries any stray electric current into the ground. b) It carries electric current to the appliance. c) It carries electric current away from the appliance. d) none of the above ...
... 5. What is the purpose of the round prong on a three-prong plug? a) It carries any stray electric current into the ground. b) It carries electric current to the appliance. c) It carries electric current away from the appliance. d) none of the above ...
CIRCUIT IDEAS FOR DESIGNERS Current Source/Current Sink
... This circuit, when VAB > 2|Vth|, will pass a fixed current independent of VAB. When node A is connected to the positive supply the circuit will act as a current source with node B as the output. When node B is connected to ground the circuit will act as a current sink with node A as the input. The c ...
... This circuit, when VAB > 2|Vth|, will pass a fixed current independent of VAB. When node A is connected to the positive supply the circuit will act as a current source with node B as the output. When node B is connected to ground the circuit will act as a current sink with node A as the input. The c ...
Ohm`s Law Quiz - cloudfront.net
... 9. Assume that an electric wire is connected to a 9-volt battery and the wire has a resistance of 3 ohms. How much current is flowing through the wire? a) 27 amps b) 12 amps c) 9 amps d) 3 amps ...
... 9. Assume that an electric wire is connected to a 9-volt battery and the wire has a resistance of 3 ohms. How much current is flowing through the wire? a) 27 amps b) 12 amps c) 9 amps d) 3 amps ...
logical_circuits - Kent State University
... In this Errata, I wish to share the corrections submitted to me by Prof. Kenneth Batcher of Kent State University. The complete set of comments are available on his Web site: http://www.cs.kent.edu/~batcher/4_3_2/. As Prof. Batcher explains, the problem with diagrams 4.16-4.18 is "There are no resis ...
... In this Errata, I wish to share the corrections submitted to me by Prof. Kenneth Batcher of Kent State University. The complete set of comments are available on his Web site: http://www.cs.kent.edu/~batcher/4_3_2/. As Prof. Batcher explains, the problem with diagrams 4.16-4.18 is "There are no resis ...
CSLA2CD
... CSLA2CD CSLA Series linear current sensor, 72 A sensed current, sink or source output, through-hole, operates on AC or DC current, bottom mount Actual product appearance may vary. ...
... CSLA2CD CSLA Series linear current sensor, 72 A sensed current, sink or source output, through-hole, operates on AC or DC current, bottom mount Actual product appearance may vary. ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.