IBO 2001 Theory part A_CCL - International Biology Olympiad
... The exam papers can be used freely for educational purposes as long as IBO is credited and new creations are licensed under identical terms. No commercial use is allowed. ...
... The exam papers can be used freely for educational purposes as long as IBO is credited and new creations are licensed under identical terms. No commercial use is allowed. ...
Theorie Partie A.p65
... are not eluted, DNA is double stranded and replicates semi-conservative. as the A and T, respectively C and G percentages are different, DNA is single - stranded; it is replicated by special enzymes, following a particular replication pattern, with single - stranded chain as a template. because A do ...
... are not eluted, DNA is double stranded and replicates semi-conservative. as the A and T, respectively C and G percentages are different, DNA is single - stranded; it is replicated by special enzymes, following a particular replication pattern, with single - stranded chain as a template. because A do ...
1008invertebrates - Michigan State University
... has become a model organism for studying genotype to phenotype ...
... has become a model organism for studying genotype to phenotype ...
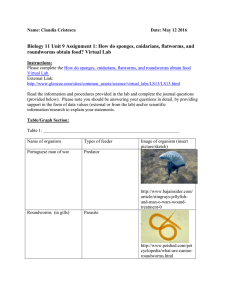
Biology 11 Unit 9 Assignment 1 How do sponges
... various invertebrates have adapted to feeding in their environment. Filter feeders filter bacteria, algae, protozoans and other bacteria from the water in which they live. Types of organisms with this method of feeding are usually sessile and relatively inactive. On the other hand organisms that are ...
... various invertebrates have adapted to feeding in their environment. Filter feeders filter bacteria, algae, protozoans and other bacteria from the water in which they live. Types of organisms with this method of feeding are usually sessile and relatively inactive. On the other hand organisms that are ...
Class-11
... any special preparation required for it? Anurag Shahi : For the International round of the exam, we were prepared by the teachers at HBCSE. They guided us and provided us books to study. The training camp was excellent and exhaustive and one can really learn a l ...
... any special preparation required for it? Anurag Shahi : For the International round of the exam, we were prepared by the teachers at HBCSE. They guided us and provided us books to study. The training camp was excellent and exhaustive and one can really learn a l ...
Printable PDF
... energy into energy that our cells can use. Q: What carbohydrate molecule is the basic component of your food energy? Q: What is different about how animal cells and plant cells obtain this molecule? Q:What molecule is the product of metabolism used to do cellular work? From the Virtual Cell Biology ...
... energy into energy that our cells can use. Q: What carbohydrate molecule is the basic component of your food energy? Q: What is different about how animal cells and plant cells obtain this molecule? Q:What molecule is the product of metabolism used to do cellular work? From the Virtual Cell Biology ...
Biology Review
... A. I am one of the first to see the cell structure for cell division. B. I found that by combining amino acids and electrical current I could create protocells. C. I invented a blood preservation technique still used today. D. I am the head of many cancer associations & head researcher. E. I invente ...
... A. I am one of the first to see the cell structure for cell division. B. I found that by combining amino acids and electrical current I could create protocells. C. I invented a blood preservation technique still used today. D. I am the head of many cancer associations & head researcher. E. I invente ...
Exemplar A
... At Merit the standard requires the student to demonstrate in-depth understanding using biological ideas to explain how humans manipulate genetic transfer (EN 3) and the biological implications of these manipulations (EN 2). The student provides evidence of in-depth understanding of biological ideas ...
... At Merit the standard requires the student to demonstrate in-depth understanding using biological ideas to explain how humans manipulate genetic transfer (EN 3) and the biological implications of these manipulations (EN 2). The student provides evidence of in-depth understanding of biological ideas ...
Ch. 19 (Part I): Bacteria (Monera)
... **Photosynthetic bacteria invaluable to producing earth’s atmosphere! **Bacteria critical in molecular biology (plasmids) ...
... **Photosynthetic bacteria invaluable to producing earth’s atmosphere! **Bacteria critical in molecular biology (plasmids) ...
Essential Biology 06.4 Gas Exchange Core
... Highlight all objective 1 command terms in yellow and complete these before class. Highlight all objective 2 and 3 command terms in green – these will be part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid pri ...
... Highlight all objective 1 command terms in yellow and complete these before class. Highlight all objective 2 and 3 command terms in green – these will be part of the discussions in class. After class, go back and review them. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid pri ...
1993 Werner Franke While many scientists find themselves fighting
... Department of Cell Biology. Franke enjoyed teaching, but found the German system of teaching science to be over-structured and intellectually stifling. He feels that science teaching in Germany, from grade school through higher education, still places too much emphasis on textbooks and memorization, ...
... Department of Cell Biology. Franke enjoyed teaching, but found the German system of teaching science to be over-structured and intellectually stifling. He feels that science teaching in Germany, from grade school through higher education, still places too much emphasis on textbooks and memorization, ...
Honors Biology Differentiation
... Something to think about as your open up your notes Humans have approx. 50-75 trillion cells and these cells are all different types (hair, skin, liver, stomach cells, etc.). ...
... Something to think about as your open up your notes Humans have approx. 50-75 trillion cells and these cells are all different types (hair, skin, liver, stomach cells, etc.). ...
Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry Exam Questions 2008/09
... 90. G-proteins: types, significance, mechanism of function, their GTPase activity. 91. The basic cellular signaling pathways: cAMP, phosphatidylinositols, calcium, Ras/MAPKinases, connection to transcription factors. 92. Projects of human genome sequencing, results and impact. Structure of human gen ...
... 90. G-proteins: types, significance, mechanism of function, their GTPase activity. 91. The basic cellular signaling pathways: cAMP, phosphatidylinositols, calcium, Ras/MAPKinases, connection to transcription factors. 92. Projects of human genome sequencing, results and impact. Structure of human gen ...
Unit 2: Dichotomous Keys, Phylogenetic Trees,
... 26. If a reaction happens when bird blood is mixed with dinosaur antibody, what does that mean? 27. What did birds evolve from? 28. What is evolution? 29. What is natural selection? 30. How are fossils dated? 31. What type of dating is used for the last 5000 years? 4.3 billion years? 32. Why is rela ...
... 26. If a reaction happens when bird blood is mixed with dinosaur antibody, what does that mean? 27. What did birds evolve from? 28. What is evolution? 29. What is natural selection? 30. How are fossils dated? 31. What type of dating is used for the last 5000 years? 4.3 billion years? 32. Why is rela ...
AQA Knowledge test ANSWERS Unit 2 Biology B2.1_Cells and
... 2. Why are scientists not certain about how life began on Earth? Because early forms of life did not leave much fossil evidence, they did not have bones and may have been disrupted by the Earth’s natural movements. 3. What is a fossil? The ‘remains’ of organisms from many years ago, found in roc ...
... 2. Why are scientists not certain about how life began on Earth? Because early forms of life did not leave much fossil evidence, they did not have bones and may have been disrupted by the Earth’s natural movements. 3. What is a fossil? The ‘remains’ of organisms from many years ago, found in roc ...
Chapter 16.
... The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
... The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
... Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Hershey & Chase (1952) Watson & Crick (1953) Meselson & Stahl (1958) ...
ICSE Board Class IX Biology Gold Series Sample Paper
... (v) A plant which propagates by leaves. ...
... (v) A plant which propagates by leaves. ...
Assessment of JiTT on Student Learning
... cystic fibrosis, an inherited, recessive disease. How did the child inherit a life-threatening disease from healthy people? Why weren't the parents affected by cystic fibrosis? Can this couple give birth to a child without cystic fibrosis? Why or why not? ...
... cystic fibrosis, an inherited, recessive disease. How did the child inherit a life-threatening disease from healthy people? Why weren't the parents affected by cystic fibrosis? Can this couple give birth to a child without cystic fibrosis? Why or why not? ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/TaxHsilent teaparty
... 9. Name the single DOMAIN which is made up of eukaryotes Eukarya ...
... 9. Name the single DOMAIN which is made up of eukaryotes Eukarya ...
Chapter 1 honors review questions
... Which of the following statements is NOT correct about evolution? New variations within certain members of a species allow them to capture fewer A)resources. Members of a population with advantageous variations tend to survive and have B)more offspring. Each successive generation will include more m ...
... Which of the following statements is NOT correct about evolution? New variations within certain members of a species allow them to capture fewer A)resources. Members of a population with advantageous variations tend to survive and have B)more offspring. Each successive generation will include more m ...
Preparing for S3 Parents Information Evening
... • Preparing for Third Year • Seminars on Curriculum Areas • If you have any questions please note them on the post-it notes and we will make the answers available on School Website • Available at the end for any individual questions ...
... • Preparing for Third Year • Seminars on Curriculum Areas • If you have any questions please note them on the post-it notes and we will make the answers available on School Website • Available at the end for any individual questions ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.