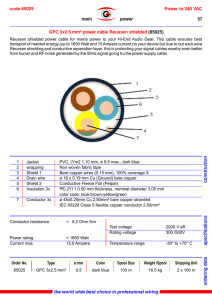
Electric Current - Wissahickon School District
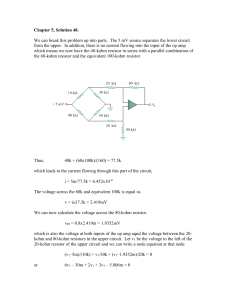
... electrical energy into Thermal energy and light Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω) Making wires thinner, longer, or hotter increases the resistance Ohm’s Law- the current in a circuit equals the voltage difference divided by the resistance I = V/R ...
... electrical energy into Thermal energy and light Resistance is measured in Ohms (Ω) Making wires thinner, longer, or hotter increases the resistance Ohm’s Law- the current in a circuit equals the voltage difference divided by the resistance I = V/R ...
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR, UJT, SCR, TRIAC
... Thus as VE along with IE increases, RB1, η and VA decreases. This produce further decrease in RB1, η and VA. This process is regenerative. VA as well as VE decreases as IE increases. Due to this the UJT has negative resistance region in its VI characteristics. The curve between Emitter voltage VE an ...
... Thus as VE along with IE increases, RB1, η and VA decreases. This produce further decrease in RB1, η and VA. This process is regenerative. VA as well as VE decreases as IE increases. Due to this the UJT has negative resistance region in its VI characteristics. The curve between Emitter voltage VE an ...
... voltage, Q3 will start to turn on. It will not turn on abruptly, however, but will operate in its linear region momentarily due to the RC time constant created by R6 and C2. The momentary operation in the linear region allows for inrush current limiting because Q3 will act like a resistor during thi ...
, One.. Temperature Pressure Dryness Proximity Voltage Current
... To = +125° C, rectangular current waveform. Rate of rise of current <10A/^sec. Rate reversal of current <5A//isec. ITH = lA (50 /isec. pulse). Rep. Rate = 60 pps. VMM = Rated, V« = 15V Min., V™ = Rated. Rate of Rise of reapplied off-state voltage = 20V/ psec. ; Gate Bias = 0 Volts, 100 Ohms (during ...
... To = +125° C, rectangular current waveform. Rate of rise of current <10A/^sec. Rate reversal of current <5A//isec. ITH = lA (50 /isec. pulse). Rep. Rate = 60 pps. VMM = Rated, V« = 15V Min., V™ = Rated. Rate of Rise of reapplied off-state voltage = 20V/ psec. ; Gate Bias = 0 Volts, 100 Ohms (during ...
Explore: How does electricity work? Supplies: Batteries of different
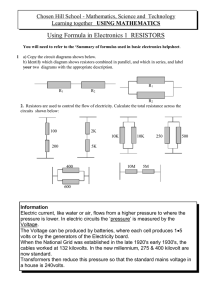
... source through conductive material whenever there is a complete loop of power source/conductors/loads.) R = Resistance (Resistance is the opposition {to flow} that a material body offers to the passage of an electric current. Resistance is measured in Ohms. Examples of items with resistance used in ...
... source through conductive material whenever there is a complete loop of power source/conductors/loads.) R = Resistance (Resistance is the opposition {to flow} that a material body offers to the passage of an electric current. Resistance is measured in Ohms. Examples of items with resistance used in ...
NTE1979 Integrated Circuit Negative 3 Terminal Voltage Regulator
... The NTE1979 is a 3–terminal fixed negative output voltage regulatgor in a TO92 type package designed for use in power circuits with current capacity up to 100mA. Stabilized fixed output voltage is obtained from unstable DC input voltage without the use of external components. Features: D No External ...
... The NTE1979 is a 3–terminal fixed negative output voltage regulatgor in a TO92 type package designed for use in power circuits with current capacity up to 100mA. Stabilized fixed output voltage is obtained from unstable DC input voltage without the use of external components. Features: D No External ...
ET 4
... 5. Explain the advantages of high power factor. A coil of 10 resistance and 0.2 H inductance is connected in parallel with a variable condenser across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply. Determine the capacitance of the condenser so that the current drawn may be in phase with the supply voltage. 6. A rudder mo ...
... 5. Explain the advantages of high power factor. A coil of 10 resistance and 0.2 H inductance is connected in parallel with a variable condenser across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply. Determine the capacitance of the condenser so that the current drawn may be in phase with the supply voltage. 6. A rudder mo ...
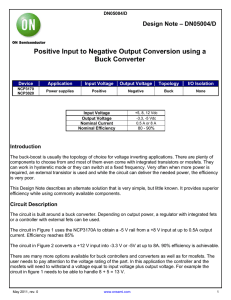
Positive Input to Negative Output Conversion
... The buck-boost is usually the topology of choice for voltage inverting applications. There are plenty of components to choose from and most of them even come with integrated transistors or mosfets. They can work in hysteretic mode or they can switch at a fixed frequency. Very often when more power i ...
... The buck-boost is usually the topology of choice for voltage inverting applications. There are plenty of components to choose from and most of them even come with integrated transistors or mosfets. They can work in hysteretic mode or they can switch at a fixed frequency. Very often when more power i ...
Primary lithium batteries LS 14250 LST 14250
... current, yield voltage readings above 3.0 V. The readings may vary according to the pulse characteristics, the temperature, and the cell's previous history. Fitting the cell with a capacitor may be recommended in severe conditions. Consult Saft) Continuous current permitting 50% of the nominal capac ...
... current, yield voltage readings above 3.0 V. The readings may vary according to the pulse characteristics, the temperature, and the cell's previous history. Fitting the cell with a capacitor may be recommended in severe conditions. Consult Saft) Continuous current permitting 50% of the nominal capac ...
| PeRfeCT BalanCe WiTH 100 % ReDunDanCy
... current is 10 A, this cabinet component ensures that both units supply 5 A. If one of the two power supply units fails, the other can continue to work because it is decoupled. The only condition is that each unit is in the position to supply the nominal current of the load. MB Redundancy Balance ope ...
... current is 10 A, this cabinet component ensures that both units supply 5 A. If one of the two power supply units fails, the other can continue to work because it is decoupled. The only condition is that each unit is in the position to supply the nominal current of the load. MB Redundancy Balance ope ...
how do metal oxide varistors work
... Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) technology is the most prevalent technology utilized in electrical transient protection products today. Many industry manufacturers, including Current Technology, integrate various sizes of radial or strap-type MOVs into their products: 20mm, 32mm and 40mm diameter MOVs ar ...
... Metal Oxide Varistor (MOV) technology is the most prevalent technology utilized in electrical transient protection products today. Many industry manufacturers, including Current Technology, integrate various sizes of radial or strap-type MOVs into their products: 20mm, 32mm and 40mm diameter MOVs ar ...
Maxstar 150 S
... starts, automatically increases the output amperage at the start of a weld should the start require it. Prevents the electrode from sticking and creating an inclusion. ...
... starts, automatically increases the output amperage at the start of a weld should the start require it. Prevents the electrode from sticking and creating an inclusion. ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.