* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 - Napa Valley College
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Neohumanism wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
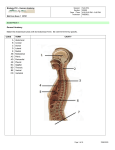
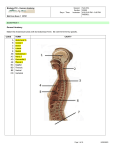
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 SCANTRON 1 General Anatomy Match the COMPONENTS and the FUNCTIONS with the respective SYSTEM to which they are most closely associated. See Column 1 for choices 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. SELECT CONSTITUENTS GENERAL FUNCTIONS esophagus, liver, pancreas, and anus brain stem and spinal nerves tonsils, thymus, and spleen thyroid, pancreas, ovary, and pituitary fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles kidneys and bladder sudiferous and sebaceous glands and hair larynx, pharynx, trachea, bronchus and lungs tendons, axial and appendicular muscles arteries and veins and heart 11. Chemical control of growth, development, homeostasis, reproduction and sexual dimorphism C 12. Consciousness, electro-chemical signaling and homeostasis 13. External defense, thermal homeostasis 14. Gametogenesis and copulation 15. Maceration, salivation, AND absorption 16. Micturition / voidance and control of blood volume and pressure 17. Support, movement and blood formation 18. Voluntary Movement, Motility, Mobility Match the DEFINITION with its TERM # Definition CODE 19. The study of the internal structure of cells 20. The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment suitable for the survival of body cells and tissues 21. The property by which organisms respond to changes in their immediate environment 22. The process in which individual cells, in multicellular organisms, become specialized to perform particular functions 23. Located within the thoracic cavity in between the right and left pleural cavities 24. Toward an attached base 25. Sectional plane that separates the body into anterior and posterior portions 26. A decision about the nature of an patients health D 27. _ Sectional plane that separates the body into unequal right and left portions Page 1 of 27 A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD TERM coronal cytology diagnosis differentiation distal homeostasis mediastinum parasagittal proximal responsiveness/irritability sagittal transverse vulgate 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Membranes MATCHING: Match membranes with their respective location and definition Membranes 28. Cutaneous 29. Mucous 30. Synovial Choices A. B. C. D. E. Shoulder, knee, elbow, inter-digital, vertebral facets Digestive, respiratory, urinary tracts Peritoneum, Pleura and pericardia Integument Cranium and vertebral cavity Place the generally recognized levels of organization, of anatomical interest, in order, from MOST to LEAST complex. It will be easier to work your way up the list from atoms. CHOICES LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION 31. ______________ORGANISM 32. _____________ 33. ______________ 34. ______________ 35. ______________ 36. ______________ 37. ______________ ATOMS A. ATOMS B. BIOSPHERE C. CELLS D. COMMUNITY E. ECOSYSTEM AB. ELECTROLYTES AC. ENERGY AD. LIFE CYCLE AE. METABOLISM BC. MOLECULES BD. ORGAN BE. ORGAN SYSTEM CD. ORGANELLES CE. ORGANISM DE. PLANET ABC. POPULATION ABD. TISSUE Page 2 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Levels of Anatomical Organization Anatomical Location / Perspective / Planes and Aspect MATCHING: Match the term that best fills in the positional relationship. Choose answers from Column IV 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. The pelvic cavity is ____ to the abdominal cavity The vertebral column is _____ to the thoracic cage The coracoid process is ____ to the acromion The wrist is ______ to the elbow. The sternum is ____ to the vertebral column The Cervicis is ______ to the Thoracicis MATCHING: Match the section name with its respective definition Section Definition 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. A. Divides left from right / laterally but not equally B. Divides superior from inferior C. Divides anterior from posterior D. Divides the structure at an angle, not perpendicular or parallel E. divides equilaterally, left from right Coronal / Frontal Medial / sagittal Parasagittal Transverse / cross Oblique Page 3 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Anatomical Terminology - Regions of the Body MATCHING: Match the anatomical terminology to the common term ANATOMICAL 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. Antebrachial Antecubital Axillary Buccal Calcaneal Crural Glossal Inguinal Pedal Plantar Popliteal Scapular Sternal Sural CODE A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE. CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE ABCDE COMMON TERM ankle anterior elbow arm calf cheek chest chin ear elbow foot forearm forehead groin hand head heel lower back mid-chest, anterior thorax nose palm posterior knee reproductive shin shoulder shoulder blade sole thigh tongue underarm, armpit wrist Page 4 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Illustration of Body Cavities See Column II for Choices 63. Name this body region ILLUSTRATION 66. Name this organ ## 64. Name this aspect / side / view @@ 67. This illustration of a cross section is from a specimen lying in _________ position 65. Name the specific bone structure %% 68. If we were looking from the caudal perspective / direction, the indicators ## and %% would represent patient L or R? Page 5 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Cells 69. Extracellular fluid found within blood vessels is called: A. lymph. B. plasma. C. cytosol. D. blood. 70. Extracellular fluid found between the cells (not within any vessel) is called: A. lymph. B. intercellular fluid. C. cytosol. D. interstitial fluid. Mark the locations of the following cellular structures by placing a check mark in the column(s)…Mark all that apply. # Structure 71. Chrosomes 72. Interstitial Fluid 73. Mitochondria 74. Nucleus 75. Cytoskeleton A Extracellular B Intracellular C Intercellular D Infranuclear D Table of Cell Junctions / Connections Mark all codes that apply to these broad functional classes of cell junctions # Primary Function 76. Anchoring cell to basal membrane D 77. Anchoring cell skeleton to cell skeleton C 78. Communicative B 79. Taut, rigid, securing, occluding E CODE A. B. C. D. E. Choices Adherens Gap Desmosome Hemidesmosome Tight Page 6 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Tissues 80. The type of muscular tissue found in the cutaneous membrane is: A. cardiac B. skeletal C. vesicular D. smooth 81. The type of epithelial tissue found lining the mouth and esophagus is: A. stratified cuboidal B. stratified squamous C. simple columnar D. transitional 82. All connective tissues have an extracellular matrix (material between the cells). Which connective tissue's matrix includes translucent chondroitin surrounding lacunae? A. blood B. bone C. reticular D. areolar E. cartilage 83. Heart valves need to be able to resist stress in various directions. Which type of connective tissue best serves this purpose? A. dense regular B. reticular C. areolar D. dense irregular Page 7 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 THIS PAGE LEFT PURPOSELY BLANK____ Page 8 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Table of Tissues Classification; Fill in the following tables of histological classification. Resort to alphabetical order if more than one choice is required for a given list in, a given level. Use the following lists of choices for your answers. List of Choices: Classes and Subtypes CODE CLASS / TYPE SHAPE / A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCE Adipose Areolar Blood Bone Cardiac Cartilage Cells Connective Epithelial Fibrous / Fibro Fluid Hyaline Lymph Muscle Neuroglia Neuronal / Nerv Plasma Pseudostratified Simple Stratified Supportive Transitional Columnar Cuboidal Squamous FEATURES Ciliated Keratinized Non-ciliated Non-keratinized FORM Cardiac Compact Dense Elastic Irregular Loose Regular Reticular Skeletal Smooth Spongy LOCATION / RELATION Central Peripheral CELL NAME Astrocytes Basophil Eiosinophil Ependymal Erythrocytes Leukocytes Lymphocyte Macrophage Microglia Monocyte Neuron Neutrophil Oligodendrocytes Platelets Satellite Schwann Page 9 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 THIS PAGE PURPOSELY LEFT BLANK Page 10 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Histology Classification Main CLASS 84. Sub Type MAIN DIVISION Fibrous Sub Type Dense Sub Type FEATURES Cell Formed Element Type Elastic Irregular Regular 85. Adipose 86. Reticular 87. Blood Form Elem / Cells 88. Leukocytes Basophil Eiosinophil Lymphocyte Monocyte 89. Neutrophil __BE Platelets 90. Lymph 91. 92. Compact Spongy Cartilage Elastic Fibro 93. Page 11 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 SCANTRON 2 Histology Classification continued Main CLASS 94. Epithelial __AE Sub Type MAIN DIVISION Sub Type SHAPE / FORM Sub Type FEATURES Cell Name Cell (Cyte) / Loc Pseudostratified 95. Cuboidal Columnar Ciliated Non Ciliated Squamous 96. Cuboidal Columnar Squamous Non Keratinized Keratinized Transitional 97. Cardiac Skeletal 98. 99. Neuroglia Central 100. Astrocytes A Ependymal Oligodendrocytes Microglia Peripheral Satellite Schwan Neurons Page 12 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Integuement Check Box: Mark A for True / Present, or B for False / Not present Definition / Identification Stratum corneum Thick Skin 101. Stratum lucidum Epidermal ridges 102. 103. Dermis Stratum basale 104. 105. Stratum Spinosum Stratum Granulosum Thin Skin 106. 107. 108. A patient was admitted to the ER, having been scalded from her navel to the knees anteriorly, in a restaurant kitchen. What % of her body is estimated to have sufferd injury? 109. See Rule of 9’s on Website A . 9% B. 18% C. 27% D. 36% E . 54% Page 13 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Bone Tissue 110. Which type of bone cell is responsible for forming bone matrix? A. osteocyte B. osteoclast C. osteobyte D. osteoblast 111. The space between the struts or trabeculae in spongy bone is filled with: __________. A. air B. yellow bone marrow C. water D. red bone marrow 112. The main types of fetal ossification include: Mark all that apply. A. intrchondral B. endochondral C. endomembranous D. intramermbranous E. extrachondral AB. membrochondral AC. intromentalextracombomendralous Skeleton Bone membership Classification; Indicate which region of the skeleton for each of the listed bones is a member . Place a check mark in the appropriate column. Mark A for Appendicular and B for Axial and C for Associated # 113. 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. BONE _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ APPENDICULAR A AXIAL B ASSOCIATED C Calcaneus Carpals Clavicle Costal Coxal Hyoid Incus Phalanx Sacrum Sphenoid Page 14 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Matching: Match the descriptions with the class of articulations: Mark ALL that apply for each Class CLASS 123. 124. 125. Definition / Description Amphiarthrotic Diarthrotic Synarthrotic A. Simple, not readily moveable B. Moderately complex, some shared movement C. Complex structure, Highly flexible D. Synovial E. Suture Matching: Match the EXAMPLE structures with appropriate class of articulations: Mark ALL that apply for each CLASS. CLASS 126. 127. 128. Example Type Amphiarthrotic Diarthrotic Synarthrotic A. Synovial B. Ball and Socket C. Gomphosis D. Suture E. Distal Tibial Fibula 129. The main function of the appendicular skeleton is to: A) facilitate movement. B) protect internal organs. C) produce hormones for regulation of calcium balance. D) store iron for blood cell production. E) help regulate body temperature. 130. An interosseous membrane joins the: Mark ALL that apply A) radius and ulna. B). fibula and tibia C) femur and tibia. D) left and right scapulae E) none of the above 131. The large hole in the coxal bone through which blood vessels and nerves pass is the: A) acetabulum. B) pubic symphysis. C) obturator foramen. D) iliac fossa. E) glenoid cavity. Page 15 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 132. A. B. C. D. Which of the following applies to the sella turcica? it supports and protects the pituitary gland it is bounded directly laterally by the foramen spinosum as is true for the mastoid process and air cells, it does not develop until after birth it permits passage of the optic nerves 133. A. B. C. D. The hyoid bone serves as a base of attachment for muscles that move the tongue is part of the mandible is located inferior to the larynx articulates with the maxillae 134. A. B. C. D. The role of fontanels is to allow for compression of the skull during childbirth serve as ossification centers for the facial bones serve as the final bony plates of the skull lighten the weight of the skull bones 135. A. B. C. D. E. The sacrum provides protection for reproductive, digestive, and excretory organs bears the most weight in the vertebral column articulates with the pectoral girdle is composed of vertebrae that are completely fused by puberty all of the above 136. A. B. C. D. The portion of the sternum that articulates with the clavicles is the manubrium body xiphoid process angle 137. The prominent groove along the inferior border of the internal rib surface A. provides an attachment for intercostal muscles B. is called the costal groove C. marks the path of nerves and blood vessels D. both b and c are correct Page 16 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Identification: Select the correct anatomical term from Column VII, and IX of Choices for the respective request for identification as marked by its symbol. 138. 139. 140. 141. Name this bone(s) % Name this suture @ Name this suture $ Name this suture & Identify the bones that form the orbit. Name them in alphabetical order. See Column VII of CHOICES # 142. 143. 144. 145. 146. 147. 148. _ _ _ _ _ _ _ BONE __Ethmoid __Frontal __Lacrimal __Maxilla __Palatine __Sphenoid __Zygomatic Page 17 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Fill in the following table for the axial skeleton: Rely on alphabetic order to complete the respective sections and lists. See Column VII for bones and XI for count choices Skull Bone Cranium Facial 149. 1 Frontal 1 150. 1 Parietal 151. 152. 1 Temporal 2 Inf Nasal Conchae 2 Lacrimal 153. Mandible 1 154. 155. Nasal 2 156. Vertebral Column Count Palatine 157. 158. 1 Zygomatic 2 Cervical 159. Coccyx 1 160. 5 Sacral 1 161. T 12 Fill in the following Table. Choose your answers from Column XI # Skeleton Division Bone Count 162. _ Vertebral Column ____ 163. _ Axial ___ 164. _ Right Appendages (Hand & Foot) ___ 165. _ Total Phalanges ___ 166. _ Thoracic Cage ___ 167. _ Left Appendicular Skeleton ___ Page 18 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Identification: Select the correct anatomical term from Column VIII, X and XI of Choices for the respective identifications 168. Column VIII Name this bone specific 169. Name the fused coxal bone that is shown but not indicated in this illustration PUBIS DE 170. Column X Name this structure % 171. Name this structure ?? ABD 172. Name the structure that provides additional support and articulating surface between % and && Column XI 173. How many of these bones, of the ones pictured, are members of the axial skeleton. (ohhh for the keen observer only) Page 19 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Identification: Select the correct anatomical term from Column X. Column X 174. 175. 176. 177. Name this structure # Name this structure + Name this process $$ Name this region of this bone $ Page 20 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 MATCHING: Match the structure / bone with its corresponding or articulating structure or bone. # 178. 179. 180. 181. 182. 183. 184. 185. 186. 187. Structure / Bone _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Auricular Surface Of Sacrum Head Of Femur Medial Extremity Of Clavicle CDE Head Of Humerus Glenoid Cavity Distal End Of The Tibia Olecranon articulates with Head Of Ulna Articulates with Coxal Bones Articulate With Costal Tubercle Articulates With CODE A B C D E. AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE ABCDE ARTICULATING, OR CORRESPONDING STRUCTURE / BONE Acetabulum Acromion Of Scapula Capitulum Of Humerus Clavicle Condyle, Capitulum / Trochlea Coronoid Fossa Coxal Femur Fibula Glenoid Cavity Head Of Fibula Head Of Radius Head of Humerus Ilium Interosseous Membrane Ischium Lunate Medial Condyle Of Femur Olecrenon Fossa Radial notch of ulna Radius Sacrum Scaphoid Scapula Sternum / Manubrium Styloid Process Talus Thoracic vertebrae Tibia Transverse process of Vertebrae Page 21 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Match the Term with it representation in the Illustration # Movement (single letter) Illustration Articulation Type (double letter) 188. Flexion 193. Gliding 189. Plantar flexion 194. Hinge 190. Abduction 195. Ball & Socket 191. Hyper Extension 192. Protraction Page 22 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 Greek and Latin Lexicon # 196. 197. 198. 199. 200. 201. Definition _ _ _ _ _ _ Disease To cut Inside In between Outside Ology CODE A B C D E. AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE ABCDE Greek / Latin Prefix, Root or Suffix Ana Bi Derma Dura Endo Epi Erythro Exo Extra Gastric Hyper Inter Ipsi Iso Knowledge Leuko Lyse Medi Pathos Phago Physio Squamous Sub Study of Tomy Tonic Page 23 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 THIS PAGE PURPOSELY REMAINS BLANK – USE for QUESTIONS, PROTESTS, PROPOSALS, TYPOGRAPHIAL ERRORS, SPELLING CORRECTIONS, ALPHABETIZATIONS, NOTES, DRAWINGS, DIAGRAMS, DOUBLE CHECKS, DOODLES, A draft Letter to your Dean, or your Mom, or President Obama, about how difficult this course is, and how and why it should be “dumbed” down for poor and struggling PRE-MED students like you………….and that there are just too many parts to the Human Body to memorize ….and its too complicated to understand……and how God should have made this whole thing, including you, more simple….and how we should use American English instead of all that Latin and Greek stuff……..and how its too much information for your tired brain to contain in a single semester……and…….how come the tests are so long…….and ………whine……..whine……..whine……..and WHATEVER!, OTHER !!!! Page 24 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 CODE A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE BCDE ABCDE I Organ Systems Cardiovascular Digestive Endocrine Integuement Lymphatic Immune Muscular Nervous Reproductive Respiratory Skeletal Urinary II Body Cavities Abdomen Anterior Back Dead Heart Inferior Kidney Left Lumbar Vertebrae Lung Medial Mediastinum Pelvis Pericardial Cavity Pleural Cavity Posterior Prone Right Sternum Stomach Superior Supine Thoracic Cavity Thoracic Vertebrae Thorax Vertebral Body Vertebral Canal Vertebral Transverse Process III Vertebrae Body Costal Facet Dens Desmosome Foramina Groove Head Inferior Articular Facet Inferior Notch Lamina Pedicle Spinous Process Superior Articular Facet Superior Costal facet Sulcus Transverse Costal Facet Transverse Foramen Transverse Process Tubercle Vertebral Arch Vertebral Body Vertebral Foramen Vertebrae IV Loc / View / Relat Anterior Artificial Deep Distal External Inferior Inferior Internal Lateral Left Medial Natural Oblique Parasaggital Posterior Prone Proximal Right Sub-Cutaneous Superficial Superior Superior Sagittal Superior Transverse Supine Transverse V Integument Apocrine Attachment, lipid storage, vessels, Ceruminous Cutaneous Membrane Dermis Epidermis Exocrine Glands Follicles Glands Hair Follicle Holocrine Lipid Mammary Merocrine Milk Nails Oil Oil / Hormones / Pheromones Papillary Perspiration Protection, Touch Waterproofing Refined fine motor Reticular Sebaceous Sudiferous Wax Page 25 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 THIS PAGE LEFT PURPOSELY BLANK Page 26 of 27 478168426 Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Session: Section: Days / Time: Instructor: Fall 2013 52999 M W 5:00 PM – 9:20 PM RIDDELL Example Mid-Term Exam 1 EMTX1 CODE A B C D E AB AC AD AE BC BD BE CD CE DE ABC ABD ABE ACD ACE ADE BCD BCE BDE CDE ABCD ABCE ABDE ACDE BCDE ABCDE VII Bones Axial Auditory Coccyx Costal Cranial Ethmoid Facial Frontal Hyoid Incus Inferior Nasal Conchae Lacrimal Malleus Mandible Maxillae Nasal Occipital Palatine Parietal Sacrum Sphenoid Stapes Temporal Vertebrae Vertebrae, Cervical Vertebrae, Lumbar Vertebrae, Thoracic Vomer Zygomatic VIII Bones Appendicular Carpals Clavicle Coxal Femur Fibula Humerus Ilium Ischium Metacarpals Metatarsals Patella Pectoral Pelvic Phalanges Pubis Radius Sacrum Scapula Sternum Tarsals Thoracic Tibia Ulna X Skel Structures / Sections Arch of Hyoid Arch of Vertebrae Capitulum Condyle, lateral Condyle, medial Cranium Epicondyle , medial Epicondyle, lateal Facet, inferior Facet, superior Foramen Head Lamina Malleous, lateral Malleous, medial Mastoid process Meatus Meniscus Olecranon Orbit Sphenoidal Foramen Sphenoidal Sinus Styloid process Suture Temporal Arch Transverse process Trochlea Zygomatic process IX Sutures Coronal / Frontal Infero-Temporal Lambdoidal Posterior Sagittal Squamous Supra-Temporal Synovial Temporal Temporal-Zygomatic Tibial Transverse XI Numbers / Counts 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 16 20 25 26 28 53 56 60 63 76 80 86 103 106 126 206 212 Page 27 of 27 478168426