Grade 5 Life Science Unit (5.L.1)
... Decision 5: Acquisition Lesson One Language Objective(s), where appropriate: RI.5.3. Explain the relationships or interactions between two or more individuals, events, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text based on specific information in the text. ...
... Decision 5: Acquisition Lesson One Language Objective(s), where appropriate: RI.5.3. Explain the relationships or interactions between two or more individuals, events, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text based on specific information in the text. ...
Licensed to: iChapters User
... BASIC CELL FUNCTIONS All cells, whether they exist as solitary cells or as part of a multicellular organism, perform certain basic functions essential for their own survival. These basic cell functions include the following: ...
... BASIC CELL FUNCTIONS All cells, whether they exist as solitary cells or as part of a multicellular organism, perform certain basic functions essential for their own survival. These basic cell functions include the following: ...
3-5 - Wave Foundation
... general, sharks are darker on top and lighter below. This is a type of camouflage known as countershading. Countershading aids many aquatic animals, including sharks, as they are more difficult to see because their light undersides blend in with the sunlight. The darker upper body blends in with the ...
... general, sharks are darker on top and lighter below. This is a type of camouflage known as countershading. Countershading aids many aquatic animals, including sharks, as they are more difficult to see because their light undersides blend in with the sunlight. The darker upper body blends in with the ...
Cell Biology - Hardin County Schools
... In 1858, after using microscopes much better than Hooke’s first microscope, Rudolf Virchow developed the hypothesis that cells only come from other cells. For example, bacteria, which are single-celled organisms, divide in half (after they grow some) to make new bacteria. In the same way, your body ...
... In 1858, after using microscopes much better than Hooke’s first microscope, Rudolf Virchow developed the hypothesis that cells only come from other cells. For example, bacteria, which are single-celled organisms, divide in half (after they grow some) to make new bacteria. In the same way, your body ...
GRT Task 1 BIOCHEMISTRY Competency 208.5.1: DNA, RNA
... carbohydrates; demonstrates how adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is essential to energy transfer in the cell and how irregularities in ATP synthesis in the cell can cause cytopathologies. Introduction: More and more researchers are discovering that many diseases are caused by biochemical deficiencies o ...
... carbohydrates; demonstrates how adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is essential to energy transfer in the cell and how irregularities in ATP synthesis in the cell can cause cytopathologies. Introduction: More and more researchers are discovering that many diseases are caused by biochemical deficiencies o ...
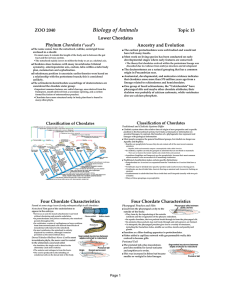
Topic 1 Patterns in Nature
... compound composed of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. Sucrose (a type of sugar) is a compound composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Chemical compounds can be divided into two groups, inorganic and organic compounds. Organic compounds have a structure based on carbon atoms which are ...
... compound composed of the elements hydrogen and oxygen. Sucrose (a type of sugar) is a compound composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Chemical compounds can be divided into two groups, inorganic and organic compounds. Organic compounds have a structure based on carbon atoms which are ...
PPT Version - OMICS International
... OMICS Journals are welcoming Submissions OMICS International welcomes submissions that are original and technically so as to serve both the developing world and developed countries in the best possible way. OMICS Journals are poised in excellence by publishing high quality research. OMICS Internati ...
... OMICS Journals are welcoming Submissions OMICS International welcomes submissions that are original and technically so as to serve both the developing world and developed countries in the best possible way. OMICS Journals are poised in excellence by publishing high quality research. OMICS Internati ...
Life Science Leoce review
... •New scientific discoveries are often based on previous data or concepts •Theories are based on the best available evidence, but they may change as new evidence is discovered ...
... •New scientific discoveries are often based on previous data or concepts •Theories are based on the best available evidence, but they may change as new evidence is discovered ...
TEKS 8
... (i.e., circulatory, skeletal, respiratory, excretory, integumentary, nervous, digestive, endocrine, reproductive, immune, lymphatic, and muscular systems). In this TEKS, we will introduce students to the common structures of each system and their basic functions. A brief description of these systems ...
... (i.e., circulatory, skeletal, respiratory, excretory, integumentary, nervous, digestive, endocrine, reproductive, immune, lymphatic, and muscular systems). In this TEKS, we will introduce students to the common structures of each system and their basic functions. A brief description of these systems ...
Chapter 2: Cell Structure And Cell Organization
... Amoeba sp is made up of only a single cell, it can perform all living processes Explain the living process that enables Amoeba sp to survive in fresh water which is hypotonic to the cytoplasmic fluid of Amoeba sp P1-the living process is osmoregulation P2-Osmoregulation is in Amoeba sp. involved con ...
... Amoeba sp is made up of only a single cell, it can perform all living processes Explain the living process that enables Amoeba sp to survive in fresh water which is hypotonic to the cytoplasmic fluid of Amoeba sp P1-the living process is osmoregulation P2-Osmoregulation is in Amoeba sp. involved con ...
Question paper - Paper 2H - June 2010
... Albinism is an inherited condition in which animals have white fur. Albinism is controlled by a single gene that has two alleles. The allele for albinism, a, is recessive. The dominant allele, A, produces brown fur. ...
... Albinism is an inherited condition in which animals have white fur. Albinism is controlled by a single gene that has two alleles. The allele for albinism, a, is recessive. The dominant allele, A, produces brown fur. ...
Now - Lachoo Memorial College
... Unit I: History of Microbiology; A general account on ultrastructure, nutrition, reproduction, biology and economic importance of Archaebacteria, Eubacteria and Cyanobacteria. Recent trends in the classification of bacteria. Genetic recombination in bacteria: Transduction, Conjugation & Transformati ...
... Unit I: History of Microbiology; A general account on ultrastructure, nutrition, reproduction, biology and economic importance of Archaebacteria, Eubacteria and Cyanobacteria. Recent trends in the classification of bacteria. Genetic recombination in bacteria: Transduction, Conjugation & Transformati ...
13-Lower Chordates
... • They are not now considered a direct ancestor, although they may closely resemble the ancestor. • They lack a brain and the specialized sensory equipment of vertebrates. • There are no gills in the pharynx and no mouth for pumping water. ...
... • They are not now considered a direct ancestor, although they may closely resemble the ancestor. • They lack a brain and the specialized sensory equipment of vertebrates. • There are no gills in the pharynx and no mouth for pumping water. ...
sponge fact sheet - World Animal Foundation
... few days. They then settle down and start growing. The next time the sponges reproduce, they may change sexual roles. Sponges are also known for regenerating from fragments that are broken off, although this only works if the fragments include the right types of cells. A few species reproduce by bud ...
... few days. They then settle down and start growing. The next time the sponges reproduce, they may change sexual roles. Sponges are also known for regenerating from fragments that are broken off, although this only works if the fragments include the right types of cells. A few species reproduce by bud ...
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name
... are the disadvantages of an exoskeleton? The exoskeleton is not living tissue and therefore ___________________ and must be ________________________________ __________________________________________________ to attack from other organisms. This is costly in terms of energy and may be part of the rea ...
... are the disadvantages of an exoskeleton? The exoskeleton is not living tissue and therefore ___________________ and must be ________________________________ __________________________________________________ to attack from other organisms. This is costly in terms of energy and may be part of the rea ...
bio 1407 notes ch 28 to 38
... Fungi classified in the phylum Chytridiomycota, called the chytrids, are ubiquitous in lakes, ponds, and soil. Some are saprobes, while others parasitize protists, plants, and animals. However, recent molecular evidence supports the hypothesis that chytrids diverged earliest in fungal evolution. Lik ...
... Fungi classified in the phylum Chytridiomycota, called the chytrids, are ubiquitous in lakes, ponds, and soil. Some are saprobes, while others parasitize protists, plants, and animals. However, recent molecular evidence supports the hypothesis that chytrids diverged earliest in fungal evolution. Lik ...
COLEGIO DECROLY AMERICANO
... Discuss the evidence that supports the theory of evolution. Compare Lamarck’s and Darwin’s theories of evolution. Compare and contrast the mechanisms of evolution. Explain natural selection and its role in the evolution of species. Describe adaptations and variations. Trace the evolutionary history ...
... Discuss the evidence that supports the theory of evolution. Compare Lamarck’s and Darwin’s theories of evolution. Compare and contrast the mechanisms of evolution. Explain natural selection and its role in the evolution of species. Describe adaptations and variations. Trace the evolutionary history ...
Taxonomic Key to Benthic Macroinvertebrates
... The purpose of this taxonomic key is to assist volunteer monitors, who are not trained in taxonomy, with the identification of benthic macroinvertebrates found in Indiana. This key is a simplified version of more complex keys. The taxonomic level of this key is intended for use by citizen monitoring ...
... The purpose of this taxonomic key is to assist volunteer monitors, who are not trained in taxonomy, with the identification of benthic macroinvertebrates found in Indiana. This key is a simplified version of more complex keys. The taxonomic level of this key is intended for use by citizen monitoring ...
Polar Covalent Bond ~ Eg: H2O
... Cells are the smallest unit of life ~ “building blocks” Human Body has billions of cells ~ 100’s of different types MANY types of Chemical Reactions takes place in cells ...
... Cells are the smallest unit of life ~ “building blocks” Human Body has billions of cells ~ 100’s of different types MANY types of Chemical Reactions takes place in cells ...
Structure and Function in Living Things
... What are algae? The Kingdom Protista, often called protists, contains many groups that evolved separately. For that reason, many scientists think that protists should be classified into several smaller kingdoms. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are plant-like in many ways. Scientists have clas ...
... What are algae? The Kingdom Protista, often called protists, contains many groups that evolved separately. For that reason, many scientists think that protists should be classified into several smaller kingdoms. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are plant-like in many ways. Scientists have clas ...
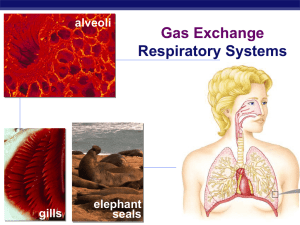
Gas Exchange print ppt
... Water carrying gas flows in one direction, blood flows in opposite direction ...
... Water carrying gas flows in one direction, blood flows in opposite direction ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.