Anatomy – structure
... 1. cytology – cellular 2. histology – study of tissue C. Levels of biological organization 1. chemical level 2. cellular level 3. tissue level – mass of similar functioning cells 4.organ – two or more tissues 5. system – several organs 6.organismic – all systems D.life processes 1. - metabolism – su ...
... 1. cytology – cellular 2. histology – study of tissue C. Levels of biological organization 1. chemical level 2. cellular level 3. tissue level – mass of similar functioning cells 4.organ – two or more tissues 5. system – several organs 6.organismic – all systems D.life processes 1. - metabolism – su ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... 3. Compare the flow of chemical nutrients and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. 4. Explain how cells function as the structural and functional units of life. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Define the principle of emergent properties and describe an example of it. ...
... 3. Compare the flow of chemical nutrients and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. 4. Explain how cells function as the structural and functional units of life. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Define the principle of emergent properties and describe an example of it. ...
Cellular Component of Blood
... Oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. ...
... Oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. ...
Notes Pages
... There are trillions (1,000,000,000,000’s) of cells in the human body. All cells were formed in your body from just one cell, the fertilized egg. Cells take on different jobs, (specialize) as they are formed in the egg. Cells that all work together to form a specific function form tissues. There are ...
... There are trillions (1,000,000,000,000’s) of cells in the human body. All cells were formed in your body from just one cell, the fertilized egg. Cells take on different jobs, (specialize) as they are formed in the egg. Cells that all work together to form a specific function form tissues. There are ...
Levels of Structural Organization Levels of Structural
... • Cellular – cells are made of molecules • Tissue – consists of similar types of cells • Organ – made up of different types of tissues • Organ system – consists of different organs that work ...
... • Cellular – cells are made of molecules • Tissue – consists of similar types of cells • Organ – made up of different types of tissues • Organ system – consists of different organs that work ...
Cell, Mitosis and Cell Membrane Transport
... all the information needed to form and run the cell. The segments of DNA are called Genes. Nuclear Envelope: is formed of 2 membranes with a gap between them. It has a large number of Nuclear Pores usually bound by a nuclear complex. The pores are large enough to allow RNA and proteins to pass thro ...
... all the information needed to form and run the cell. The segments of DNA are called Genes. Nuclear Envelope: is formed of 2 membranes with a gap between them. It has a large number of Nuclear Pores usually bound by a nuclear complex. The pores are large enough to allow RNA and proteins to pass thro ...
Stem Cells and cell division
... which protein synthesis is increased. • If cell receives the correct chemical signal, it enters the S phase, which DNA replication occurs. • When DNA replication is complete cell enters G2 phase where it get ready for either mitosis or meiosis. ...
... which protein synthesis is increased. • If cell receives the correct chemical signal, it enters the S phase, which DNA replication occurs. • When DNA replication is complete cell enters G2 phase where it get ready for either mitosis or meiosis. ...
7 grade life science review packet
... 4. Example: A student set up the experiment shown to learn about plant growth. The student added a different amount of water to 4 identical containers, each containing 4 seeds in 100 cubic centimeters of soil. All of the containers were placed in the same sunny location. The height of the plants wer ...
... 4. Example: A student set up the experiment shown to learn about plant growth. The student added a different amount of water to 4 identical containers, each containing 4 seeds in 100 cubic centimeters of soil. All of the containers were placed in the same sunny location. The height of the plants wer ...
4- Blood
... facilitates gas exchange. The normal concentration of erythrocytes in blood is approximately 3.9–5.5 million per microliter in women and 4.1– 6 million per microliter in men. Erythrocyte cytoplasm is densely filled with hemoglobin, the tetrameric O2-carrying protein that accounts for the cells' unif ...
... facilitates gas exchange. The normal concentration of erythrocytes in blood is approximately 3.9–5.5 million per microliter in women and 4.1– 6 million per microliter in men. Erythrocyte cytoplasm is densely filled with hemoglobin, the tetrameric O2-carrying protein that accounts for the cells' unif ...
8.3 - Patterns in Nature
... Water: The most abundant inorganic substance in the body. 70% of the body’s molecules are water. Most reactions in cells require water. Nutrients and wastes are carried around in water. It has many other uses in the body. ...
... Water: The most abundant inorganic substance in the body. 70% of the body’s molecules are water. Most reactions in cells require water. Nutrients and wastes are carried around in water. It has many other uses in the body. ...
Multicellular Organisms National 5 Biology Overview Multicellular
... Receptors detect sensory input/stimuli. Electrical impulses carry messages along neurons. A synapse occurs between neurons. Chemicals transfer these messages across synapses. ii. Structure and function of reflex arc. b. Hormonal control i. Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood stream. Hor ...
... Receptors detect sensory input/stimuli. Electrical impulses carry messages along neurons. A synapse occurs between neurons. Chemicals transfer these messages across synapses. ii. Structure and function of reflex arc. b. Hormonal control i. Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood stream. Hor ...
What is osmosis?
... _____ Cellular respiration releases Carbon dioxide. _____ The red blood cells carry the Carbon dioxide to your lungs. _____ The mitochondria in your cells use the oxygen to break down glucose and release energy. _____ Your red blood cells carry oxygen to the rest of your cells. ...
... _____ Cellular respiration releases Carbon dioxide. _____ The red blood cells carry the Carbon dioxide to your lungs. _____ The mitochondria in your cells use the oxygen to break down glucose and release energy. _____ Your red blood cells carry oxygen to the rest of your cells. ...
The Cell - ESC-2
... your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body ...
... your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body ...
Biology Midterm Study Guide Ch 1-9 spring 11
... 76. What percentage of light energy absorbed by chlorophyll does the orange spectrum ...
... 76. What percentage of light energy absorbed by chlorophyll does the orange spectrum ...
Levels of Organization Notes (pg 418-427)
... Complex jobs in organisms require more than one type of tissue. Organs are groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. Your stomach is an organ that breaks down food. It is made of all four types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, nervous, and connective. Each type of tissu ...
... Complex jobs in organisms require more than one type of tissue. Organs are groups of different tissues working together to perform a particular job. Your stomach is an organ that breaks down food. It is made of all four types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, nervous, and connective. Each type of tissu ...
Exam 3
... A. Adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in any environment, such that organisms can easily move into different environments. B. Adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in a particular environment. C. Adaptations allow organisms to tolerate dramatic changes in their environment ( ...
... A. Adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in any environment, such that organisms can easily move into different environments. B. Adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in a particular environment. C. Adaptations allow organisms to tolerate dramatic changes in their environment ( ...
Digestive System Digestion: Functions of Digestive Organs: 1. Mouth
... Fill in the following to trace the path of sperm through the body: Sperm are produced in the _______________ and mature in the ______________________. From there, they travel in a long tube called the _________ _______________ to the __________________. When they reach the urethra, they mix with ___ ...
... Fill in the following to trace the path of sperm through the body: Sperm are produced in the _______________ and mature in the ______________________. From there, they travel in a long tube called the _________ _______________ to the __________________. When they reach the urethra, they mix with ___ ...
Development and Apoptosis
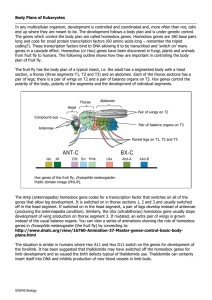
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
Name
... __________________ 8. The integumentary system is mostly made up of your skin. This forms a flexible barrier between the inside and outside of your body. What organelle does this same job for the cell? __________________ 9. Glands within the endocrine system control body processes by making and rele ...
... __________________ 8. The integumentary system is mostly made up of your skin. This forms a flexible barrier between the inside and outside of your body. What organelle does this same job for the cell? __________________ 9. Glands within the endocrine system control body processes by making and rele ...
Cell organization and Diffusion
... Identify the structures listed. Choose the correct letter A, B, C, D or E for each structure. i ...
... Identify the structures listed. Choose the correct letter A, B, C, D or E for each structure. i ...
Physiology 2008
... common function and possess similar extra-cellular substances located between the cells the result is a tissue. The microscopic study of tissue structure is called histology, which you have been and will continue to cover in lab. Our objective for this unit - is to discuss how the structure of speci ...
... common function and possess similar extra-cellular substances located between the cells the result is a tissue. The microscopic study of tissue structure is called histology, which you have been and will continue to cover in lab. Our objective for this unit - is to discuss how the structure of speci ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.