1 - BEHS Science
... 15.complementary: the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other strand 16.replication: the process of synthesizing a new strand of DNA 17.helicase: enzymes that catalyze the unwinding and separation of double-stranded DNA or RNA during its replication 18.replicati ...
... 15.complementary: the sequence of bases on one strand determines the sequence of bases on the other strand 16.replication: the process of synthesizing a new strand of DNA 17.helicase: enzymes that catalyze the unwinding and separation of double-stranded DNA or RNA during its replication 18.replicati ...
Nucleic acid worksheet
... 2. These monomers of DNA contain the bases: __________________, ___________________, ________________________, and _____________________. 3. _________________________ is the sugar found in all DNA molecules. 4. The shape of a DNA molecules is called the __________________________. 5. _______________ ...
... 2. These monomers of DNA contain the bases: __________________, ___________________, ________________________, and _____________________. 3. _________________________ is the sugar found in all DNA molecules. 4. The shape of a DNA molecules is called the __________________________. 5. _______________ ...
genetics i - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... Infer any 3 properties of genetic code with examples from the above information 14. i) Why does DNA replication occur in small replication occur in small replication forks and not in its entire length? ii) Why is DNA replication continuous and discontinuous in a replication fork? iii) Explain the im ...
... Infer any 3 properties of genetic code with examples from the above information 14. i) Why does DNA replication occur in small replication occur in small replication forks and not in its entire length? ii) Why is DNA replication continuous and discontinuous in a replication fork? iii) Explain the im ...
Name______________________________________
... During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand with the bases ...
... During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand with the bases ...
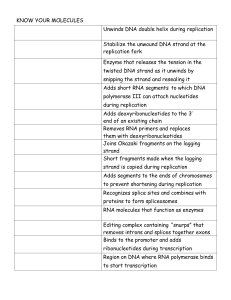
Know your molecules organizer
... replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA pri ...
... replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA pri ...
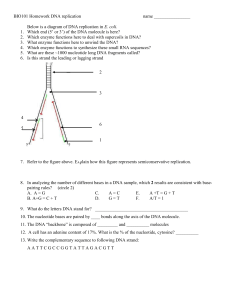
Ch 16 homework
... Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
... Which enzyme functions to synthesize these small RNA sequences? What are these ~1000 nucleotide long DNA fragments called? Is this strand the leading or lagging strand ...
CH 12 STUDY GUIDE YOU DO NOT NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THE
... ACCORDING TO THE FIGURE WHICH SHOWS AMINO ACIDS BE ABLE TO DETERMINE THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE WHAT HAPPENS TO THE LAC REPRESSORS IN E. COLI WHEN LACTOSE IS PRESENT? WHY ARE HOX GENES THAT ARE FOUND IN DIFFERENT ANIMALS VERY SIMILAR TO ONE ANOTHER? USING SCIENCE SKILLS THERE IS A DIAGRAM OF PROTIEN SY ...
... ACCORDING TO THE FIGURE WHICH SHOWS AMINO ACIDS BE ABLE TO DETERMINE THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE WHAT HAPPENS TO THE LAC REPRESSORS IN E. COLI WHEN LACTOSE IS PRESENT? WHY ARE HOX GENES THAT ARE FOUND IN DIFFERENT ANIMALS VERY SIMILAR TO ONE ANOTHER? USING SCIENCE SKILLS THERE IS A DIAGRAM OF PROTIEN SY ...
name period ______ date
... 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the complementary bases be if one side of a DNA molecule had the bases adenine, cytosine, cytosine, thymine, thy ...
... 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the complementary bases be if one side of a DNA molecule had the bases adenine, cytosine, cytosine, thymine, thy ...
Problem Set 3A
... give a single phrase, or sentence description that distinguishes what each of them does. The description should have enough detail to distinguish each enzyme from any of the others involved in DNA synthesis. 3. In the figure you have drawn for question 1, place a number encoding a most likely locati ...
... give a single phrase, or sentence description that distinguishes what each of them does. The description should have enough detail to distinguish each enzyme from any of the others involved in DNA synthesis. 3. In the figure you have drawn for question 1, place a number encoding a most likely locati ...
DNA Structure
... -What did she study? -What did the photos suggest? Watson and Crick (Last Paragraph) -What did Watson observe? -What did he immediately know? -What did Watson and Crick complete? What year? Chargaff (2nd Paragraph) -What did he find? -Give an example -What is Chargaff’s rule? ...
... -What did she study? -What did the photos suggest? Watson and Crick (Last Paragraph) -What did Watson observe? -What did he immediately know? -What did Watson and Crick complete? What year? Chargaff (2nd Paragraph) -What did he find? -Give an example -What is Chargaff’s rule? ...
DNA-ReplicationName-Per
... You will draw out the steps of the S phase of Interphase, DNA replication. In each box, draw the event described. You will use 3 different colors: one for the original strands of DNA, one for the leading strand, and one for the lagging strand. You must label all the bold words in each drawing and in ...
... You will draw out the steps of the S phase of Interphase, DNA replication. In each box, draw the event described. You will use 3 different colors: one for the original strands of DNA, one for the leading strand, and one for the lagging strand. You must label all the bold words in each drawing and in ...
Ch. 16 Molecular Basis of Genetics
... -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from the old molecule, and one newly made strand) telos - = an end (telomere: the protective structur ...
... -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replication in which the replicated double helix consists of one old strand, derived from the old molecule, and one newly made strand) telos - = an end (telomere: the protective structur ...
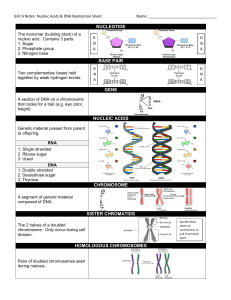
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a trait (e.g. eye color, ...
... A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a trait (e.g. eye color, ...
a copy of the Candy DNA Replication
... 2. Make more nucleotides and assemble into a polynucleotide strand that has 6 nitrogen bases. Assemble a complementary strand by matching the proper “bases” and attaching them together. Assign 5’ and 3’ ends to your model and label them with the sticky notes. Add at least 1 labeled picture. 3. To de ...
... 2. Make more nucleotides and assemble into a polynucleotide strand that has 6 nitrogen bases. Assemble a complementary strand by matching the proper “bases” and attaching them together. Assign 5’ and 3’ ends to your model and label them with the sticky notes. Add at least 1 labeled picture. 3. To de ...
ap: chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 15. Label the diagram of DNA replication. Include the directions and the terms. ...
... 15. Label the diagram of DNA replication. Include the directions and the terms. ...
DNA REPLICATION HANDOUT
... 1) Template strands: Original DNA strands that were ripped apart. 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running ...
... 1) Template strands: Original DNA strands that were ripped apart. 2) Replication Fork: Y-shaped region where new strands of DNA are elongated 3) Okazaki Fragments: Only found on the lagging strand. Since DNA is connected by base pairs, as the original strand “unzips” one of the templates is running ...
DNA Structure and Replication Constructed Response
... A DNA molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder. Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the nucleotides on opposite strands. The nitrogenous bases form hydrogen bonds with on ...
... A DNA molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder. Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the nucleotides on opposite strands. The nitrogenous bases form hydrogen bonds with on ...
dna-discovery - WordPress.com
... • scientists worked for over 100 years before DNA was confirmed to be the hereditary material for all life Late 1869 • Fredrich Miescher isolated nonprotein substance from the nucleus of pus cells • he noted that a phosphorus rich substance was present and it did not behave like a protein (at the ti ...
... • scientists worked for over 100 years before DNA was confirmed to be the hereditary material for all life Late 1869 • Fredrich Miescher isolated nonprotein substance from the nucleus of pus cells • he noted that a phosphorus rich substance was present and it did not behave like a protein (at the ti ...
Name:
... 2. Scroll down the page until you find the section about Chargaff’s rule. What are the full names of the four nitrogenous bases? 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? ...
... 2. Scroll down the page until you find the section about Chargaff’s rule. What are the full names of the four nitrogenous bases? 3. Which bases have two carbon-nitrogen rings? Which have only one? 4. What are the two base pairing rules? 5. How would the DNA strand look if A paired with G and T w/ C? ...
DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video
... DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
... DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
DNA Replication - The Biology Corner
... Problem: it reaches the replication fork, but the helicase is moving in the opposite direction. It stops, and another polymerase binds farther down the chain. This process creates several fragments, called Okazaki Fragments, that are bound together by DNA ligase. 6. During replication, there are man ...
... Problem: it reaches the replication fork, but the helicase is moving in the opposite direction. It stops, and another polymerase binds farther down the chain. This process creates several fragments, called Okazaki Fragments, that are bound together by DNA ligase. 6. During replication, there are man ...
Questions on DNA Replication and Enzymes used in DNA replication
... Approximately how many bases make up the human genome? What is the error rate for duplicating DNA? What contributes to errors being made during replication? What prevents this from becoming permanent damage? ...
... Approximately how many bases make up the human genome? What is the error rate for duplicating DNA? What contributes to errors being made during replication? What prevents this from becoming permanent damage? ...
Use the diagram to match the letter (A-C) to the correct term(1
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
... 4. ______ Complementary base pair. 5. ______ Hydrogen bond. 6. ______ Individual nitrogen base. 7. ______ Sugar-phosphate backbone. 8. In DNA, which of the following determines the traits of an organism? a. Amount of adenine b. Number of sugars c. Sequence of nitrogen bases d. Strength of hydrogen b ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.