Review Guide for Body Systems and Cells Test
... Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal orga ...
... Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal orga ...
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
... CYTOPLASM: the watery liquid inside and outside the organelles, but outside the nucleus. NEUCLEOPLASM: the liquid inside the nucleus. CYTOSOL: another liquid that is thicker than water, and is NOT inside the organelles. It is only found outside of the organelles and nucleus. Cytosol contains t ...
... CYTOPLASM: the watery liquid inside and outside the organelles, but outside the nucleus. NEUCLEOPLASM: the liquid inside the nucleus. CYTOSOL: another liquid that is thicker than water, and is NOT inside the organelles. It is only found outside of the organelles and nucleus. Cytosol contains t ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
... Goblet (mucus) and cilia cells are found in the lining of the gut and the tubes into the lungs. They are specialised to release and move mucus. Helps food slide down easily in the gut and helps trap dirt and bacteria before they enter the lungs. The cilia cells help move the mucus especially in the ...
The Lymphatic System A. 1.
... D. The Lymphatic System and Homeostasis 1. The lymphatic system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating buildup around cells. ...
... D. The Lymphatic System and Homeostasis 1. The lymphatic system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating buildup around cells. ...
31.2 Immune System
... • Three types of proteins fight off invading pathogens. – Complement proteins weaken pathogen membranes. – Antibodies: Protein that causes pathogens to clump or become ineffective. – Interferon: Proteins that stop viruses from reproducing. antibody ...
... • Three types of proteins fight off invading pathogens. – Complement proteins weaken pathogen membranes. – Antibodies: Protein that causes pathogens to clump or become ineffective. – Interferon: Proteins that stop viruses from reproducing. antibody ...
HISTOLOGY
... Tissues that cover and line all surfaces and cavities of the body. • These cells are close together with very little intercellular material. • Can be arranged in one layer (simple) or more than one layer (stratified) • Functions include: protection, absorption, and secretion • Some possess specializ ...
... Tissues that cover and line all surfaces and cavities of the body. • These cells are close together with very little intercellular material. • Can be arranged in one layer (simple) or more than one layer (stratified) • Functions include: protection, absorption, and secretion • Some possess specializ ...
s1-biology-unit-1-need-to-know
... The human body responds to cold by shivering, hairs on body standing on end to trap air. We can use technology to measure the health of our body – blood pressure is measured by a sphygmomanometer, pulse rate by a pulsometer, temperature by a clinical thermometer. Animal cells contain a nucleus, cell ...
... The human body responds to cold by shivering, hairs on body standing on end to trap air. We can use technology to measure the health of our body – blood pressure is measured by a sphygmomanometer, pulse rate by a pulsometer, temperature by a clinical thermometer. Animal cells contain a nucleus, cell ...
Chapter 1 - Cell Biology Review Extended Response Answers
... b. plasma membrane – a continuous single line; c. cytoplasm/cytosol; d. nucleoid/(naked) DNA – shown as a tangle of thread or irregular shape without a nuclear membrane; e. (70S) ribosomes – drawn as a small circle or dark dot; f. pili – hair like structures / flagellum – shown to be longer than any ...
... b. plasma membrane – a continuous single line; c. cytoplasm/cytosol; d. nucleoid/(naked) DNA – shown as a tangle of thread or irregular shape without a nuclear membrane; e. (70S) ribosomes – drawn as a small circle or dark dot; f. pili – hair like structures / flagellum – shown to be longer than any ...
What is the function of the Muscular System? What is the function of
... Lisa was not blindfolded and knew which plane she was throwing. Since she favors planes with winglets maybe she threw #1 harder without even realizing it. ...
... Lisa was not blindfolded and knew which plane she was throwing. Since she favors planes with winglets maybe she threw #1 harder without even realizing it. ...
Body Systems REVIEW
... Body Systems Objectives 10C - Analyze the levels of organization in biological systems relate the levels to each other & to the whole system 11A - Describe the role of internal feedback mechanisms in the maintenance of homeostasis 9A - Compare the structure & functions of carbohydrates, lipids, prot ...
... Body Systems Objectives 10C - Analyze the levels of organization in biological systems relate the levels to each other & to the whole system 11A - Describe the role of internal feedback mechanisms in the maintenance of homeostasis 9A - Compare the structure & functions of carbohydrates, lipids, prot ...
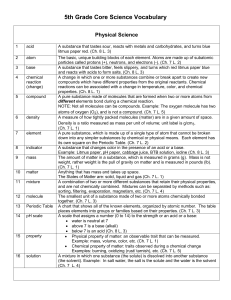
5th Grade - IUSD.org
... compounds which have different properties from the original reactants. Chemical reactions can be associated with a change in temperature, color, and chemical properties. (Ch. 8 L. 1) A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemi ...
... compounds which have different properties from the original reactants. Chemical reactions can be associated with a change in temperature, color, and chemical properties. (Ch. 8 L. 1) A pure substance made of molecules that are formed when two or more atoms from different elements bond during a chemi ...
File
... gradient- The rate of change in growth, metabolism, or physiological activity of a cell or organism. equilibrium- The condition in which all acting influences are balanced or cancelled by equal opposing forces, resulting in a stable system. Hypertonic- Having a greater degree of tone or tension. Hav ...
... gradient- The rate of change in growth, metabolism, or physiological activity of a cell or organism. equilibrium- The condition in which all acting influences are balanced or cancelled by equal opposing forces, resulting in a stable system. Hypertonic- Having a greater degree of tone or tension. Hav ...
CHAPTER 2: CELL FUNCTION 2.1.
... and taken up by roots that are not photosynthetic, but the principal energy conversion happens through photosynthesis, which is unique only to cells containing chloroplasts, which animals don’t have. Thinking Critically (p. 68) 23. Explain why chemical reactions are essential to living creatures. Mo ...
... and taken up by roots that are not photosynthetic, but the principal energy conversion happens through photosynthesis, which is unique only to cells containing chloroplasts, which animals don’t have. Thinking Critically (p. 68) 23. Explain why chemical reactions are essential to living creatures. Mo ...
Science 14 Unit C Review
... 4. Identify and compare, in general terms, the life functions common to living systems, from cells to organ systems • describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of biological energy storage; i.e., capture of energy from the Sun in glucose during photosynthesis ...
... 4. Identify and compare, in general terms, the life functions common to living systems, from cells to organ systems • describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of biological energy storage; i.e., capture of energy from the Sun in glucose during photosynthesis ...
syllabus - Hudson Area Schools
... arguments play a role in personal choice and public policy decisions. New technology and scientific discoveries ...
... arguments play a role in personal choice and public policy decisions. New technology and scientific discoveries ...
Cells, tisand mito, practice Test answers - Coristines
... algae. Then one day in May following a rainstorm algae was observed in the same pond. People concluded that the rain brought algae. Use the cell theory to explain what really happened. [3 marks] Thus this had nothing to do with rain creating living organisms. The cell theory states that all living t ...
... algae. Then one day in May following a rainstorm algae was observed in the same pond. People concluded that the rain brought algae. Use the cell theory to explain what really happened. [3 marks] Thus this had nothing to do with rain creating living organisms. The cell theory states that all living t ...
Biology 1 End-of-Course Assessment Practice Test For Multiple
... Which of the following best describes how the process of crossing over during meiosis leads to an increase in genetic diversity? A. During prophase I, DNA replication takes place, and homologous chromosome ...
... Which of the following best describes how the process of crossing over during meiosis leads to an increase in genetic diversity? A. During prophase I, DNA replication takes place, and homologous chromosome ...
Biology 1st Semester Study Guide
... peroxisomes g. Chloroplastk. cell wall h. Rough ER l. lysosomes 26. List, in order, the correct order of organization of structures in living things. 27. Determine the power of magnification of an object viewed at high power (40x). 28. Describe the functions of the microscope. a. diaphragm b. eye pi ...
... peroxisomes g. Chloroplastk. cell wall h. Rough ER l. lysosomes 26. List, in order, the correct order of organization of structures in living things. 27. Determine the power of magnification of an object viewed at high power (40x). 28. Describe the functions of the microscope. a. diaphragm b. eye pi ...
scientific method
... peroxisomes g. Chloroplastk. cell wall h. Rough ER l. lysosomes 26. List, in order, the correct order of organization of structures in living things. 27. Determine the power of magnification of an object viewed at high power (40x). 28. Describe the functions of the microscope. a. diaphragm b. eye pi ...
... peroxisomes g. Chloroplastk. cell wall h. Rough ER l. lysosomes 26. List, in order, the correct order of organization of structures in living things. 27. Determine the power of magnification of an object viewed at high power (40x). 28. Describe the functions of the microscope. a. diaphragm b. eye pi ...
AB Biology Summer Assignment (Word)
... 41) What are the functions of the nervous system? How does it control reflexes? ...
... 41) What are the functions of the nervous system? How does it control reflexes? ...
chapter28_Sections 1
... • Of a multicelled organism, body fluid outside of cells • Serves as the body’s internal environment • Provides cells with nutrients and removes wastes ...
... • Of a multicelled organism, body fluid outside of cells • Serves as the body’s internal environment • Provides cells with nutrients and removes wastes ...
Six Grade Science Vocabulary
... concentration of white blood cells found in lymph nodes. A network of organs and tissues that collect the fluid that leaks from blood and returns it to blood vessels; includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph; the place where certain white blood cells mature. A cell organelle that contains dige ...
... concentration of white blood cells found in lymph nodes. A network of organs and tissues that collect the fluid that leaks from blood and returns it to blood vessels; includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph; the place where certain white blood cells mature. A cell organelle that contains dige ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.