levels of organization directed reading
... Organisms are made of multiple systems; each system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissues is made up of various kinds of cells. ...
... Organisms are made of multiple systems; each system is composed of different organs; each organ can be divided into different tissues; each tissues is made up of various kinds of cells. ...
REVIEW QUESTIONS- Structure and Function of
... 3. In a living organism, what is an organ? A. the shell or skin of an organism B. a group of similar cells that perform a common function C. functional unit, or building block, of all organisms; smallest unit that can carry on the activities of life D. a structure composed of a number of tissues tha ...
... 3. In a living organism, what is an organ? A. the shell or skin of an organism B. a group of similar cells that perform a common function C. functional unit, or building block, of all organisms; smallest unit that can carry on the activities of life D. a structure composed of a number of tissues tha ...
TAKS Review - Greenslime
... – series of predictable changes in a community that occur over time – Begins on new land such as a volcanic island – After major event: volcanic eruption, fire ...
... – series of predictable changes in a community that occur over time – Begins on new land such as a volcanic island – After major event: volcanic eruption, fire ...
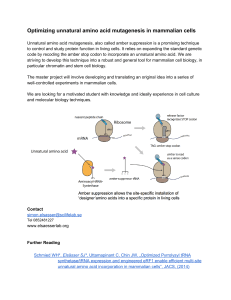
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Hello!!! - Elida Local Schools
... Organelles are specialized subunits in the cell, which each have their own specific function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of ...
... Organelles are specialized subunits in the cell, which each have their own specific function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of ...
Taxonomy #4
... •Open circulatory system •External fertilization •Females may store sperm •External development •metamorphosis ...
... •Open circulatory system •External fertilization •Females may store sperm •External development •metamorphosis ...
CELL SPECIALIZATION - Biology with Miss Amy
... All living organisms are able to – GRIMNER – grow, reproduce, irritability (sense), move, nutrition, ...
... All living organisms are able to – GRIMNER – grow, reproduce, irritability (sense), move, nutrition, ...
Specialized Cells Notes
... Specialized cells arise from the differentiation of unspecialized cells during embryological development. Unspecialized cells are called STEM cells that have the ability to reproduce and differentiate into a diverse range of specialized cells that make up the organism. This is determined by the DNA, ...
... Specialized cells arise from the differentiation of unspecialized cells during embryological development. Unspecialized cells are called STEM cells that have the ability to reproduce and differentiate into a diverse range of specialized cells that make up the organism. This is determined by the DNA, ...
Q11 Outline the formation, structure and function of the adult red
... decreases in size, gradually losing cytoplasmic organelles and increasing its haemoglobin content Reticulocytes then lose their ribosomes to become mature erythrocytes The differentiation from stem cell to erythro ...
... decreases in size, gradually losing cytoplasmic organelles and increasing its haemoglobin content Reticulocytes then lose their ribosomes to become mature erythrocytes The differentiation from stem cell to erythro ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... Ability of a solution to change the tone or shape of cells by altering their internal water volume. – Isotonic solute in = solute out; no NET movement of water. – Hypertonic number of solute particles is larger outside the cell than inside the cell; net movement of water is out; cause cell to ...
... Ability of a solution to change the tone or shape of cells by altering their internal water volume. – Isotonic solute in = solute out; no NET movement of water. – Hypertonic number of solute particles is larger outside the cell than inside the cell; net movement of water is out; cause cell to ...
Cell Specialization and Organization
... This type of cell is found all over the body, usually under the skin. We were born with the same number of this kind of cell as we have now. This cell's function is storage. When we exercise and eat healthy foods the storage gets depleted. When we don't exercise and we eat what we want these cells g ...
... This type of cell is found all over the body, usually under the skin. We were born with the same number of this kind of cell as we have now. This cell's function is storage. When we exercise and eat healthy foods the storage gets depleted. When we don't exercise and we eat what we want these cells g ...
Unit 2 Exam Cell Cell organelles Plant and Animal Tissue
... some signals are long lived, reach distant organs by way of the circulatory system. These signals are called…. ...
... some signals are long lived, reach distant organs by way of the circulatory system. These signals are called…. ...
KeystoneReview Guide Cells
... Oxygen regulation O2 levels must be regulated according to activity level. The more active the body/cells then more oxygen needed. During periods of slower activity level less oxygen is needed. Rate is controlled by the brain/brain stem to make sure carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are suitable for ...
... Oxygen regulation O2 levels must be regulated according to activity level. The more active the body/cells then more oxygen needed. During periods of slower activity level less oxygen is needed. Rate is controlled by the brain/brain stem to make sure carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are suitable for ...
Meiosis
... • G1 – cell growth • S – replication of chromosoms • G2 – growth and preparation for cell division ...
... • G1 – cell growth • S – replication of chromosoms • G2 – growth and preparation for cell division ...
Review Guide Cells
... Oxygen regulation O2 levels must be regulated according to activity level. The more active the body/cells then more oxygen needed. During periods of slower activity level less oxygen is needed. Rate is controlled by the brain/brain stem to make sure carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are suitable for ...
... Oxygen regulation O2 levels must be regulated according to activity level. The more active the body/cells then more oxygen needed. During periods of slower activity level less oxygen is needed. Rate is controlled by the brain/brain stem to make sure carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are suitable for ...
BioBoot Camp – Cells
... BIO.A.1.2.2 Describe and interpret relationships between structures and function at various levels of biological organization (ie organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms) Cell – smallest unit that can perform all life’s processes. o Organelles - inside of cell ...
... BIO.A.1.2.2 Describe and interpret relationships between structures and function at various levels of biological organization (ie organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms) Cell – smallest unit that can perform all life’s processes. o Organelles - inside of cell ...
Cells Study Guide
... o Most cells are small because their volume is limited by how large their surface area is. o Cells produce more cells by cell division. ...
... o Most cells are small because their volume is limited by how large their surface area is. o Cells produce more cells by cell division. ...
Key - Edquest
... Growth and development occur in all living organisms. When this organ in a human gets worn away it is replaced … liver lung skin kidney ...
... Growth and development occur in all living organisms. When this organ in a human gets worn away it is replaced … liver lung skin kidney ...
File
... Plant cell – eukaryotic cell that is different from animals in that it has a cell wall and chloroplasts; generally a large ...
... Plant cell – eukaryotic cell that is different from animals in that it has a cell wall and chloroplasts; generally a large ...
Illustrate and Label the movement parts of the three protists
... Illustrate and label the body shapes of the THREE bacteria Spirilla ...
... Illustrate and label the body shapes of the THREE bacteria Spirilla ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.