Biology 3A
... Watching T.V. D Sleeping 12. Where do plants get the glucose that they use for respiration? A From nutrients in the soil B From osmosis of water C From photosynthesis D From respiration 13. When might your body experience an oxygen debt? A After waking up in the morning B After going for a long walk ...
... Watching T.V. D Sleeping 12. Where do plants get the glucose that they use for respiration? A From nutrients in the soil B From osmosis of water C From photosynthesis D From respiration 13. When might your body experience an oxygen debt? A After waking up in the morning B After going for a long walk ...
HBSGlossary - Kenwood Academy High School
... Abdominal Cavity: The body cavity in mammals that primarily houses parts of the digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems. It is separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm. Abduction: Movement away from the midline of the body. Accommodation: The automatic adjustment of the eye for see ...
... Abdominal Cavity: The body cavity in mammals that primarily houses parts of the digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems. It is separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm. Abduction: Movement away from the midline of the body. Accommodation: The automatic adjustment of the eye for see ...
video slide
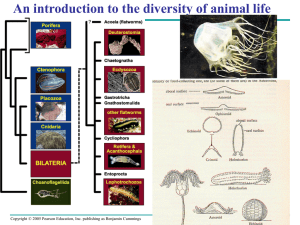
... These are essentially colonial protozoa, whose colonies are reinforced with solid spicules of various shapes and composition. Silica SiO2 and Calcite CaCO3 are the commonest. They are exclusively aquatic, mainly marine, and live by filter feeding. The feeding cells are called choanocytes, which inco ...
... These are essentially colonial protozoa, whose colonies are reinforced with solid spicules of various shapes and composition. Silica SiO2 and Calcite CaCO3 are the commonest. They are exclusively aquatic, mainly marine, and live by filter feeding. The feeding cells are called choanocytes, which inco ...
unit 3 – how do living
... Through nutrition, organisms obtain matter and energy. They are necessary to build new cells, to increase in size, to renew cells, to reconstruct lost parts etc. Energy is required to carry out some processes. There are processes that do not require energy, for example when we sleep we don’t use ene ...
... Through nutrition, organisms obtain matter and energy. They are necessary to build new cells, to increase in size, to renew cells, to reconstruct lost parts etc. Energy is required to carry out some processes. There are processes that do not require energy, for example when we sleep we don’t use ene ...
Biology (SPA)
... (1635–1703), one of the first scientists to use a microscope to examine pond water, cork and other things, was the first to refer to the cavities he saw in cork as ‘cells’, Latin for chambers. Subsequent scientists developed Hooke’s discovery of the cell into the Cell Theory on which modern Biology ...
... (1635–1703), one of the first scientists to use a microscope to examine pond water, cork and other things, was the first to refer to the cavities he saw in cork as ‘cells’, Latin for chambers. Subsequent scientists developed Hooke’s discovery of the cell into the Cell Theory on which modern Biology ...
the animal body: introduction tostructure and function
... 4. Generate heat. There are three types of muscles: striated, smooth and cardiac. MUSCLE STRUCTURE In vertebrates, muscles are organs. Muscle cells are called fibers. Muscle fibers are huge cells ranging between 10 and 100 μm (10-6 m), up to 10x that of an average body cell; their length could reach ...
... 4. Generate heat. There are three types of muscles: striated, smooth and cardiac. MUSCLE STRUCTURE In vertebrates, muscles are organs. Muscle cells are called fibers. Muscle fibers are huge cells ranging between 10 and 100 μm (10-6 m), up to 10x that of an average body cell; their length could reach ...
What Are Bacteria?
... Survival of the Fittest! Bacteria have an uncanny ability to survive. They can form endospores when conditions are unfavorable for survival. An endospore is made of a tough coating, the chromosome, and a bit of cytoplasm. Endospores can survive high temperatures, dryness, freezing condition ...
... Survival of the Fittest! Bacteria have an uncanny ability to survive. They can form endospores when conditions are unfavorable for survival. An endospore is made of a tough coating, the chromosome, and a bit of cytoplasm. Endospores can survive high temperatures, dryness, freezing condition ...
What is Life? - bms8thgradescience
... Response – an action or change in behavior that occurs as a result of a stimulus How do living things react to their surroundings? ...
... Response – an action or change in behavior that occurs as a result of a stimulus How do living things react to their surroundings? ...
Blood Policy and Technology (Part 11 of 14)
... method used to separate plasma into its major protein groups. A three-variable system (temperature, ionic strength, and ethanol concentration (pH)) is used to precipitate different proteins in the following order: Fraction I (chiefly Factor VIII and fibrinogen); Fraction II (the immune globulins); F ...
... method used to separate plasma into its major protein groups. A three-variable system (temperature, ionic strength, and ethanol concentration (pH)) is used to precipitate different proteins in the following order: Fraction I (chiefly Factor VIII and fibrinogen); Fraction II (the immune globulins); F ...
AP Biology
... 3. Why are cells so small? Explain the importance of the surface area to volume ratio. ...
... 3. Why are cells so small? Explain the importance of the surface area to volume ratio. ...
Development for Class
... The eggs and zygotes of many animals, except mammals, have a definite polarity The polarity is defined by distribution of yolk, with the vegetal pole having the most yolk The development of body axes in frogs is influenced by the egg’s polarity ...
... The eggs and zygotes of many animals, except mammals, have a definite polarity The polarity is defined by distribution of yolk, with the vegetal pole having the most yolk The development of body axes in frogs is influenced by the egg’s polarity ...
The Respiratory System - BIOLOGY and HONORS PHYSIOLOGY Mr
... epithelium. Between the alveoli you may see a thin layer of areolar connective tissue and ...
... epithelium. Between the alveoli you may see a thin layer of areolar connective tissue and ...
Reproduction and Development
... Ovulation • When follicle has completely matured, the ovum is released – Ovulation • Follicle literally ruptures – Ovum is swept from the surface of the ovary into the opening of one of the two Fallopian tubes – Ovum moves through the fluid-filled Fallopian tubes, pushed along by cilia » Egg can b ...
... Ovulation • When follicle has completely matured, the ovum is released – Ovulation • Follicle literally ruptures – Ovum is swept from the surface of the ovary into the opening of one of the two Fallopian tubes – Ovum moves through the fluid-filled Fallopian tubes, pushed along by cilia » Egg can b ...
The Molecular Basis of Life
... the Paris Academy of Sciences offered a prize to anyone who could prove or disprove the spontaneous generation of life. The biologist Louis Pasteur took up the challenge. The two Erlenmeyer flasks shown here reproduce the results of Pasteur’s winning experiment. Each flask and the stopper were steri ...
... the Paris Academy of Sciences offered a prize to anyone who could prove or disprove the spontaneous generation of life. The biologist Louis Pasteur took up the challenge. The two Erlenmeyer flasks shown here reproduce the results of Pasteur’s winning experiment. Each flask and the stopper were steri ...
Type AB Blood
... volume. They are made from stem cells in bone marrow. • There are five types of leukocytes. Each is an important component of the immune system. If a germ or infection enters the body various forms of leucocytes go into action. • Neutrophils destroy foreign substances such as bacteria. The neutrophi ...
... volume. They are made from stem cells in bone marrow. • There are five types of leukocytes. Each is an important component of the immune system. If a germ or infection enters the body various forms of leucocytes go into action. • Neutrophils destroy foreign substances such as bacteria. The neutrophi ...
Interaction of Systems - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... 3. Your body is said to be in “homeostasis” when there is a healthy balance in its internal conditions and processes (body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate). Explain how the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems contribute to homeostasis. 4. Single-celled or ...
... 3. Your body is said to be in “homeostasis” when there is a healthy balance in its internal conditions and processes (body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate). Explain how the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and nervous systems contribute to homeostasis. 4. Single-celled or ...
B2-Topic-3-notes - Greenacre Academy Trust
... Growth in animals also involves cell division…but unlike plants, animals stop growing when they become adults In an animal, cells that can differentiate to form many different types of specialised cells are called stem cells: o Embryonic stem cells can differentiate and form almost any type of cell ...
... Growth in animals also involves cell division…but unlike plants, animals stop growing when they become adults In an animal, cells that can differentiate to form many different types of specialised cells are called stem cells: o Embryonic stem cells can differentiate and form almost any type of cell ...
Question paper - Paper 1F - November 2010
... Instructions to Candidates In the boxes above, write your centre number, candidate number, your surname, initial(s) and signature. The paper reference is shown above. Check that you have the correct question paper. Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in this question paper. Do not use pe ...
... Instructions to Candidates In the boxes above, write your centre number, candidate number, your surname, initial(s) and signature. The paper reference is shown above. Check that you have the correct question paper. Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in this question paper. Do not use pe ...
AQA Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology Specification Specification
... The scientific terms used in this specification are clearly defined by the ASE in The Language of Measurement: Terminology used in school science investigations (Association for Science Education, 2010). Teachers should ensure that they, and their students, are familiar with these terms. Definitions ...
... The scientific terms used in this specification are clearly defined by the ASE in The Language of Measurement: Terminology used in school science investigations (Association for Science Education, 2010). Teachers should ensure that they, and their students, are familiar with these terms. Definitions ...
Csyllabus_CHS215_MohamedFawzi_modified for students
... The purpose of this course is to study the basics of physiology that aid in the applying of clinical nutrition. The course covers the functions of various systems and organs in the body and studies the cell, tissues, blood vessels, digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, endocrine, exocrine ...
... The purpose of this course is to study the basics of physiology that aid in the applying of clinical nutrition. The course covers the functions of various systems and organs in the body and studies the cell, tissues, blood vessels, digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, endocrine, exocrine ...
tissues - Linn-Benton Community College
... provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis). ...
... provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis). ...
Human Biology
... List the levels of organization in humans. What are the four basic types of human tissue? List the organ systems of the human body. Using any type of machine as an example, explain how each part of the machine works together with every other part so that the machine can do its job. Compare this with ...
... List the levels of organization in humans. What are the four basic types of human tissue? List the organ systems of the human body. Using any type of machine as an example, explain how each part of the machine works together with every other part so that the machine can do its job. Compare this with ...
Hierarchy of Life
... humans.) Pathogenic Bacteria (Disease causing) A. These prokaryotes account for more than half of all non- genetic diseases in humans. B. Opportunists (such as streptococcus) become a problem when the body is busy fighting something else, such as a cold virus. (They see an opportunity to reproduce a ...
... humans.) Pathogenic Bacteria (Disease causing) A. These prokaryotes account for more than half of all non- genetic diseases in humans. B. Opportunists (such as streptococcus) become a problem when the body is busy fighting something else, such as a cold virus. (They see an opportunity to reproduce a ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.