ch 23 S2016
... A sensor is inserted into the mother’s uterus and positioned against the cheek of the fetus. Two light-emitting diodes are located within the sensor, and each shines light of a different wavelength (or color) into the fetal tissue. The light is reflected by the oxygen-carrying red blood cells and is ...
... A sensor is inserted into the mother’s uterus and positioned against the cheek of the fetus. Two light-emitting diodes are located within the sensor, and each shines light of a different wavelength (or color) into the fetal tissue. The light is reflected by the oxygen-carrying red blood cells and is ...
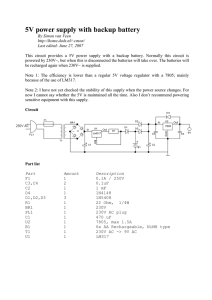
Circuit with partlist and explanation of how it works
... voltages will provide power to U2,in and shut the other diode. The lower voltage can’t let it’s diode conduct. Normally, UC1 is higher so it will provide the current. But when PL1 is not plugged in at 230V, this means UC1 will be zero Volts, so the batteries will provide power. U2 then uses this pow ...
... voltages will provide power to U2,in and shut the other diode. The lower voltage can’t let it’s diode conduct. Normally, UC1 is higher so it will provide the current. But when PL1 is not plugged in at 230V, this means UC1 will be zero Volts, so the batteries will provide power. U2 then uses this pow ...
EUP6514 5V/12V Synchronous Buck PWM Controller
... triggered delay. A hiccup restart sequence will be operating until UV state is exited. ...
... triggered delay. A hiccup restart sequence will be operating until UV state is exited. ...
Document
... possibility to eliminate the step-up transformer in medium voltage applications. An additional feature which makes this converter suitable for the StatCom application is its linear relationship between level number and component count, as opposed to monolithic multilevel converters where this rel ...
... possibility to eliminate the step-up transformer in medium voltage applications. An additional feature which makes this converter suitable for the StatCom application is its linear relationship between level number and component count, as opposed to monolithic multilevel converters where this rel ...
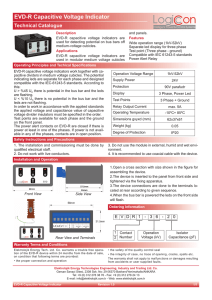
EVD-R Capacitive Voltage Indicator
... indicating leds are separate for each phase and designed compatible with the IEC-61243-5 standards. According to this: U > %45 Un there is potential in the bus bar and the leds are flashing. U < %10 Un there is no potential in the bus bar and the leds are not flashing. In order to work in accordance ...
... indicating leds are separate for each phase and designed compatible with the IEC-61243-5 standards. According to this: U > %45 Un there is potential in the bus bar and the leds are flashing. U < %10 Un there is no potential in the bus bar and the leds are not flashing. In order to work in accordance ...
1E6_Tutorial 8
... A series circuit consists of 0.5 F capacitor, a coil of inductance 0.32 H and a resistance of 40 , and a 20 non-inductive resistor. Calculate the value of the resonant frequency of the circuit. When the circuit is connected to a 30 V a.c. supply at this resonant frequency, determine: (a) the pot ...
... A series circuit consists of 0.5 F capacitor, a coil of inductance 0.32 H and a resistance of 40 , and a 20 non-inductive resistor. Calculate the value of the resonant frequency of the circuit. When the circuit is connected to a 30 V a.c. supply at this resonant frequency, determine: (a) the pot ...
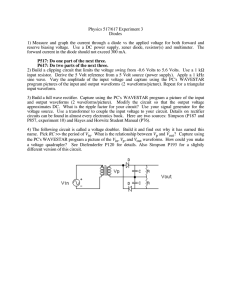
Physics 517/617 Experiment 3 Diodes
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
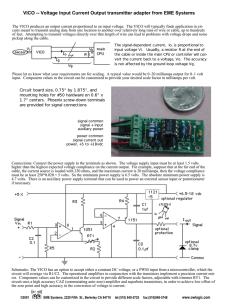
VICO -- Voltage Input Current Output transmitter
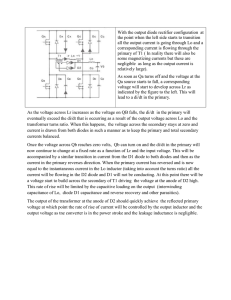
... circuit will average via R1/C2. The operational amplifiers in conjunction with the transistors implement a precision current mirror. Component values can be customized in the circuit to provide different scale factors, adjustable with trimmer RT1. The circuit uses a high accuracy CAZ (commutating au ...
... circuit will average via R1/C2. The operational amplifiers in conjunction with the transistors implement a precision current mirror. Component values can be customized in the circuit to provide different scale factors, adjustable with trimmer RT1. The circuit uses a high accuracy CAZ (commutating au ...
412 Laboratory #1: Input Resistance, Output Resistance, and
... Q4: Based on this measurement only, determine the apparent smallsignal voltage gain Av vo vi with this output load applied. Q5: Now use your equivalent amplifier circuit model (i.e., not the equivalent small-signal MOSFET model) to calculate the theoretic voltage gain. In other words, connect the ...
... Q4: Based on this measurement only, determine the apparent smallsignal voltage gain Av vo vi with this output load applied. Q5: Now use your equivalent amplifier circuit model (i.e., not the equivalent small-signal MOSFET model) to calculate the theoretic voltage gain. In other words, connect the ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 12. What is the need for biasing the transistor? Explain the Fixed Bias method and the disadvantages faced in this method of biasing. 13. Draw the circuit of i) Summing & ii) Difference Amplifier using Op-Amp and obtain an expression for their output. 14. Draw the logic circuit of a D- Flip Flop and ...
... 12. What is the need for biasing the transistor? Explain the Fixed Bias method and the disadvantages faced in this method of biasing. 13. Draw the circuit of i) Summing & ii) Difference Amplifier using Op-Amp and obtain an expression for their output. 14. Draw the logic circuit of a D- Flip Flop and ...
Lecture-3: Transistors - Dr. Imtiaz Hussain
... three doped semiconductor regions separated by two pn junctions • Regions are called emitter, base and collector ...
... three doped semiconductor regions separated by two pn junctions • Regions are called emitter, base and collector ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.