Human Body Systems
... Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
Glossary of Terms and Acronyms
... as the production of speech. Risk assessment: The analytical process by which the nature and magnitude of risk are identified. Four steps make up a complete risk assessment: hazard identification, dose-response assessment, exposure assessment, and risk characterization. Secretory cells: Cells that s ...
... as the production of speech. Risk assessment: The analytical process by which the nature and magnitude of risk are identified. Four steps make up a complete risk assessment: hazard identification, dose-response assessment, exposure assessment, and risk characterization. Secretory cells: Cells that s ...
Biology EOC review
... blue-green bacteria - Eukaryote – contain a clearly defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles; found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists ...
... blue-green bacteria - Eukaryote – contain a clearly defined nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles; found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists ...
1 Notes for Friday September 13, 2002 Outline • Body cavities
... => protect from UV & provide skin color ...
... => protect from UV & provide skin color ...
IBO 1991 Theory_CCL - International Biology Olympiad
... a) transference some food elements from an organism to atmosphere; b) joining the most food elements to food webs through animals; c) increasing of population density in that regions where food elements storage are more than in another; d) number limitation of ecosystem organisms caused by shortage ...
... a) transference some food elements from an organism to atmosphere; b) joining the most food elements to food webs through animals; c) increasing of population density in that regions where food elements storage are more than in another; d) number limitation of ecosystem organisms caused by shortage ...
Midterm Exam
... (5 points) Describe the FIRST stage of chemical evolution. What were some of the small molecules that came together to form monomers and what energy sources were available? Where did this occur? What gas was missing? Give the names of several monomers that resulted. How can this process be demonstr ...
... (5 points) Describe the FIRST stage of chemical evolution. What were some of the small molecules that came together to form monomers and what energy sources were available? Where did this occur? What gas was missing? Give the names of several monomers that resulted. How can this process be demonstr ...
Kingdom Eubacteria
... Can live in boiling water or freezing cold environments or even buried 5m deep ...
... Can live in boiling water or freezing cold environments or even buried 5m deep ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... Cells May be Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Prokaryotes include bacteria & lack a nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membranebound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) copyright cmassengale ...
... Cells May be Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Prokaryotes include bacteria & lack a nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membranebound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) copyright cmassengale ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... – Nucleus with DNA – Nucleolus – Ribosomes Have a greater division of labor. Organelles are specialized. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells both contain ribosomes, cytoplasm, a plasma membrane, and genetic material ...
... – Nucleus with DNA – Nucleolus – Ribosomes Have a greater division of labor. Organelles are specialized. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells both contain ribosomes, cytoplasm, a plasma membrane, and genetic material ...
File
... 9. The stomach uses ______________________ to break up food. 10. Your stomach’s ______________________ tells your body you are full after eating. 11. The inside of your stomach is covered with _________________________. 12. Organs that work together are part of a(n) __________________________. WORKI ...
... 9. The stomach uses ______________________ to break up food. 10. Your stomach’s ______________________ tells your body you are full after eating. 11. The inside of your stomach is covered with _________________________. 12. Organs that work together are part of a(n) __________________________. WORKI ...
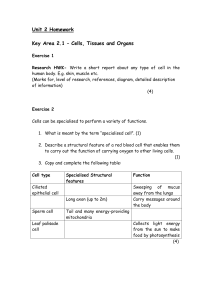
Unit 2 Homework
... You teacher will have given you a title that you will be debating and also whether you are for or against the idea. Prepare your arguments, either for or against, using information you have researched and been given in class. You should look for evidence like statistics or quotes from professionals ...
... You teacher will have given you a title that you will be debating and also whether you are for or against the idea. Prepare your arguments, either for or against, using information you have researched and been given in class. You should look for evidence like statistics or quotes from professionals ...
sample pages
... Seed coat protects the new plant from wet or from drying out before it is ready to grow. The food store feeds the seedling until it is big enough to make its own food. Beans, peas, lentils, rice, wheat (as flour, bread, etc), corn, almonds, etc. Because they both contain a concentrated food store. ...
... Seed coat protects the new plant from wet or from drying out before it is ready to grow. The food store feeds the seedling until it is big enough to make its own food. Beans, peas, lentils, rice, wheat (as flour, bread, etc), corn, almonds, etc. Because they both contain a concentrated food store. ...
function - mselder
... pairs of chromosomes with identical chromatids Differences: During meiosis cell divides twice instead of only once, in meiosis the four daughter cells end up with only half the genetic material while in mitosis the two daughter cells have the same genetic material as parent cell ...
... pairs of chromosomes with identical chromatids Differences: During meiosis cell divides twice instead of only once, in meiosis the four daughter cells end up with only half the genetic material while in mitosis the two daughter cells have the same genetic material as parent cell ...
Document
... a. sodium and potassium ions is higher on the inside of its membrane b. sodium and potassium ions is equal on both sides of its membrane c. sodium ions are found in higher concentration on the inside than on the outside of its membrane d. sodium ions are found in higher concentration on the outside ...
... a. sodium and potassium ions is higher on the inside of its membrane b. sodium and potassium ions is equal on both sides of its membrane c. sodium ions are found in higher concentration on the inside than on the outside of its membrane d. sodium ions are found in higher concentration on the outside ...
Plants and Pollinators
... • Our immune system mobilizes with increased activation (immune system) ...
... • Our immune system mobilizes with increased activation (immune system) ...
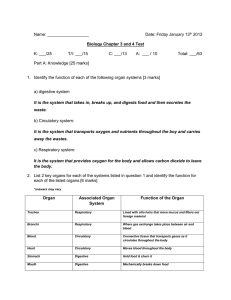
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
Bacterial Transformation
... human gut. It has been extensively studied in the laboratory and is an important research organism for molecular biology. E. coli reproduce very rapidly; a single microscopic cell can divide to form a visible colony with millions of cells overnight. Like all bacteria, E. coli has no nuclear envelope ...
... human gut. It has been extensively studied in the laboratory and is an important research organism for molecular biology. E. coli reproduce very rapidly; a single microscopic cell can divide to form a visible colony with millions of cells overnight. Like all bacteria, E. coli has no nuclear envelope ...
Immune System New
... caused disease. Pasteur’s investigation led to the theory that many diseases are caused by biological agents, like bacteria. This is called the Germ Theory of Disease ...
... caused disease. Pasteur’s investigation led to the theory that many diseases are caused by biological agents, like bacteria. This is called the Germ Theory of Disease ...
BiologyHonors-CourseExpectation
... 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 ...
... 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 ...
doc - AState.edu
... 1. Pathological anatomy-changes caused by disease 2. Molecular biology-studies the link between structure and function E. Subdivisions of physiology 1. Renal physiology-urine production and kidney function 2. Neurophysiology-study of nervous system 3. Cardiac physiology-study of the workings of the ...
... 1. Pathological anatomy-changes caused by disease 2. Molecular biology-studies the link between structure and function E. Subdivisions of physiology 1. Renal physiology-urine production and kidney function 2. Neurophysiology-study of nervous system 3. Cardiac physiology-study of the workings of the ...
Cells
... o Enzymes: Special types of proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body but are not changed by the reactions Nucleic acids: DNA genetic information, RNA – protein synthesis, ATP – energy for cells ...
... o Enzymes: Special types of proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body but are not changed by the reactions Nucleic acids: DNA genetic information, RNA – protein synthesis, ATP – energy for cells ...
The Circulatory System
... When your heart beats it pushes blood out of the right ventricle to the lungs. The bloods cells that are carried to the lungs release carbon dioxide and gain oxygen so that when you breath in you inhale oxygen and when you exhale your lungs release carbon dioxide. Then the red blood cells take oxyge ...
... When your heart beats it pushes blood out of the right ventricle to the lungs. The bloods cells that are carried to the lungs release carbon dioxide and gain oxygen so that when you breath in you inhale oxygen and when you exhale your lungs release carbon dioxide. Then the red blood cells take oxyge ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems - E
... Like in animal cells, plant cells are also specifically designed to function along with their rolls and produce life. Millions of cells work together to produce food for these green plants by taking light and turning it into energy. A pollen cell, for example is like a male sperm cell compared to an ...
... Like in animal cells, plant cells are also specifically designed to function along with their rolls and produce life. Millions of cells work together to produce food for these green plants by taking light and turning it into energy. A pollen cell, for example is like a male sperm cell compared to an ...
The Tissue Level of Organization
... Collagen fibers packed tightly, parallel to one another Tendons – attach muscle to bone Ligaments – attach bone to bone; often contain elastic fibers ...
... Collagen fibers packed tightly, parallel to one another Tendons – attach muscle to bone Ligaments – attach bone to bone; often contain elastic fibers ...
The Tissue Level of Organization
... Collagen fibers packed tightly, parallel to one another Tendons – attach muscle to bone Ligaments – attach bone to bone; often contain elastic fibers ...
... Collagen fibers packed tightly, parallel to one another Tendons – attach muscle to bone Ligaments – attach bone to bone; often contain elastic fibers ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.