6SN7 SE TJ FullMusic
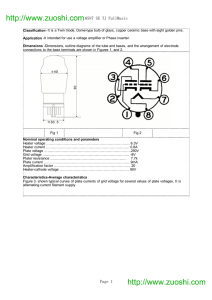
... Classification- It is a Twin triode. Dome-type bulb of glass, copper ceramic base with eight golden pins. Application -It intended for use a voltage amplifier or Phase inuerter. Dimensions -Dimensions, outline diagrams of the tube and bases, and the arrangement of electrode connections to the base t ...
... Classification- It is a Twin triode. Dome-type bulb of glass, copper ceramic base with eight golden pins. Application -It intended for use a voltage amplifier or Phase inuerter. Dimensions -Dimensions, outline diagrams of the tube and bases, and the arrangement of electrode connections to the base t ...
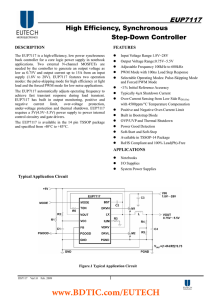
EUP7117 High Efficiency, Synchronous Step-Down Controller
... The EUP7117 is a high-efficiency, low power synchronous buck controller for a core logic power supply in notebook applications. Two external N-channel MOSFETs are needed by the controller to generate an output voltage as low as 0.75V and output current up to 15A from an input supply (1.8V to 28V). E ...
... The EUP7117 is a high-efficiency, low power synchronous buck controller for a core logic power supply in notebook applications. Two external N-channel MOSFETs are needed by the controller to generate an output voltage as low as 0.75V and output current up to 15A from an input supply (1.8V to 28V). E ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... This lab begins with some experiments on a junction field effect transistor (JFET), type 2N5458 and then continues with op amps using the TL082/084 dual/quad op amp chips. Details of these devices, including pin-out, can be found on the data sheets in the supplementary reading section on your web pa ...
... This lab begins with some experiments on a junction field effect transistor (JFET), type 2N5458 and then continues with op amps using the TL082/084 dual/quad op amp chips. Details of these devices, including pin-out, can be found on the data sheets in the supplementary reading section on your web pa ...
Slide 1
... • Resistance- the opposition to the flow of charge by a material or device. • Symbol is R, unit is ohms (W). • Ohms law R = V/I or V = IR • Resistance depends on the following factors: Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials hav ...
... • Resistance- the opposition to the flow of charge by a material or device. • Symbol is R, unit is ohms (W). • Ohms law R = V/I or V = IR • Resistance depends on the following factors: Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials hav ...
ACD-477 Specifications
... • It is normal for this unit to generate some heat when working at its maximum capacity for an extended period of time. • Carefully check and set the DC voltage on the unit. Your device may not work properly if improper voltage is chosen. • Do Not set the polarity in reverse. Reversed polarity may c ...
... • It is normal for this unit to generate some heat when working at its maximum capacity for an extended period of time. • Carefully check and set the DC voltage on the unit. Your device may not work properly if improper voltage is chosen. • Do Not set the polarity in reverse. Reversed polarity may c ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... • As each device uses power, the power carried by current is reduced. • As a result… • Voltage drop-voltage gets lower after each device that uses power. ...
... • As each device uses power, the power carried by current is reduced. • As a result… • Voltage drop-voltage gets lower after each device that uses power. ...
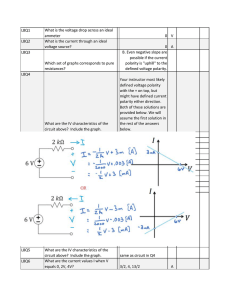
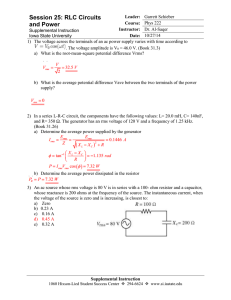
Session 25 Answers - Iowa State University
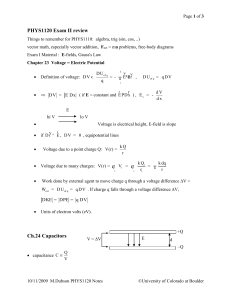
... 4) An R-L-C series circuit is constructed using a 175-ohm resistor, a 12.5-µF capacitor, and an 8.00-mH inductor, all connected across an ac source having a variable frequency and a voltage amplitude of 25.0 V. a) At what angular frequency will the impedance be smallest? ...
... 4) An R-L-C series circuit is constructed using a 175-ohm resistor, a 12.5-µF capacitor, and an 8.00-mH inductor, all connected across an ac source having a variable frequency and a voltage amplitude of 25.0 V. a) At what angular frequency will the impedance be smallest? ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutral object. Current, which is the flow of (voltage, charge), flows from (high, low) voltage to (high, low) voltage. Th ...
... (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutral object. Current, which is the flow of (voltage, charge), flows from (high, low) voltage to (high, low) voltage. Th ...
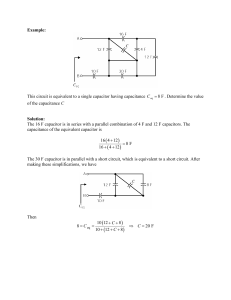
Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit at the terminals U, V.
... Begin by applying a 1V source and arranging the current according to passive sign convention. So it should enter the terminal associated with the positive voltage. This means that Va is 1V, so our left dependent source is 2 V. We want the current that flows through this mesh, specifically current Ib ...
... Begin by applying a 1V source and arranging the current according to passive sign convention. So it should enter the terminal associated with the positive voltage. This means that Va is 1V, so our left dependent source is 2 V. We want the current that flows through this mesh, specifically current Ib ...
Basic Electricity Study Guide
... 2. How did we define voltage in terms of electron movement? Voltage is the force, push or pressure which makes the electrons move. 3. How did we define current in terms of electron movement? Current is the actual number or amount of electrons that are moving at any given time. 4. How did we define r ...
... 2. How did we define voltage in terms of electron movement? Voltage is the force, push or pressure which makes the electrons move. 3. How did we define current in terms of electron movement? Current is the actual number or amount of electrons that are moving at any given time. 4. How did we define r ...
MOC211, MOC212 and MOC213 Small Outline
... These devices consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled to a monolithic silicon phototransistor detector, in a surface mountable, small outline, plastic package. They are ideally suited for high density applications, and eliminate the need for through–the–board mounting ...
... These devices consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled to a monolithic silicon phototransistor detector, in a surface mountable, small outline, plastic package. They are ideally suited for high density applications, and eliminate the need for through–the–board mounting ...
Unit 2 PowerPoint Slides
... Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): Around any closed loop in a circuit, the sum of the voltage rises is equal to the sum of the voltage drops. ...
... Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): Around any closed loop in a circuit, the sum of the voltage rises is equal to the sum of the voltage drops. ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.