Mid-Term Planning - Newtoniasecondary.com
... Know the 78characteristics of a living organism Recognise cell structures, nucleus, cytoplasm, cell memebrane, cell wall, chlorplast, vacuole and describe functions Describe the difference between plant and animal cell Undertand the role of enzymes, catalyst and metabolic reactions Understand how fu ...
... Know the 78characteristics of a living organism Recognise cell structures, nucleus, cytoplasm, cell memebrane, cell wall, chlorplast, vacuole and describe functions Describe the difference between plant and animal cell Undertand the role of enzymes, catalyst and metabolic reactions Understand how fu ...
Structure and Function of Animals syllabus
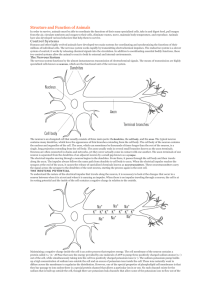
... THE ACTION POTENTIAL While most cells have some sort of resting potential from the movement of ions across their membranes, neurons are among only a few types of cells that can also form an action potential. The action potential is the electrochemical impulse that can travel along the neuron. In add ...
... THE ACTION POTENTIAL While most cells have some sort of resting potential from the movement of ions across their membranes, neurons are among only a few types of cells that can also form an action potential. The action potential is the electrochemical impulse that can travel along the neuron. In add ...
lymphatic system
... The ANS can be subclassified, once again, into the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. Both divisions provide directions to the viscera, but they are constructed differently and use different neurotransmitters when conveying impulses to their target organs. These two subdivisi ...
... The ANS can be subclassified, once again, into the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. Both divisions provide directions to the viscera, but they are constructed differently and use different neurotransmitters when conveying impulses to their target organs. These two subdivisi ...
Compounds of Living Things
... cells. Cells use a difference in electrical charge inside and outside the cell membrane to move materials in and out. Cells use the charges carried by salt ions to do this. Salts are also used to conduct electrical signals throughout your body. This is especially important for nerve cells, muscle ce ...
... cells. Cells use a difference in electrical charge inside and outside the cell membrane to move materials in and out. Cells use the charges carried by salt ions to do this. Salts are also used to conduct electrical signals throughout your body. This is especially important for nerve cells, muscle ce ...
4- Phylum CNIDARIA Contains about 9000 living species(at 1977
... 3 -Phylum exhibits polymorphism. The two main structural types are the polyp and the medusa. 4-May be solitary or colonial. 5-Typical larval form is the planula. 6-Exhibit some form of radial symmetry. 7 -Generally possess a ring of tentacles around the oral end. 8-The single body cavity is the coel ...
... 3 -Phylum exhibits polymorphism. The two main structural types are the polyp and the medusa. 4-May be solitary or colonial. 5-Typical larval form is the planula. 6-Exhibit some form of radial symmetry. 7 -Generally possess a ring of tentacles around the oral end. 8-The single body cavity is the coel ...
Lecture Notes - Austin Community College
... c. Alveolar Sacs - The alveolar ducts end at alveolar sacs. Many alveoli are interconnected at each alveolar sac. These are made of simple squamous epithelium. d. Alveoli are blind pockets at the end of the respiratory tree, lined by a simple squamous epithelium, supported by a hin elastic basement ...
... c. Alveolar Sacs - The alveolar ducts end at alveolar sacs. Many alveoli are interconnected at each alveolar sac. These are made of simple squamous epithelium. d. Alveoli are blind pockets at the end of the respiratory tree, lined by a simple squamous epithelium, supported by a hin elastic basement ...
CO 2
... Instead of being fixed by rubisco, CO2 combines with a 3Carbon molecule PEP to form OAA, using the fixing enzyme PEP carboxylase. • OAA is then converted to malate, and that is shuttled to the bundle sheath cells. • Here, malate is converted to pyruvate and CO2. ...
... Instead of being fixed by rubisco, CO2 combines with a 3Carbon molecule PEP to form OAA, using the fixing enzyme PEP carboxylase. • OAA is then converted to malate, and that is shuttled to the bundle sheath cells. • Here, malate is converted to pyruvate and CO2. ...
BD Pharmingen™ Purified Hamster Anti-Human Bcl-2
... Bcl-2 is considered to be novel among proto-oncogenes because it blocks apoptosis (programmed cell death) in many cell types. Apoptosis is an active form of cellular suicide that typically requires new RNA and protein synthesis and is associated with distinct morphological changes including cell shr ...
... Bcl-2 is considered to be novel among proto-oncogenes because it blocks apoptosis (programmed cell death) in many cell types. Apoptosis is an active form of cellular suicide that typically requires new RNA and protein synthesis and is associated with distinct morphological changes including cell shr ...
4.20.05 Histology and Digestion
... • Smooth muscle contracts more slowly than skeletal muscle but can remained contracted for a longer period. ...
... • Smooth muscle contracts more slowly than skeletal muscle but can remained contracted for a longer period. ...
Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... hormones) into bloodstream (e.g. pituitary gland, pancreas secretes insulin into the blood). Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. ...
... hormones) into bloodstream (e.g. pituitary gland, pancreas secretes insulin into the blood). Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. ...
Overview
... 1) Typical mucosa but deepest layer is lacking (i.e., neither a muscularis mucosae nor an elastic lamina is present). 2) Patency maintained by bones or cartilage. c. Olfactory region 1) Upside-down, U-shaped area in posterior, superior region of each nasal fossa, extending over superior conchae and ...
... 1) Typical mucosa but deepest layer is lacking (i.e., neither a muscularis mucosae nor an elastic lamina is present). 2) Patency maintained by bones or cartilage. c. Olfactory region 1) Upside-down, U-shaped area in posterior, superior region of each nasal fossa, extending over superior conchae and ...
Ch. 5 AP PP
... Ridge patterns are GENETICALLY DETERMINED, and do not change over a lifetime FINGERPRINTS! ...
... Ridge patterns are GENETICALLY DETERMINED, and do not change over a lifetime FINGERPRINTS! ...
Sexual Reproduction
... - few eggs produced - protected - could have either internal (mammals) or external (birds) development External Fertilization - fertilization occurs outside the body of the female ...
... - few eggs produced - protected - could have either internal (mammals) or external (birds) development External Fertilization - fertilization occurs outside the body of the female ...
OPEN - Cherry Hill Tuition
... conferences by all the examiners involved in the assessment. The conferences were held shortly after the papers were taken so that reference could be made to the full range of candidates' responses, with photocopied scripts forming the basis of discussion. The aim of the conferences was to ensure th ...
... conferences by all the examiners involved in the assessment. The conferences were held shortly after the papers were taken so that reference could be made to the full range of candidates' responses, with photocopied scripts forming the basis of discussion. The aim of the conferences was to ensure th ...
Multicellular Organisms National 5 Biology: Learning Outcomes
... Each topic of biology requires you to learn and understand a variety of subject specific vocabulary. The words you will be expected to define are in bold. To help you learn these words you could produce a topic glossary or flashcards. ...
... Each topic of biology requires you to learn and understand a variety of subject specific vocabulary. The words you will be expected to define are in bold. To help you learn these words you could produce a topic glossary or flashcards. ...
M.Sc. (Prev.) ZOOLOGY Exam. –2014 Distribution of Marks Paper
... Note : The question paper will contain three sections as under – Section-A : One compulsory question with 10 parts, having 2 parts from each unit, short answer in 20 words for each part. Total marks : 10 Section-B : 10 questions, 2 questions from each unit, 5 questions to be attempted, taking one fr ...
... Note : The question paper will contain three sections as under – Section-A : One compulsory question with 10 parts, having 2 parts from each unit, short answer in 20 words for each part. Total marks : 10 Section-B : 10 questions, 2 questions from each unit, 5 questions to be attempted, taking one fr ...
Chapter 8 NUTRITION and DIGESTION
... Main function is to allow chemical reactions to occur in body – Required in minute amounts Help release energy trapped in carbohydrates, lipids and proteins ...
... Main function is to allow chemical reactions to occur in body – Required in minute amounts Help release energy trapped in carbohydrates, lipids and proteins ...
The Integumentary System
... keratin, the tough fibrous protein that gives the epidermis its protective qualities Tightly connected by desmosomes Keratinocytes arise from constant cell mitosis at the deepest layer of the epidermis Keratinocyte cells manufacture keratin during their migration to the skin surface ...
... keratin, the tough fibrous protein that gives the epidermis its protective qualities Tightly connected by desmosomes Keratinocytes arise from constant cell mitosis at the deepest layer of the epidermis Keratinocyte cells manufacture keratin during their migration to the skin surface ...
Digestion
... • Wastes of the digestive tract, the feces, become more solid as they move through the colon • Feces is stored in the rectum until it exits via the anus ...
... • Wastes of the digestive tract, the feces, become more solid as they move through the colon • Feces is stored in the rectum until it exits via the anus ...
29.1 How Organ Systems Communicate - Morales Biology
... How do the organ systems communicate? By the Nervous System and Endocrine System ...
... How do the organ systems communicate? By the Nervous System and Endocrine System ...
Skeletal System
... keratin, the tough fibrous protein that gives the epidermis its protective qualities Tightly connected by desmosomes Keratinocytes arise from constant cell mitosis at the deepest layer of the epidermis Keratinocyte cells manufacture keratin during their migration to the skin surface ...
... keratin, the tough fibrous protein that gives the epidermis its protective qualities Tightly connected by desmosomes Keratinocytes arise from constant cell mitosis at the deepest layer of the epidermis Keratinocyte cells manufacture keratin during their migration to the skin surface ...
Bios 1130 Bacteria Lab 1 - Faculty Site Listing
... massive recyclers, returning nutrients back into the ecosystem with decomposition of almost any type of material, organic or inorganic. However bacteria can also be very harmful to organisms. Some common diseases caused by bacteria are the bubonic plague, Lyme disease, tooth decay, as well as certai ...
... massive recyclers, returning nutrients back into the ecosystem with decomposition of almost any type of material, organic or inorganic. However bacteria can also be very harmful to organisms. Some common diseases caused by bacteria are the bubonic plague, Lyme disease, tooth decay, as well as certai ...
Biology lecture # 1 Levels of Life (From Atom to Biosphere)
... Structure and Functions of Cell Membrane Structure of cell membrane is described by Fluid Mosaic Modal. It consists of lipid bilayer, proteins and carbohydrates. Lipid bilayer provides it with fluidity, flexibility and transport of lipid like substances. Proteins are integrated inside the membrane o ...
... Structure and Functions of Cell Membrane Structure of cell membrane is described by Fluid Mosaic Modal. It consists of lipid bilayer, proteins and carbohydrates. Lipid bilayer provides it with fluidity, flexibility and transport of lipid like substances. Proteins are integrated inside the membrane o ...
Living Organisms
... A cell is the smallest living part of an organism Some living organisms are made up of only one cell. That single cell is the organism's entire body. Bacteria are an example of a single cell organism. ...
... A cell is the smallest living part of an organism Some living organisms are made up of only one cell. That single cell is the organism's entire body. Bacteria are an example of a single cell organism. ...
METABOLISM
... within the cytoplasm. Support cytoplasm and transport materials within the cytoplasm. Move particles along surface of cell or move cell. Supports nucleus and controls passage of materials between nucleus and cytoplasm. Forms ribosomes ...
... within the cytoplasm. Support cytoplasm and transport materials within the cytoplasm. Move particles along surface of cell or move cell. Supports nucleus and controls passage of materials between nucleus and cytoplasm. Forms ribosomes ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.