Study Questions 2
... 6. Describe reasons why the major groove is more often used by proteins to recognize specific DNA sequences than the minor groove. Consider the sequence AATCGG; what information, in terms of hydrogen bond donors, hydrogen bond acceptors, nonpolar hydrogen, and methyl groups, are provided by the maj ...
... 6. Describe reasons why the major groove is more often used by proteins to recognize specific DNA sequences than the minor groove. Consider the sequence AATCGG; what information, in terms of hydrogen bond donors, hydrogen bond acceptors, nonpolar hydrogen, and methyl groups, are provided by the maj ...
Document
... • Discovery of DNA ligase that catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester link for final site closure. ...
... • Discovery of DNA ligase that catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester link for final site closure. ...
Manipulating and Analyzing DNA
... DNA and gel electrophoresis. You will use two different websites to understand both topics. By the end of today you should be able answer the flooring questions: What are restriction enzymes? How and why are they used in biotechnology? How do restriction enzymes play a role in recombinant DNA? How d ...
... DNA and gel electrophoresis. You will use two different websites to understand both topics. By the end of today you should be able answer the flooring questions: What are restriction enzymes? How and why are they used in biotechnology? How do restriction enzymes play a role in recombinant DNA? How d ...
DNA upgrade supplement WITH PICS
... purines are adenine and guanine. These bases are commonly abbreviated as C, T, A, and G. Also, it helps to remember which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines if you note that thymine and cytosine are spelled with a "Y," and so is pyrimidine. Scene 13: Levene also discovered one phosphate group and one ...
... purines are adenine and guanine. These bases are commonly abbreviated as C, T, A, and G. Also, it helps to remember which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines if you note that thymine and cytosine are spelled with a "Y," and so is pyrimidine. Scene 13: Levene also discovered one phosphate group and one ...
Using GenomiPhi DNA Amplification Kit for the Representative
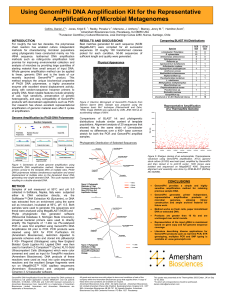
... using phylogenetic trees constucted mainly via 16s rRNA sequence. Isothermal DNA amplification methods such as rolling-circle amplification hold promise for improving environmental collection and analysis of microbes by providing large quantities of starting material from small amount of input DNA. ...
... using phylogenetic trees constucted mainly via 16s rRNA sequence. Isothermal DNA amplification methods such as rolling-circle amplification hold promise for improving environmental collection and analysis of microbes by providing large quantities of starting material from small amount of input DNA. ...
Biology: DNA (Ch.8) Review
... Use the letters P (phosphate) and S (sugar) to label the sugar and phosphate of the DNA molecule to the right. ...
... Use the letters P (phosphate) and S (sugar) to label the sugar and phosphate of the DNA molecule to the right. ...
Page 1 Name KEY_______________________ Genetics C3032
... Both W-linked recessive and autosomal recessive mutations result in WT males and hermaphrodites. However, the hermaphrodites with the W-linked mutation give rise only to WT progeny, whereas those with the autosomal mutation give rise to WT and mutant progeny. In other words, look in the next generat ...
... Both W-linked recessive and autosomal recessive mutations result in WT males and hermaphrodites. However, the hermaphrodites with the W-linked mutation give rise only to WT progeny, whereas those with the autosomal mutation give rise to WT and mutant progeny. In other words, look in the next generat ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Linear DNA fragments of different sizes are resolved according to their size through gels made of polymeric materials such as polyacrylamide and agarose. For instance, agarose is a polysaccharide derived from seaweed - and gels formed from between 0.5% to 2% (mass/volume i.e. 0.5 to 2.0g agarose/100 ...
... Linear DNA fragments of different sizes are resolved according to their size through gels made of polymeric materials such as polyacrylamide and agarose. For instance, agarose is a polysaccharide derived from seaweed - and gels formed from between 0.5% to 2% (mass/volume i.e. 0.5 to 2.0g agarose/100 ...
Lab Practicum #2
... 5. What happens in conjugation? Know possible conjugation results for the following matings: F+ x F-, Hfr x F-. Given locations (F-plasmid versus chromosome) and types of antibiotic resistance genes (AmpR, StrR, NalR) for different E. coli strains, be able to predict which will grow on different ant ...
... 5. What happens in conjugation? Know possible conjugation results for the following matings: F+ x F-, Hfr x F-. Given locations (F-plasmid versus chromosome) and types of antibiotic resistance genes (AmpR, StrR, NalR) for different E. coli strains, be able to predict which will grow on different ant ...
DNA repair disorders
... DNA is continually subjected to both exogenous and endogenous mutagenesis. Cells have built up sophisticated mechanisms to minimise the eVects of this. Mutations in actively transcribed genes are preferentially repaired and all DNA should be repaired before DNA replication when a mutation can become ...
... DNA is continually subjected to both exogenous and endogenous mutagenesis. Cells have built up sophisticated mechanisms to minimise the eVects of this. Mutations in actively transcribed genes are preferentially repaired and all DNA should be repaired before DNA replication when a mutation can become ...
Chapter 12
... Approximately 145 bp are in contact with the histone octamer Connection between nucleosomes requires approximately 60 bp of linker DNA ...
... Approximately 145 bp are in contact with the histone octamer Connection between nucleosomes requires approximately 60 bp of linker DNA ...
Double- stranded DNA Single
... The bases in DNA will only pair in very specific ways, G with C and A with T In short DNA sequences, imprecise base pairing will not be tolerated Long sequences can tolerate some mispairing only if -G of the majority of bases in a sequence exceeds the energy required to keep mispaired bases togethe ...
... The bases in DNA will only pair in very specific ways, G with C and A with T In short DNA sequences, imprecise base pairing will not be tolerated Long sequences can tolerate some mispairing only if -G of the majority of bases in a sequence exceeds the energy required to keep mispaired bases togethe ...
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA I. Tools of Biotechnology
... portion of the Ti plasmid (T-DNA) is transferred into the plant cell. • This system has been well characterized and is now used to introduce foreign DNA into plants as well as some animal cells. iv. Screening or Detection of Recombinant Molecules • May be creating a scenario not much different than ...
... portion of the Ti plasmid (T-DNA) is transferred into the plant cell. • This system has been well characterized and is now used to introduce foreign DNA into plants as well as some animal cells. iv. Screening or Detection of Recombinant Molecules • May be creating a scenario not much different than ...
2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA
... DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. Crick and Watson’s elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making. Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single In diagrams of DNA structure, the helical n ...
... DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. Crick and Watson’s elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making. Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single In diagrams of DNA structure, the helical n ...
DNA and Heredity
... helix during DNA replication. These proteins wedge themselves between the two strands of the double helix and break the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. ...
... helix during DNA replication. These proteins wedge themselves between the two strands of the double helix and break the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. ...
Research news
... A study of the unusual 3’–3’ 1,4-GG interstrand cross-link (IXL) formation in duplex DNA by a series of polynuclear platinum anticancer complexes has been performed. To examine the effect of possible preassociation through charge and hydrogen-bonding effects the closely related compounds [{transPtCl ...
... A study of the unusual 3’–3’ 1,4-GG interstrand cross-link (IXL) formation in duplex DNA by a series of polynuclear platinum anticancer complexes has been performed. To examine the effect of possible preassociation through charge and hydrogen-bonding effects the closely related compounds [{transPtCl ...
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer – a
... of their size. Adenine – a purine base; one of the four molecules containing nitrogen present in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA; designated by letter A. Allele – one of two or more alternative forms of a gene. Allele Frequency – the proportion of a particular allele among the chromosomes carried by i ...
... of their size. Adenine – a purine base; one of the four molecules containing nitrogen present in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA; designated by letter A. Allele – one of two or more alternative forms of a gene. Allele Frequency – the proportion of a particular allele among the chromosomes carried by i ...
PROVING THAT DNA REPLICATION IS SEMICONSERVATIVE
... During the 1950s, scientists uncovered many of biological facts we now take for granted, beginning with the discovery that genetic information is passed on through deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and continuing through the elucidation of DNA’s three-dimensional structure. As the decade neared a close, ...
... During the 1950s, scientists uncovered many of biological facts we now take for granted, beginning with the discovery that genetic information is passed on through deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and continuing through the elucidation of DNA’s three-dimensional structure. As the decade neared a close, ...
Teacher quality grant
... DNA Replication DNA Replication Yield: – 2 double stranded DNA molecules identical to each other – Half of each double helix is new (daughter strand) and half is the original (parent strand) ...
... DNA Replication DNA Replication Yield: – 2 double stranded DNA molecules identical to each other – Half of each double helix is new (daughter strand) and half is the original (parent strand) ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... DNA Replication DNA Replication Yield: – 2 double stranded DNA molecules identical to each other – Half of each double helix is new (daughter strand) and half is the original (parent strand) ...
... DNA Replication DNA Replication Yield: – 2 double stranded DNA molecules identical to each other – Half of each double helix is new (daughter strand) and half is the original (parent strand) ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.