* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 PowerPoint Slides
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
EGR 1101 Unit 2
Quadratic Equations in Engineering
(Chapter 2 of Rattan/Klingbeil text)
Mathematical Review
In linear equations, which we studied
last time, the two variables (x and y) are
both raised to the first power:
y 5 x 10
In a quadratic equation, the dependent
variable is raised to the first power and
the independent variable is raised to
the second power. For example:
y 2 x 3x 10
2
Graphical Interpretation
The graph of a quadratic equation is a
parabola. In MATLAB:
> fplot('2*x^2 + 3*x + 10', [-10, 10])
Two Common Questions Involving
Quadratic Equations
1.
2.
Given a quadratic equation, find the value
of y for a particular value of x. (Easy!)
Given a quadratic equation, find the value
of x for a particular value of y. (Harder!)
Three Methods
1.
2.
3.
We’ll study three ways to answer the
second type of question:
Factoring
Quadratic formula
Completing the square
Today’s Examples
1.
2.
3.
Height of a projectile
Power and current in a circuit
Resistors in parallel
Some Symbols Used in Electrical
Drawings
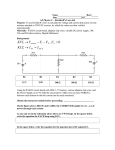
Resistor:
Voltage Source:
Lamp (light bulb):
Circuit containing these
three components:
Three Basic Electrical Laws
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): Around
any closed loop in a circuit, the sum of the
voltage rises is equal to the sum of the
voltage drops.
•
Ohm’s Law: For a resistor, voltage equals
current times resistance:
V = IR
•
Power Law: For any component, power
equals current times voltage:
P = IV
Resistors in Series or Parallel
If two resistors are connected in series
(end-to-end), total resistance is the sum of
the two resistances:
If two resistors are connected in parallel
(connected at both ends), total resistance is
given by the product-over-sum rule: