genetics science learning center – internet lesson
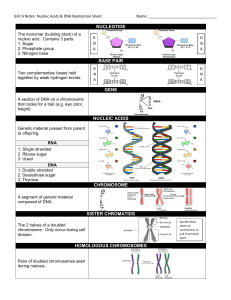
... Click on the link that says “Tour the basics”. A new window will open, you can navigate sections by using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four b ...
... Click on the link that says “Tour the basics”. A new window will open, you can navigate sections by using the top toolbar. WHAT IS DNA? 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. Why is DNA called a blueprint? 3. The “twisted ladder” shape of the DNA molecule is called a _____________________ 4. Name the four b ...
2nd Semester Review The second semester test covers Meiosis
... The second semester test covers Meiosis, DNA, DNA Technologies, Genetics, Evolution, Basics of Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for ...
... The second semester test covers Meiosis, DNA, DNA Technologies, Genetics, Evolution, Basics of Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for ...
DNA damage and repair
... •Occurs when DNA Polymerase puts in the wrong nucleotide during replication and the proofreading activity does not correct it. •Repair would ideally occur on the correct strand, the newly synthesized strand. •E. coli methylates A of GATC sequence. •There is a time lapse before newly synthesized stra ...
... •Occurs when DNA Polymerase puts in the wrong nucleotide during replication and the proofreading activity does not correct it. •Repair would ideally occur on the correct strand, the newly synthesized strand. •E. coli methylates A of GATC sequence. •There is a time lapse before newly synthesized stra ...
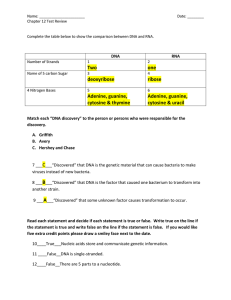
DNA - TeacherWeb
... Chargaff determined that different species carry differing amounts of the nitrogenous bases. He also determined that some of the bases always showed equality: C=G and A=T ...
... Chargaff determined that different species carry differing amounts of the nitrogenous bases. He also determined that some of the bases always showed equality: C=G and A=T ...
Guanine – Cytosine
... If you unraveled all your chromosomes from all of your cells and laid out the DNA end to end, the strands would stretch from the Earth to the Moon about 6,000 times. ...
... If you unraveled all your chromosomes from all of your cells and laid out the DNA end to end, the strands would stretch from the Earth to the Moon about 6,000 times. ...
DNA, Proteins and Biotechnology Unit Test Study Guide AP Biology
... the strand look like? If translated to amino acids, how would the peptide strand read? (need codon chart) -Mutations—what effect do they have on proteins? -Virus structure -Compare and contrast lytic and lysogenic cycles -Compare bacterial DNA transfer processes -Transposons -Biotechnology and recom ...
... the strand look like? If translated to amino acids, how would the peptide strand read? (need codon chart) -Mutations—what effect do they have on proteins? -Virus structure -Compare and contrast lytic and lysogenic cycles -Compare bacterial DNA transfer processes -Transposons -Biotechnology and recom ...
Document
... •Mutation refers to a change in a base-pair (e.g. G-C bp to A-T bp is a mutation) •Problems arise when DNA damage is converted to mutation ...
... •Mutation refers to a change in a base-pair (e.g. G-C bp to A-T bp is a mutation) •Problems arise when DNA damage is converted to mutation ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... concluded that DNA was the factor that transmits genetic information from one generation to the next. ...
... concluded that DNA was the factor that transmits genetic information from one generation to the next. ...
DrMoran
... make up genes. Genes make different things for our body. They are packaged up into chromosomes Chromosomes are like a big recipe box for our bodies and DNA is the recipe! ...
... make up genes. Genes make different things for our body. They are packaged up into chromosomes Chromosomes are like a big recipe box for our bodies and DNA is the recipe! ...
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a trait (e.g. eye color, ...
... A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a trait (e.g. eye color, ...
Type of sugar
... a cell. It is made up of millions of tiny subunits called ____________________. In each nucleotide, there is a ______________, a phosphate, and a ____________________ base (_______________, guanine, ______________, cytosine). When connected, these nucleotides form the shape of DNA, a _______________ ...
... a cell. It is made up of millions of tiny subunits called ____________________. In each nucleotide, there is a ______________, a phosphate, and a ____________________ base (_______________, guanine, ______________, cytosine). When connected, these nucleotides form the shape of DNA, a _______________ ...
DNA Structure Student Practice (12.1)
... DNA Structure Student Practice (12. 1) Modified True/False Statements: If the statement true, write True in the blank. If the statement is is false, write False in the blank and correct the underlined word to make the statement true. 1. The building blocks of DNA molecules are amino acids. ...
... DNA Structure Student Practice (12. 1) Modified True/False Statements: If the statement true, write True in the blank. If the statement is is false, write False in the blank and correct the underlined word to make the statement true. 1. The building blocks of DNA molecules are amino acids. ...
13-2 Manipulating DNA
... 5) Used to locate and identify a particular genes or used to compare individuals. Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, and to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. ...
... 5) Used to locate and identify a particular genes or used to compare individuals. Knowing the sequence of an organism’s DNA allows researchers to study specific genes, to compare them with the genes of other organisms, and to try to discover the functions of different genes and gene combinations. ...
3-Slides
... Need correction/repair Despite complexity and the considerable energy required all multicelled creatures have such a repair mechanism ...
... Need correction/repair Despite complexity and the considerable energy required all multicelled creatures have such a repair mechanism ...
chapter 12 test review key
... mutation will be the daughter cells of that one cell. Only a certain group of cells will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries th ...
... mutation will be the daughter cells of that one cell. Only a certain group of cells will carry the incorrect information. If a mutation or change of information occurs in a sex cell that means that as mitosis occurs as the organism grows and develops every cell in that particular organism carries th ...
Study Guide for LS
... - Understand what a complementary strand of DNA is. Example: The complementary strand of ATTGCCG is TAACGGC because A goes to T and G always goes to C. ...
... - Understand what a complementary strand of DNA is. Example: The complementary strand of ATTGCCG is TAACGGC because A goes to T and G always goes to C. ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and ...
... Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers 1. In the nucleus of the cell 2. Wrapped around the chromosomes 3. A gene is a smaller portion of the chromosome, both of which are portions of the DNA molecule that is packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and ...
3.5 – Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
... a. Therapeutic cloning starts with production of human embryos - Is it ethically acceptable to generate a new human embryo for the sole purpose of medical research? b. In nature, embryos are created only for reproduction and many people believe that using them for experiments is unnatural and wrong ...
... a. Therapeutic cloning starts with production of human embryos - Is it ethically acceptable to generate a new human embryo for the sole purpose of medical research? b. In nature, embryos are created only for reproduction and many people believe that using them for experiments is unnatural and wrong ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... statements apply to your use of the textbook on this unit. •______I read the entire reading for this chapter •______I read part of the reading for this chapter •______I used the textbook to assist in my understanding of vocabulary from this unit •______I used the textbook to assist in my understandi ...
... statements apply to your use of the textbook on this unit. •______I read the entire reading for this chapter •______I read part of the reading for this chapter •______I used the textbook to assist in my understanding of vocabulary from this unit •______I used the textbook to assist in my understandi ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
Agriscience Unit 11 worksheet
... 22. Which is the most likely result of genetic manipulation of plants and animals or microorganisms in agriculture today? ...
... 22. Which is the most likely result of genetic manipulation of plants and animals or microorganisms in agriculture today? ...
Introduction
... life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determining the characteristic of an organism. The DNA molecule is arranged as a double helix, whic ...
... life. DNA can be linked up to form a long chain of molecule called chromosome. DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell. DNA controls all the cellular activities. The order of bases is important in determining the characteristic of an organism. The DNA molecule is arranged as a double helix, whic ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.