SnapShot: Key Numbers in Biology
... numbers are scattered in the vast biological literature in a way that often leads to a frustrating literature-mining ordeal. Here, we have collected a set of basic numbers in biology that we find extremely useful for obtaining an order of magnitude feel for the molecular processes in cells. Several ...
... numbers are scattered in the vast biological literature in a way that often leads to a frustrating literature-mining ordeal. Here, we have collected a set of basic numbers in biology that we find extremely useful for obtaining an order of magnitude feel for the molecular processes in cells. Several ...
modularity and mereology - Birkbeck, University of London
... Willi Hennig’s method is based on Darwin’s theory of descent with modification: ‘Evolution is a transformation of organisms in form and mode of life through which the descendants become different from their ancestors’ (Zimmerman, quoted in Hennig, 1966: 88). Limbs are transformed fins; fins are prim ...
... Willi Hennig’s method is based on Darwin’s theory of descent with modification: ‘Evolution is a transformation of organisms in form and mode of life through which the descendants become different from their ancestors’ (Zimmerman, quoted in Hennig, 1966: 88). Limbs are transformed fins; fins are prim ...
Biology Department YEAR 9 SCHEME OF WORK 2014
... topic(s), but the scripts should not be returned to candidates until the whole year group have completed the test. Marks should be recorded centrally onto the spreadsheet in the shared area. 6. Addition or subtraction of resources will be discussed at departmental meetings 7. There is an assortment ...
... topic(s), but the scripts should not be returned to candidates until the whole year group have completed the test. Marks should be recorded centrally onto the spreadsheet in the shared area. 6. Addition or subtraction of resources will be discussed at departmental meetings 7. There is an assortment ...
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
... Cite two significant findings that resulted from the research of Beadle and Tatum. ...
... Cite two significant findings that resulted from the research of Beadle and Tatum. ...
Document Here - What is BioInformatics?
... resources: COGS, ProDom, Pfam, Blocks, Domo, WIT, CATH, Scop.... ...
... resources: COGS, ProDom, Pfam, Blocks, Domo, WIT, CATH, Scop.... ...
Answer - My CCSD
... Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. A. Speciation rates can vary, especially when adaptive radiation occurs when new habitats become available. B. Species extinction rates are rapid at times of ecological stress ...
... Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. A. Speciation rates can vary, especially when adaptive radiation occurs when new habitats become available. B. Species extinction rates are rapid at times of ecological stress ...
Cytokinesis Cytokinesis Cytokinesis Cytokinesis
... determination, and which microtubules are involved? ...
... determination, and which microtubules are involved? ...
Minor Sheet - College of Arts and Sciences
... Biology, 300 Aronoff Laboratory, 318 W. 12th Ave., Columbus, OH 43210-1293; 614-292-8088; https://eeob.osu.edu/ The minor in evolution and ecology focuses on the descent and interrelationships of organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. These two disciplines provide an understanding ...
... Biology, 300 Aronoff Laboratory, 318 W. 12th Ave., Columbus, OH 43210-1293; 614-292-8088; https://eeob.osu.edu/ The minor in evolution and ecology focuses on the descent and interrelationships of organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. These two disciplines provide an understanding ...
Chapter 24 guided notes the origin of species answers
... discussed in Chapter. ORIGIN OF SPECIES ———— DARWIN. LONDON. JOHN MURRAY. [front cover] [inside front cover] THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES. [page ii] ~~~~~ "But with regard to the. Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed t ...
... discussed in Chapter. ORIGIN OF SPECIES ———— DARWIN. LONDON. JOHN MURRAY. [front cover] [inside front cover] THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES. [page ii] ~~~~~ "But with regard to the. Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed t ...
Classification and Organisms Review Sheet Modified True/False
... 11. A(n) ____________________ organism is a living thing that is composed of many cells. 12. Organisms that make their own food are called ____________________. 13. The process of grouping things based on similarities is called ____________________. 14. Biologists find ____________________ useful be ...
... 11. A(n) ____________________ organism is a living thing that is composed of many cells. 12. Organisms that make their own food are called ____________________. 13. The process of grouping things based on similarities is called ____________________. 14. Biologists find ____________________ useful be ...
Chapter 24 guided notes the origin of species answers
... Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed to the scientific conclusion that they. CHAPTER I. THE PERIOD BEFORE THE LAW. The following two positions will be admitted without question, it is believed, by all Christians ...
... Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed to the scientific conclusion that they. CHAPTER I. THE PERIOD BEFORE THE LAW. The following two positions will be admitted without question, it is believed, by all Christians ...
CP Biology Name Date Period HOMEWORK PACKET UNIT 1A
... Directions: Read ALL of the following sentences and number them in the CORRECT order based upon Charles Darwin’s concept of natural selection. ________Lighter moths were hard to spot against the light colored trees found around England. ________The population of peppered moths now consists of predom ...
... Directions: Read ALL of the following sentences and number them in the CORRECT order based upon Charles Darwin’s concept of natural selection. ________Lighter moths were hard to spot against the light colored trees found around England. ________The population of peppered moths now consists of predom ...
jeopardy - AMERICAN-HISTORY
... The dolphin’s land-dwelling ancestors were probably made up of populations with different body shapes and limbs. Those land-dwellers began to spend more time in the ocean, perhaps because food was easier to find. In each generation, those with bodies that moved efficiently in water survived longer a ...
... The dolphin’s land-dwelling ancestors were probably made up of populations with different body shapes and limbs. Those land-dwellers began to spend more time in the ocean, perhaps because food was easier to find. In each generation, those with bodies that moved efficiently in water survived longer a ...
Biology, High School
... different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendo ...
... different parts of the body and mediates the body’s interactions with the environment. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendo ...
Answer the following
... (b) the kind of cells they are made of. Why? Answer The more basic characteristic for classifying organisms is the kind of cells they are made of because different organisms may share same habitat but may have entirely different form and structure. So, the place where they live cannot be a basis of ...
... (b) the kind of cells they are made of. Why? Answer The more basic characteristic for classifying organisms is the kind of cells they are made of because different organisms may share same habitat but may have entirely different form and structure. So, the place where they live cannot be a basis of ...
B1 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... health problems. For adults this is defined as having a BMI of over 30 When organisms need the same resources as each other, they struggle against each other to get those resources An animal, because it consumes (eats) other organisms Part of a plant normally a leaf or stem) from which a new plant c ...
... health problems. For adults this is defined as having a BMI of over 30 When organisms need the same resources as each other, they struggle against each other to get those resources An animal, because it consumes (eats) other organisms Part of a plant normally a leaf or stem) from which a new plant c ...
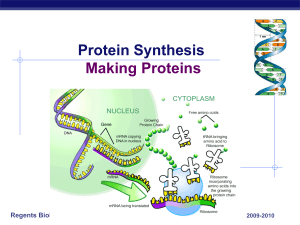
Protein Synthesis Making Proteins
... Bodies are made up of cells All cells run on a set of instructions spelled out in DNA ...
... Bodies are made up of cells All cells run on a set of instructions spelled out in DNA ...
Graph 1: Rabbits Over Time
... Gene Expression and Regulation p. 309-312 1. If all the cells in an organism (cells with nuclei) have the same DNA, explain, in terms of genes, how a nerve cell functions differently from a muscle cell. Different genes are turned on in different types of cells. 2. Why does a pancreas cell produce in ...
... Gene Expression and Regulation p. 309-312 1. If all the cells in an organism (cells with nuclei) have the same DNA, explain, in terms of genes, how a nerve cell functions differently from a muscle cell. Different genes are turned on in different types of cells. 2. Why does a pancreas cell produce in ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... 2. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell ...
... 2. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... 2. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell ...
... 2. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell ...
OB41 - OB42
... 3. The two new cells then separate …the new cells then grow to full size www.juniorscience.ie ...
... 3. The two new cells then separate …the new cells then grow to full size www.juniorscience.ie ...
CURRICULUM SUMMARY * September to October 2008
... things over time and think how families often share characteristics. They learn that this is called ʻinheritanceʼ and that it helps to explain evolution. Children play ʻChinese whispersʼ to reinforce this idea of change and adaptation. Children compare animals and discuss their similarities and diff ...
... things over time and think how families often share characteristics. They learn that this is called ʻinheritanceʼ and that it helps to explain evolution. Children play ʻChinese whispersʼ to reinforce this idea of change and adaptation. Children compare animals and discuss their similarities and diff ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... 41. A couple has 6 children and all of them are female. The probability that the couple's 7th child is a male is (A) 1/49 (D) 1/2 (B) 1/7 (E) 6/7 (C) 1/6 ...
... 41. A couple has 6 children and all of them are female. The probability that the couple's 7th child is a male is (A) 1/49 (D) 1/2 (B) 1/7 (E) 6/7 (C) 1/6 ...
History of biology

The history of biology traces the study of the living world from ancient to modern times. Although the concept of biology as a single coherent field arose in the 19th century, the biological sciences emerged from traditions of medicine and natural history reaching back to ayurveda, ancient Egyptian medicine and the works of Aristotle and Galen in the ancient Greco-Roman world. This ancient work was further developed in the Middle Ages by Muslim physicians and scholars such as Avicenna. During the European Renaissance and early modern period, biological thought was revolutionized in Europe by a renewed interest in empiricism and the discovery of many novel organisms. Prominent in this movement were Vesalius and Harvey, who used experimentation and careful observation in physiology, and naturalists such as Linnaeus and Buffon who began to classify the diversity of life and the fossil record, as well as the development and behavior of organisms. Microscopy revealed the previously unknown world of microorganisms, laying the groundwork for cell theory. The growing importance of natural theology, partly a response to the rise of mechanical philosophy, encouraged the growth of natural history (although it entrenched the argument from design).Over the 18th and 19th centuries, biological sciences such as botany and zoology became increasingly professional scientific disciplines. Lavoisier and other physical scientists began to connect the animate and inanimate worlds through physics and chemistry. Explorer-naturalists such as Alexander von Humboldt investigated the interaction between organisms and their environment, and the ways this relationship depends on geography—laying the foundations for biogeography, ecology and ethology. Naturalists began to reject essentialism and consider the importance of extinction and the mutability of species. Cell theory provided a new perspective on the fundamental basis of life. These developments, as well as the results from embryology and paleontology, were synthesized in Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection. The end of the 19th century saw the fall of spontaneous generation and the rise of the germ theory of disease, though the mechanism of inheritance remained a mystery.In the early 20th century, the rediscovery of Mendel's work led to the rapid development of genetics by Thomas Hunt Morgan and his students, and by the 1930s the combination of population genetics and natural selection in the ""neo-Darwinian synthesis"". New disciplines developed rapidly, especially after Watson and Crick proposed the structure of DNA. Following the establishment of the Central Dogma and the cracking of the genetic code, biology was largely split between organismal biology—the fields that deal with whole organisms and groups of organisms—and the fields related to cellular and molecular biology. By the late 20th century, new fields like genomics and proteomics were reversing this trend, with organismal biologists using molecular techniques, and molecular and cell biologists investigating the interplay between genes and the environment, as well as the genetics of natural populations of organisms.