23.3 What Are the Major Animal Phyla?
... 23.1 What Are the Key Features of Animals? Animals possess all of the following characteristics – Multicellularity – Their cells lack a cell wall – They obtain energy by consuming other organisms – Most reproduce sexually – They are motile at some point in the life cycle – They are able to respon ...
... 23.1 What Are the Key Features of Animals? Animals possess all of the following characteristics – Multicellularity – Their cells lack a cell wall – They obtain energy by consuming other organisms – Most reproduce sexually – They are motile at some point in the life cycle – They are able to respon ...
7 Notes (Kingdom Fungi).
... Fungi-Plant Mutualism: in addition to the relationships mycorrhizae form with plant roots, some fungi also form endophytes, or fungi (usually ascomycetes) living inside the leaf cells of plants. Endophytes sometimes produce toxins which discourage herbivores and insects from eating the leaves. Fungi ...
... Fungi-Plant Mutualism: in addition to the relationships mycorrhizae form with plant roots, some fungi also form endophytes, or fungi (usually ascomycetes) living inside the leaf cells of plants. Endophytes sometimes produce toxins which discourage herbivores and insects from eating the leaves. Fungi ...
fungi - Mr. Wells` wikispace
... • Examples are athlete’s foot & ringworm • Example that is helpful is Penicillium because it make the antibiotic • Spores called conidia come from hyphae called ...
... • Examples are athlete’s foot & ringworm • Example that is helpful is Penicillium because it make the antibiotic • Spores called conidia come from hyphae called ...
ageing Powerpoint
... disease caused by a highly penetrant dominant mutation. • 1941 Haldane: why has natural selection not acted to remove the Huntington's mutation from populations? • Average age of onset of Huntington's 35.5 years. • For much of the evolutionary history of mankind, most people did not live to be that ...
... disease caused by a highly penetrant dominant mutation. • 1941 Haldane: why has natural selection not acted to remove the Huntington's mutation from populations? • Average age of onset of Huntington's 35.5 years. • For much of the evolutionary history of mankind, most people did not live to be that ...
SYLLABUS 0610
... The wording of some learning outcomes has been changed for clarification. Some material has been reordered, removed, moved between sections, or reclassified as either Core or Supplement material. New topics 4 Biological molecules* 10 Diseases and immunity 14.2 Sense organs* 17.2 Chromosomes, genes a ...
... The wording of some learning outcomes has been changed for clarification. Some material has been reordered, removed, moved between sections, or reclassified as either Core or Supplement material. New topics 4 Biological molecules* 10 Diseases and immunity 14.2 Sense organs* 17.2 Chromosomes, genes a ...
IGCSE Biology - Cambridge International Examinations
... The wording of some learning outcomes has been changed for clarification. Some material has been reordered, removed, moved between sections, or reclassified as either Core or Supplement material. New topics 4 Biological molecules* 10 Diseases and immunity 14.2 Sense organs* 17.2 Chromosomes, genes a ...
... The wording of some learning outcomes has been changed for clarification. Some material has been reordered, removed, moved between sections, or reclassified as either Core or Supplement material. New topics 4 Biological molecules* 10 Diseases and immunity 14.2 Sense organs* 17.2 Chromosomes, genes a ...
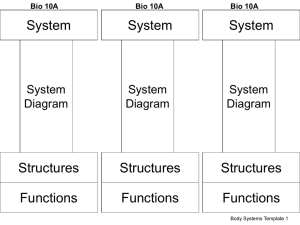
Body Systems Manipulative
... chemical breakdown of food, absorption of building blocks of food, and formation of solid wastes ...
... chemical breakdown of food, absorption of building blocks of food, and formation of solid wastes ...
File - e
... Q.6. Name any two pigments fiund in red algae. Q.7. From which algae agar is obtained? Q.8. Where is Funaria found? Q.9. Name the pigments found in cyanobacteria. Q.10. Name the male and female sex-organs in Funaria. Q.11. What is the mode of nutrition in sporophyte of Funaria? Q.12. State the func ...
... Q.6. Name any two pigments fiund in red algae. Q.7. From which algae agar is obtained? Q.8. Where is Funaria found? Q.9. Name the pigments found in cyanobacteria. Q.10. Name the male and female sex-organs in Funaria. Q.11. What is the mode of nutrition in sporophyte of Funaria? Q.12. State the func ...
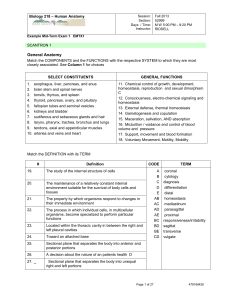
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz # 1
... 4. The ability of the body to maintain a relatively stable internal environment is referred to as: a. equilibrium c. metabolism b. homeostasis d. negative feedback 5. The anatomical term meaning away from the midline is a. distal c. medial b. inferior d. lateral 6. Select the correct answer about th ...
... 4. The ability of the body to maintain a relatively stable internal environment is referred to as: a. equilibrium c. metabolism b. homeostasis d. negative feedback 5. The anatomical term meaning away from the midline is a. distal c. medial b. inferior d. lateral 6. Select the correct answer about th ...
www.studyguide.pk
... 1. locate, select, organise and present information from a variety of sources; 2. translate information from one form to another; 3. manipulate numerical and other data; 4. use information to identify patterns, report trends, draw inferences and report conclusions; 5. present reasoned explanations f ...
... 1. locate, select, organise and present information from a variety of sources; 2. translate information from one form to another; 3. manipulate numerical and other data; 4. use information to identify patterns, report trends, draw inferences and report conclusions; 5. present reasoned explanations f ...
Respiratory Systems
... Humans breathe using a tidal mechanism Volume of thoracic cavity and lungs is increased by muscle contractions that lower the diaphragm and raise the ribs - Create negative pressure in the thoracic cavity and lungs, and then air flows into the lungs during ...
... Humans breathe using a tidal mechanism Volume of thoracic cavity and lungs is increased by muscle contractions that lower the diaphragm and raise the ribs - Create negative pressure in the thoracic cavity and lungs, and then air flows into the lungs during ...
Land Environments
... Humans breathe using a tidal mechanism Volume of thoracic cavity and lungs is increased by muscle contractions that lower the diaphragm and raise the ribs - Create negative pressure in the thoracic cavity and lungs, and then air flows into the lungs during ...
... Humans breathe using a tidal mechanism Volume of thoracic cavity and lungs is increased by muscle contractions that lower the diaphragm and raise the ribs - Create negative pressure in the thoracic cavity and lungs, and then air flows into the lungs during ...
Chapter 1 - Napa Valley College
... 17. Support, movement and blood formation 18. Voluntary Movement, Motility, Mobility ...
... 17. Support, movement and blood formation 18. Voluntary Movement, Motility, Mobility ...
Parasitology Glossary
... larval) required for completion of one life cycle (or generation), as in digenetic trematodes. In parasitology, application of this term is virtually limited to those trematodes requiring one or more intermediate hosts. ...
... larval) required for completion of one life cycle (or generation), as in digenetic trematodes. In parasitology, application of this term is virtually limited to those trematodes requiring one or more intermediate hosts. ...
Biology Class IX for SA-I 2016-17
... A cell is capable of independent existence and can carry out all the functions which are necessary for a living being. A cell carries out nutrition, respiration, excretion, transportation and reproduction; the way an individual organism does. Unicellular organisms are capable of independent existenc ...
... A cell is capable of independent existence and can carry out all the functions which are necessary for a living being. A cell carries out nutrition, respiration, excretion, transportation and reproduction; the way an individual organism does. Unicellular organisms are capable of independent existenc ...
biology - Textbooks Online
... There are 350,000 species of plants including algae, fungi, mosses and higher forms of plants. Thus the existence of different forms of a species or genus and diverse adaptations for, varied surroundings are referred to as “biodiversity”. The survival of such a vast range of living beings could be e ...
... There are 350,000 species of plants including algae, fungi, mosses and higher forms of plants. Thus the existence of different forms of a species or genus and diverse adaptations for, varied surroundings are referred to as “biodiversity”. The survival of such a vast range of living beings could be e ...
7th Grade Science - Pflugerville ISD
... Section 1: Characteristics of Living Things Section 2:The Simple Bare Necessities of Life Chapter 8: The Cell In Action Section 1: Exchange with the Environment Section 2:Energy for the Cell ...
... Section 1: Characteristics of Living Things Section 2:The Simple Bare Necessities of Life Chapter 8: The Cell In Action Section 1: Exchange with the Environment Section 2:Energy for the Cell ...
Microbiology DeMYSTiFieD
... community. During this period scientists identified microbes that caused diseases and learned how to cure those diseases and then prevent them from occurring through the use of immunization. Scientists were able to achieve these remarkable discoveries by using culturing techniques to grow colonies o ...
... community. During this period scientists identified microbes that caused diseases and learned how to cure those diseases and then prevent them from occurring through the use of immunization. Scientists were able to achieve these remarkable discoveries by using culturing techniques to grow colonies o ...
FUNGI
... – Nonmotile organism than obtain food by decomposing organic matter – Once considered plants, but contain no chlorophyll and are not photosynthetic – Also unlike animals, therefore placed in own kingdom ...
... – Nonmotile organism than obtain food by decomposing organic matter – Once considered plants, but contain no chlorophyll and are not photosynthetic – Also unlike animals, therefore placed in own kingdom ...
fungi - Stjosephcs.org
... – Nonmotile organism than obtain food by decomposing organic matter – Once considered plants, but contain no chlorophyll and are not photosynthetic – Also unlike animals, therefore placed in own kingdom ...
... – Nonmotile organism than obtain food by decomposing organic matter – Once considered plants, but contain no chlorophyll and are not photosynthetic – Also unlike animals, therefore placed in own kingdom ...
california content standards: biology/life sciences
... e. Since the majority of Biology students are enrolled in the 10th grade, they will also be taking the 10th Grade Life Science CST. Therefore, the Blueprint for the 10th Grade Life Science CST has been included in this document. f. The Pacing Guide is separated into four Instructional Segments. An o ...
... e. Since the majority of Biology students are enrolled in the 10th grade, they will also be taking the 10th Grade Life Science CST. Therefore, the Blueprint for the 10th Grade Life Science CST has been included in this document. f. The Pacing Guide is separated into four Instructional Segments. An o ...
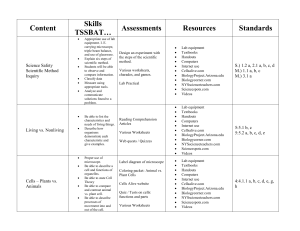
Content - erie1bocesalternativeeducation
... fertilization takes place. Describe stages of human development. Be able to describe heredity. Be able to describe cell division. IE Mitosis and Meiosis. Explain the structure of DNA. Define key terms associated with Genetics. Be able to construct a punnett square and pedigrees. Describe sex-linked ...
... fertilization takes place. Describe stages of human development. Be able to describe heredity. Be able to describe cell division. IE Mitosis and Meiosis. Explain the structure of DNA. Define key terms associated with Genetics. Be able to construct a punnett square and pedigrees. Describe sex-linked ...
2019 Syllabus - Cambridge International Examinations
... below, should be entered for Paper 1, Paper 3 and either Paper 5 or Paper 6. These candidates will be eligible for grades 1 to 5. Candidates who have studied the Extended subject content (Core and Supplement), and who are expected to achieve a grade 4 or above, should be entered for Paper 2, Paper 4 ...
... below, should be entered for Paper 1, Paper 3 and either Paper 5 or Paper 6. These candidates will be eligible for grades 1 to 5. Candidates who have studied the Extended subject content (Core and Supplement), and who are expected to achieve a grade 4 or above, should be entered for Paper 2, Paper 4 ...
Unit 1 Exam
... 34. The number of times that an objective lens can magnify an object is referred to as the____________________. 35. The movement of ink within a glass of water when the water has been left undisturbed (not shaken or stirred) could be the result ____________________. 36. Because the cell membrane all ...
... 34. The number of times that an objective lens can magnify an object is referred to as the____________________. 35. The movement of ink within a glass of water when the water has been left undisturbed (not shaken or stirred) could be the result ____________________. 36. Because the cell membrane all ...
The Evolutionary Emergence of Vertebrates From Among Their
... evidence to support evolutionary trees has been derived from analysis of skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems, development and embryology, and cell characteristics. Invariably, these different aspects of organismal biology were studied in isolation and resulted in conflicting ideas of animal rela ...
... evidence to support evolutionary trees has been derived from analysis of skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems, development and embryology, and cell characteristics. Invariably, these different aspects of organismal biology were studied in isolation and resulted in conflicting ideas of animal rela ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.