24.2 What Are the Major Groups of Vertebrates?
... heart, and are ectothermic (they rely on heat from the outside environment to regulate body temperature) – They lack a true backbone, and thus are not a true vertebrate but have a rudimentary braincase – They represent the chordate group that is most closely related to the vertebrates Biology: Life ...
... heart, and are ectothermic (they rely on heat from the outside environment to regulate body temperature) – They lack a true backbone, and thus are not a true vertebrate but have a rudimentary braincase – They represent the chordate group that is most closely related to the vertebrates Biology: Life ...
FUNGI “Plants without chlorphyll”
... 1. Mycelium intertwined hyphae which makes up the body of a fungus ...
... 1. Mycelium intertwined hyphae which makes up the body of a fungus ...
Untitled - SCUSOMA
... how the atoms will bond. The bonding also depends on the arrangement of the electrons. ...
... how the atoms will bond. The bonding also depends on the arrangement of the electrons. ...
COURSE BOOK IN GENERAL BIOLOGY
... Living things require energy from the environment and produce waste energy and chemicals. Living things need continuous supply of energy in order to stay alive. The sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living things.Both plants and animals, however, obtain energy more directly by the breakdo ...
... Living things require energy from the environment and produce waste energy and chemicals. Living things need continuous supply of energy in order to stay alive. The sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living things.Both plants and animals, however, obtain energy more directly by the breakdo ...
Systems of Gas Exchange
... The primary function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body's tissues and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product. The main structures of the human respiratory system are the nasal cavity, the trachea, and lungs. All aerobic organisms require oxygen to carry out ...
... The primary function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body's tissues and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product. The main structures of the human respiratory system are the nasal cavity, the trachea, and lungs. All aerobic organisms require oxygen to carry out ...
Systems of Gas Exchange
... split and spread through the lung. Like the trachea, the bronchi are made of cartilage and smooth muscle. At the bronchioles, the cartilage is replaced with elastic bers. Bronchi are innervated by nerves of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems that control muscle contraction (pa ...
... split and spread through the lung. Like the trachea, the bronchi are made of cartilage and smooth muscle. At the bronchioles, the cartilage is replaced with elastic bers. Bronchi are innervated by nerves of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems that control muscle contraction (pa ...
2.01 structure of cells.
... specimen. This may seem strange, but electrons behave like waves and can easily be produced (using a hot wire), focused (using electromagnets) and detected (using a phosphor screen or photographic film). The main problem with the electron microscope is that specimens must be fixed in plastic and vie ...
... specimen. This may seem strange, but electrons behave like waves and can easily be produced (using a hot wire), focused (using electromagnets) and detected (using a phosphor screen or photographic film). The main problem with the electron microscope is that specimens must be fixed in plastic and vie ...
Invertebrate Unit (Ch. 26, 27, 28, 29)
... cells of organisms often produce a “trash” substance called ammonia which is poisonous. The excretion (to get rid of) of wastes from the body varies between organisms. ...
... cells of organisms often produce a “trash” substance called ammonia which is poisonous. The excretion (to get rid of) of wastes from the body varies between organisms. ...
Biology for AIEEE - CET 2009-10
... (a) Rh-negative mothers get immunized by blood from Rh positive foetus (b) A daughter can inherit X chromosome from both parents (c) A son cannot inherit X chromosome from his father (d) Rh negative mother cannot concieve a Rh positive son ...
... (a) Rh-negative mothers get immunized by blood from Rh positive foetus (b) A daughter can inherit X chromosome from both parents (c) A son cannot inherit X chromosome from his father (d) Rh negative mother cannot concieve a Rh positive son ...
prenatal development
... Cell Replacement Cells must divide in order for an organism to grow and develop, but cell division is also required for maintenance, cell turnover and replacement. SITINOR/FEM3101/FEBRUARI 2013/PJJ ...
... Cell Replacement Cells must divide in order for an organism to grow and develop, but cell division is also required for maintenance, cell turnover and replacement. SITINOR/FEM3101/FEBRUARI 2013/PJJ ...
Using food and controlling growth - Delivery guide
... The majority of learners believe that respiration is breathing and we breath in only oxygen not realising that air contains mainly nitrogen with some oxygen, carbon dioxide and other gases. These two common misconceptions should be addressed early on by highlighting that ‘ventilation’ is breathing a ...
... The majority of learners believe that respiration is breathing and we breath in only oxygen not realising that air contains mainly nitrogen with some oxygen, carbon dioxide and other gases. These two common misconceptions should be addressed early on by highlighting that ‘ventilation’ is breathing a ...
June issue (Final Notebook)
... challenges remain the same. Field mice, for instance, shut down their normal routes of energy metabolism during hibernation and switch over to fermentation as a source of O2 during reduced metabolism. Similarly, CO2 cessation in forearm muscles of advanced meditators has been attributed to a shift t ...
... challenges remain the same. Field mice, for instance, shut down their normal routes of energy metabolism during hibernation and switch over to fermentation as a source of O2 during reduced metabolism. Similarly, CO2 cessation in forearm muscles of advanced meditators has been attributed to a shift t ...
Science CMT Review - Groton Public Schools
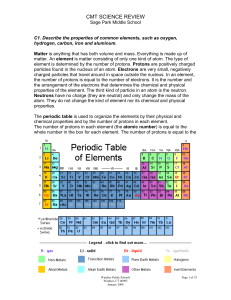
... C3. Explain how mixtures can be separated by using the properties of the substances from which they are made, such as particle size, density, solubility and boiling point. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that have not combined chemically such as chocolate chips in ice cream. A s ...
... C3. Explain how mixtures can be separated by using the properties of the substances from which they are made, such as particle size, density, solubility and boiling point. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that have not combined chemically such as chocolate chips in ice cream. A s ...
1 - Staff Web Pages
... undergoing a process that is similar to a human being who releases moisture on a hot day. This process that helps keep both the microorganism and the human body fluids in balance is known as — A ...
... undergoing a process that is similar to a human being who releases moisture on a hot day. This process that helps keep both the microorganism and the human body fluids in balance is known as — A ...
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge
... (a) A student cut thin sections of a root tip of Allium cepa and stained them to show chromosomes. A photomicrograph of part of one of these sections is shown in Fig. 4.1. A ...
... (a) A student cut thin sections of a root tip of Allium cepa and stained them to show chromosomes. A photomicrograph of part of one of these sections is shown in Fig. 4.1. A ...
Churchlands Senior High School – Science Department
... The resources or references such as texts and websites in this document are provided as examples of resources that teachers can use to support their teaching. Their inclusion does not imply that they are mandatory, preferred or that they are the only resources relevant to the course. ...
... The resources or references such as texts and websites in this document are provided as examples of resources that teachers can use to support their teaching. Their inclusion does not imply that they are mandatory, preferred or that they are the only resources relevant to the course. ...
TEKS 8.6 B
... to life. Our body’s ability to monitor and maintain homeostasis is dependent on a many complex interactions between the various body systems linked by the circulatory system. When these interactions do not function properly, a number of problems occur, some of which can be life threatening. In this ...
... to life. Our body’s ability to monitor and maintain homeostasis is dependent on a many complex interactions between the various body systems linked by the circulatory system. When these interactions do not function properly, a number of problems occur, some of which can be life threatening. In this ...
Conference Book - Epsilon Open Archive
... scientific meetings and thus, strengthen the interest in and the growth of Plant Science. The SPPS is the major community for plant physiologists in Scandinavia since 1947. With the SPPS PhD Student Conference in particular, we aim to create an open, informal and enthusiastic atmosphere to facilitat ...
... scientific meetings and thus, strengthen the interest in and the growth of Plant Science. The SPPS is the major community for plant physiologists in Scandinavia since 1947. With the SPPS PhD Student Conference in particular, we aim to create an open, informal and enthusiastic atmosphere to facilitat ...
Fungi Diversity
... The kingdom Fungi contains four major divisions that were established according to their mode of sexual reproduction. Polyphyletic, unrelated fungi that reproduce without a sexual cycle, are placed for convenience ...
... The kingdom Fungi contains four major divisions that were established according to their mode of sexual reproduction. Polyphyletic, unrelated fungi that reproduce without a sexual cycle, are placed for convenience ...
Game Board - nemsjamma
... • List the Levels of Organization starting with cells and building up. ...
... • List the Levels of Organization starting with cells and building up. ...
Cnidaria: Introduction
... secretory products. The other two are confined to only some cnidarians (spirocysts to hexacorallians and ptychocysts to cerianthids). The cnidarian body is said to be radial in symmetry, and the body axis is oral-aboral. Members of class Anthozoa, however, are actually biradial. The class is distin ...
... secretory products. The other two are confined to only some cnidarians (spirocysts to hexacorallians and ptychocysts to cerianthids). The cnidarian body is said to be radial in symmetry, and the body axis is oral-aboral. Members of class Anthozoa, however, are actually biradial. The class is distin ...
Bacteria
... Bacteria can live in temperatures above the boiling point and in cold that would freeze your blood. There's even a species of bacteria—Deinococcus radiodurans—that can withstand blasts of radiation 1,000 times greater than would kill a human being. They "eat" everything from sugar and starch to sunl ...
... Bacteria can live in temperatures above the boiling point and in cold that would freeze your blood. There's even a species of bacteria—Deinococcus radiodurans—that can withstand blasts of radiation 1,000 times greater than would kill a human being. They "eat" everything from sugar and starch to sunl ...
All About Bacteria Lab
... Many of us know bacteria only as “germs”, invisible creatures that can invade our bodies and make us sick. Few know that many bacteria not only exist with us all the time, but help us do many amazing things like make vitamins, break down some garbage, and even maintain our atmosphere. I. Where Bacte ...
... Many of us know bacteria only as “germs”, invisible creatures that can invade our bodies and make us sick. Few know that many bacteria not only exist with us all the time, but help us do many amazing things like make vitamins, break down some garbage, and even maintain our atmosphere. I. Where Bacte ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.