* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “The Classification of Living Things” Video
Survey
Document related concepts
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Invertebrate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
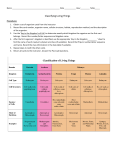
“The Classification of Living Things” Video Classify: to sort things into groups by how they are alike & different using both physical and behavioral characteristics. Seven Levels of the Classification System -Kingdom -Phylum -Class -Order -Family -Genus -Species -King -Philip -Comes -Over -For -Good -Spaghetti Classification of the house cat Royal Kitty -Kingdom -Phylum -Class -Order -Family -Genus -Species = = = = = = = Animalia Chordata Mammalia Carnivora Felidae Felis domesticus Carolus Linnaeus created the Binomial system o Binomial 2 word naming system (Genus, species) The Classification System makes it easier to find things. Scientists call organisms by their scientific name. Common Names o Mountain Lion o Puma o Cougar Only 1 Scientific Name Felis concolor (Genus) (Species) Kingdoms o (5) – Monera, Protist, Fungus, Plant, & Animal o (6) – Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protist, Fungus, Plant, & Animal Kingdom Food Movement # of Cells Animals Plants Fungi Protists Monerans Eat Make Absorb Make or obtain Make or obtain Yes No No Some move Some move Many Many Many One One Kingdom Monera Bacteria o Bacteria can be found anywhere on Earth ~ even inside your mouth. Some cause illness strep throat Many are helpful make cheese, yogurt, etc. o Most monerans trap the sun’s energy to make food. o Other bacteria, called Archaebacteria, use a chemical reaction to make food because they live where there is no sunlight (deep ocean floor). Kingdom Protista o Most are single-celled o Have a nucleus (eukaryotic) o Some can photosynthesize and others eat & absorb food Kingdom Fungi o Types of Fungi Mushrooms, molds, yeast, mildew, etc. o Made of many cells o Cannot move around o Get food by absorbing it from other living things or from organisms that are dead & decaying. Called Decomposers. Kingdom Plantae o Multicellular o Use photosynthesis to make food (H20 + Sunlight + CO2 Sugar + O2) o Some Plants are “Nonvascular” (Example: moss) Water from outside must be absorbed directly into the plants cells. The plants cells must be near water so the plant cannot grow very tall. o Most plants are “Vascular” Tube-like cells bring H20 & nutrients made to all cells in the plant. Vascular plants Seeds & No Seeds No Seeds (Example: fern) o Have tiny cells, called spores, that can grow into a new plant. Seeds Flowering & Non-flowering o Flowering largest group of plants that make seeds are flowering plants. o Non-flowering Cones Kingdom Animalia o Have many cells o Eat other organisms for energy o Can move from place to place motile o 16 Phyla Invertebrates & Vertebrates Invertebrates (15 Phyla) No Backbone Insects make up the largest group of invertebrates o Insects have 3 body parts and 6 legs Phylum Arthropoda (Insects, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, lobsters, crabs, etc.) o Legs that bend at a joint o Sectioned bodies o Exoskeleton Phylum Cnideria (Examples: jellyfish, sea anemones, coral) o Have stinging cells that protect them from other animals. Phylum Echinodermata (Examples: sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers) o Echinodermata means spiny skin Phylum Mollusca (Examples: snails, clams, etc.) o Most have shells Phylum Porifera (Example: sponges) o Look like plants but are animals o Trap their food in spaces in their bodies Vertebrates (1 Phylum Chordata) 5 Classes of the Chordata Phylum o Fish Cold-blooded body temperature is very close to the temperature of the air around them. Most fish hatch eggs All live in water & use gills to get oxygen from water Most have scales to protect them in the water Have fins to help move through the water o Amphibians (Examples: frogs & salamanders) Cold-blooded body temperature is very close to the temperature of the air around them. Hatch eggs Start life in water As adults their bodies change to allow them to live on land o Reptiles o Birds (Examples: lizards/snakes, alligators/crocs, turtles/tortoises) Cold-blooded body temperature is very close to the temperature of the air around them. Hatch eggs Have dry and scaly skin Use lungs to breath in air Warm-blooded Hatch eggs Bodies are covered with feathers All birds have wings and most birds can fly o Mammals Warm-blooded Born alive feed milk to young Usually have hair on bodies Most live on land Two mammals that live in the ocean are whales & dolphins The only mammal that can fly is the bat