“The Classification of Living Things” Video
... o Have a nucleus (eukaryotic) o Some can photosynthesize and others eat & absorb food Kingdom Fungi o Types of Fungi Mushrooms, molds, yeast, mildew, etc. o Made of many cells o Cannot move around o Get food by absorbing it from other living things or from organisms that are dead & decaying. ...
... o Have a nucleus (eukaryotic) o Some can photosynthesize and others eat & absorb food Kingdom Fungi o Types of Fungi Mushrooms, molds, yeast, mildew, etc. o Made of many cells o Cannot move around o Get food by absorbing it from other living things or from organisms that are dead & decaying. ...
Bacterial conjugation Is a primitive form of sexual reproduction
... two parent cells are involved. The benefit is that new combinations of inherited characteristics may result. This process is not actually reproduction, because there is no increase in the number of cells, however it does result in genetic recombination. The newly created cell can then divide by bina ...
... two parent cells are involved. The benefit is that new combinations of inherited characteristics may result. This process is not actually reproduction, because there is no increase in the number of cells, however it does result in genetic recombination. The newly created cell can then divide by bina ...
Cell Function CC
... Compound Light Microscope: lets light pass through an object then through 2 or more lenses Electron microscope: for objects way too small to be seen with a light microscope; uses magnetic field to bend beams of electrons and can magnify 1,000,000 times ...
... Compound Light Microscope: lets light pass through an object then through 2 or more lenses Electron microscope: for objects way too small to be seen with a light microscope; uses magnetic field to bend beams of electrons and can magnify 1,000,000 times ...
KeystoneReview Guide Cells
... Homeostasis - organisms must maintain stable internal conditions even when the external environment changes examples are organisms regulating their temperature, water levels, oxygen levels and pH ...
... Homeostasis - organisms must maintain stable internal conditions even when the external environment changes examples are organisms regulating their temperature, water levels, oxygen levels and pH ...
Lab 9: Adaptations for Survival in Terrestrial Environments
... producing many small cells. At the blastula or hollow ball stage, a cavity called a blastocoel forms near the animal pole. The next stage of development is termed gastrulation. It is marked by the appearance of a groove, called the dorsal lip, below the equator of the blastula. Gastrulation in lower ...
... producing many small cells. At the blastula or hollow ball stage, a cavity called a blastocoel forms near the animal pole. The next stage of development is termed gastrulation. It is marked by the appearance of a groove, called the dorsal lip, below the equator of the blastula. Gastrulation in lower ...
Ancient Art of Biblical Healing 50-Hour ModuleAroma Hut Institute
... Telephase, then back to interphase again. Always in a cycle, round and round. This is a very speedy process. Mitosis usually takes place in a matter of minutes. The majority of the changes occur in the nucleus, because in the main the duplication affects the DNA. These strands of DNA are packaged in ...
... Telephase, then back to interphase again. Always in a cycle, round and round. This is a very speedy process. Mitosis usually takes place in a matter of minutes. The majority of the changes occur in the nucleus, because in the main the duplication affects the DNA. These strands of DNA are packaged in ...
Cells - Effingham County Schools
... Photosynthesis: process that plants use to make food by using the energy of sunlight chloroplasts Photosynthesis takes place in the ___________ and depends on a green pigment called chlorophyll. ...
... Photosynthesis: process that plants use to make food by using the energy of sunlight chloroplasts Photosynthesis takes place in the ___________ and depends on a green pigment called chlorophyll. ...
Review Sheet
... conducting and reporting their research. 2. What mechanisms are currently in place to detect scientific misconduct? Are they adequate? Why or why not? 3. What are the main differences between bright-field, dark-field, and phase-contrast microscopy? 4. For each "Great Moment in Cell Biology": what wa ...
... conducting and reporting their research. 2. What mechanisms are currently in place to detect scientific misconduct? Are they adequate? Why or why not? 3. What are the main differences between bright-field, dark-field, and phase-contrast microscopy? 4. For each "Great Moment in Cell Biology": what wa ...
unit 1: the organisation of the human body
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
Review Guide Cells
... Homeostasis - organisms must maintain stable internal conditions even when the external environment changes examples are organisms regulating their temperature, water levels, oxygen levels and pH ...
... Homeostasis - organisms must maintain stable internal conditions even when the external environment changes examples are organisms regulating their temperature, water levels, oxygen levels and pH ...
BioBoot Camp – Cells
... Homeostasis - organisms must maintain stable internal conditions even when the external environment changes examples are organisms regulating their temperature, water levels, oxygen levels and pH Metabolism - is the sum of all the chemical reactions that take in and transform energy and material fro ...
... Homeostasis - organisms must maintain stable internal conditions even when the external environment changes examples are organisms regulating their temperature, water levels, oxygen levels and pH Metabolism - is the sum of all the chemical reactions that take in and transform energy and material fro ...
How Do Cells Know? - Teacher Created Materials
... Mitosis creates new cells. In humans, each cell contains all 46 chromosomes. Meiosis creates cells, too. But these cells each have only 23 chromosomes. Then, two sex cells can join together. They create a new organism. It will have a new set of 46 chromosomes that no one has ever had before. ...
... Mitosis creates new cells. In humans, each cell contains all 46 chromosomes. Meiosis creates cells, too. But these cells each have only 23 chromosomes. Then, two sex cells can join together. They create a new organism. It will have a new set of 46 chromosomes that no one has ever had before. ...
Cells
... nervous system: consisting of sense organs, brain, spinal cord, nerves skeletal system: consisting of vertebral column, limb bones, ribs muscular system: muscles ...
... nervous system: consisting of sense organs, brain, spinal cord, nerves skeletal system: consisting of vertebral column, limb bones, ribs muscular system: muscles ...
INTRODUCTORY QUESTIONS
... C. Living things require energy. Different organisms obtain their food from different sources. Give an example. What is autotrophic? Autotrophic organisms such as green plants make their own food through photosynthesis. What is photosynthesis? This is a process where green plants use sun energy to m ...
... C. Living things require energy. Different organisms obtain their food from different sources. Give an example. What is autotrophic? Autotrophic organisms such as green plants make their own food through photosynthesis. What is photosynthesis? This is a process where green plants use sun energy to m ...
Mitosis - benanbiology
... The cell division is mitosis. The genetic trats are same with the parent organism. Doesn’t effect evolution or variation. Seen in primitive organisms Only mutations can form variations Monoploid (n) or diploid(2n) organisms can be formed ...
... The cell division is mitosis. The genetic trats are same with the parent organism. Doesn’t effect evolution or variation. Seen in primitive organisms Only mutations can form variations Monoploid (n) or diploid(2n) organisms can be formed ...
Student Packet 16 Plant Animal Cells L.14.3
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ...
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ...
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
... gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction. • We will also talk about the reproductive systems of males and females and fertilization and development of humans. • Then we will talk about heredity and how our genes are expressed to make us who we are. ...
... gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction. • We will also talk about the reproductive systems of males and females and fertilization and development of humans. • Then we will talk about heredity and how our genes are expressed to make us who we are. ...
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
... tissue into the vascular tissue. Through the capillary action of water it moves up the xylem vessel to the leaf. The water molecule diffuses into a leaf cell, where it is used in photosynthesis, or alternatively through the stomata in the process of transpiration. 17. How do the guard cells control ...
... tissue into the vascular tissue. Through the capillary action of water it moves up the xylem vessel to the leaf. The water molecule diffuses into a leaf cell, where it is used in photosynthesis, or alternatively through the stomata in the process of transpiration. 17. How do the guard cells control ...
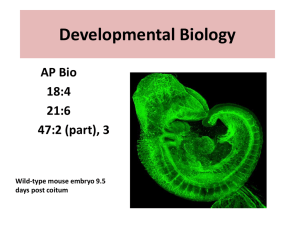
Developmental Biology
... • During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types • Cell types are organized successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism ...
... • During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types • Cell types are organized successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism ...
Diffusion and Osmosis in plant and animal cells
... • State when diffusion will stop. • Identify concentration differences and predict the direction of movement of substances by diffusion in a given diagram. • State which substances enter and leave cells by diffusion. • Explain the importance of diffusion to cells. ...
... • State when diffusion will stop. • Identify concentration differences and predict the direction of movement of substances by diffusion in a given diagram. • State which substances enter and leave cells by diffusion. • Explain the importance of diffusion to cells. ...
BIO 1101 - Makerere University Courses
... VENUE: DOSATE Biology Laboratory COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed to acquaint biology student-teachers with knowledge about the cell theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological cells. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this cours ...
... VENUE: DOSATE Biology Laboratory COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed to acquaint biology student-teachers with knowledge about the cell theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological cells. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this cours ...
OB41 - OB42
... may harm cells if not removed • examples of toxic substances are carbon dioxide and urea www.juniorscience.ie ...
... may harm cells if not removed • examples of toxic substances are carbon dioxide and urea www.juniorscience.ie ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are