Study Guide A Answer Key
... Complete the chart below by filling in the left column with the names of the introduced species that are causing the ecosystem impacts described in the right column. ...
... Complete the chart below by filling in the left column with the names of the introduced species that are causing the ecosystem impacts described in the right column. ...
VI. PHYLUM CHORDATA - Subphylum Vertebrata
... X. ECOLOGY Population Ecology, cont • Life history traits include reproductive age, frequency of reproduction, number of offspring, amount of parental care • Shaped by evolution and natural selection • Selection for life history strategies determined by population densities and conditions r-selec ...
... X. ECOLOGY Population Ecology, cont • Life history traits include reproductive age, frequency of reproduction, number of offspring, amount of parental care • Shaped by evolution and natural selection • Selection for life history strategies determined by population densities and conditions r-selec ...
1-Functional Organization of the Human Body
... Physiology team 434 Contact us : [email protected] ...
... Physiology team 434 Contact us : [email protected] ...
Unit 10 - Essential_Life_Functions_Chart revised final
... Protista refers to one of the kingdoms of organisms commonly called protists. They were first described by the German biologist Ernst Haeckel in the 1860s. Until this time, biologists recognized two kingdoms, the Plantae and Animalia. Haeckel observed a group of microscopic organisms with both plant ...
... Protista refers to one of the kingdoms of organisms commonly called protists. They were first described by the German biologist Ernst Haeckel in the 1860s. Until this time, biologists recognized two kingdoms, the Plantae and Animalia. Haeckel observed a group of microscopic organisms with both plant ...
File
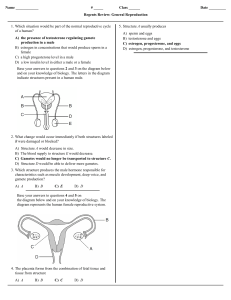
... 71. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. The reproductive cycle in a human female is not functioning properly. An imbalance of hormones is diagnosed as the cause. Identify one hormone directly involved in the human female reproductive ...
... 71. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. The reproductive cycle in a human female is not functioning properly. An imbalance of hormones is diagnosed as the cause. Identify one hormone directly involved in the human female reproductive ...
Phylum: Chordata
... plants that are decaying in the soil. Some can be eaten and some are poisonous. Examples: mushrooms, mold (shower curtain, bread), yeast, blue cheese Kingdom Plantae (5) Characteristics: Plants are multicellular and complex celled. They make their own food (autotrophs) through a process called photo ...
... plants that are decaying in the soil. Some can be eaten and some are poisonous. Examples: mushrooms, mold (shower curtain, bread), yeast, blue cheese Kingdom Plantae (5) Characteristics: Plants are multicellular and complex celled. They make their own food (autotrophs) through a process called photo ...
Topics in Computational Biology
... interaction techniques, and context-aware learning functions.) are needed to help biologists efficiently navigate through the complicated landscape of biomedical information and effectively manipulate various computational tools. • Collect information while surfing the Internet. • Manage multimedia ...
... interaction techniques, and context-aware learning functions.) are needed to help biologists efficiently navigate through the complicated landscape of biomedical information and effectively manipulate various computational tools. • Collect information while surfing the Internet. • Manage multimedia ...
Cell - General Science, Science and Technology, Ecology and
... The cristae increase the surface area of the inner membrane thereby providing more area for ATP generating chemical reactions. ATP is used to drive many energy requiring processes of the cell. The body or organisms uses energy stored in ATP for synthesis of chemical compounds and for mechanical work ...
... The cristae increase the surface area of the inner membrane thereby providing more area for ATP generating chemical reactions. ATP is used to drive many energy requiring processes of the cell. The body or organisms uses energy stored in ATP for synthesis of chemical compounds and for mechanical work ...
Cell Theory Cell Structure, Cell Transport and Mitosis
... Transport of organelles and molecules: Microtubules are the freeways used by organelles like lysosomes to move from one part of cell to another. Microfilaments are the roads/streets used by smaller things. Genes – DNA – Chromatin fiber – Chromosomes Fig. 3-17 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of ...
... Transport of organelles and molecules: Microtubules are the freeways used by organelles like lysosomes to move from one part of cell to another. Microfilaments are the roads/streets used by smaller things. Genes – DNA – Chromatin fiber – Chromosomes Fig. 3-17 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of ...
Bioinformatics
... and Methods This practical course introduces the main public domain tools, databases and methods used in bioinformatics, including DNA and protein databases such as Genbank and PBD, software tools such as BLAST, and methods for aligning sequences. Topics include multiple alignment, phylogenetic anal ...
... and Methods This practical course introduces the main public domain tools, databases and methods used in bioinformatics, including DNA and protein databases such as Genbank and PBD, software tools such as BLAST, and methods for aligning sequences. Topics include multiple alignment, phylogenetic anal ...
Experiment Bacterial genetic exchange : Conjugation of
... organic and inorganic substances. On plants, they are responsible for initiating ice formation which results in frost injury. On the other hand, the high temperature of ice catalysis conferred by bacterial ice nuclei makes them useful in ice-nucleation-limited processes such as making artificial sno ...
... organic and inorganic substances. On plants, they are responsible for initiating ice formation which results in frost injury. On the other hand, the high temperature of ice catalysis conferred by bacterial ice nuclei makes them useful in ice-nucleation-limited processes such as making artificial sno ...
Behavioral Adaptations - Effingham County Schools
... cellular respiration, and the circulatory system carries that oxygen to cells. At the end of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide is produced as a waste. The circulatory system carries carbon dioxide to the lungs, and the respiratory system removes it from the body. ...
... cellular respiration, and the circulatory system carries that oxygen to cells. At the end of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide is produced as a waste. The circulatory system carries carbon dioxide to the lungs, and the respiratory system removes it from the body. ...
What is an animal? Part 1
... carefully remove the tentacles that adhere to the skin by using sand, clothing, towels, seaweed or other available materials. As long as tentacles remain on the skin, they will continue to discharge venom. • A variety of substances have been used to reduce the effects of jellyfish stings. Meat tende ...
... carefully remove the tentacles that adhere to the skin by using sand, clothing, towels, seaweed or other available materials. As long as tentacles remain on the skin, they will continue to discharge venom. • A variety of substances have been used to reduce the effects of jellyfish stings. Meat tende ...
File - Ms. Daley Science
... NATURE OF SCIENCE/SCIENCE AS A PROCESS (Chapter 1) The Nature of Science 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. Use and define the following terms in your explanation: control group (positive and negative), hypothesis, variable (independent, dependent, and controlled), and experimental set- ...
... NATURE OF SCIENCE/SCIENCE AS A PROCESS (Chapter 1) The Nature of Science 1. Describe the steps of the scientific method. Use and define the following terms in your explanation: control group (positive and negative), hypothesis, variable (independent, dependent, and controlled), and experimental set- ...
Practice Questions 1: Cell Membrane
... cells → organelles → organs → organ systems → tissues tissues → organs → organ systems → organelles → cells organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems organs → organ systems → cells → tissues → organelles ...
... cells → organelles → organs → organ systems → tissues tissues → organs → organ systems → organelles → cells organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems organs → organ systems → cells → tissues → organelles ...
Intro TOC, etc. FINAL 7/12 - South Carolina Sea Grant Consortium
... The pelagic habitat is the water column that extends from the surface to the bottom. Pelagic habitats located far from coastlines do not receive large amounts of nutrients from coastal areas and rivers and their productivity is, therefore, not as high as that of coastal habitats. Nevertheless, pelag ...
... The pelagic habitat is the water column that extends from the surface to the bottom. Pelagic habitats located far from coastlines do not receive large amounts of nutrients from coastal areas and rivers and their productivity is, therefore, not as high as that of coastal habitats. Nevertheless, pelag ...
Hole Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life
... • two important factors in enzyme activity: temperature, pH • not consumed in chemical reactions • substrate specific • shape of active site (3D) determines which substrate(s) the enzyme can act on ...
... • two important factors in enzyme activity: temperature, pH • not consumed in chemical reactions • substrate specific • shape of active site (3D) determines which substrate(s) the enzyme can act on ...
CLASSIFICATION
... This led to the number of kingdoms increasing from three (plants, animals and minerals) to the current five (Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista and Monera). In the 1970s, a group ...
... This led to the number of kingdoms increasing from three (plants, animals and minerals) to the current five (Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista and Monera). In the 1970s, a group ...
Interactions in Animals
... from diseases, identify and respond to conditions affecting their body, and regulate internal body conditions, such as temperature and heart rate. Animals are made up of cells. In some animals, cells make up tissues specific to areas in the body. Tissues make up organs, and organs are part of organ ...
... from diseases, identify and respond to conditions affecting their body, and regulate internal body conditions, such as temperature and heart rate. Animals are made up of cells. In some animals, cells make up tissues specific to areas in the body. Tissues make up organs, and organs are part of organ ...
Cells and Reproduction
... Although most of our DNA is the same we have sections of meaningless ‘junk’ DNA in-between the genes. Enzymes can be used as ‘chemical scissors’ to chop this DNA into sections. The size and weight of these sections then let us generate a picture by running the DNA through a gel using electricity. As ...
... Although most of our DNA is the same we have sections of meaningless ‘junk’ DNA in-between the genes. Enzymes can be used as ‘chemical scissors’ to chop this DNA into sections. The size and weight of these sections then let us generate a picture by running the DNA through a gel using electricity. As ...
YES NC - WordPress.com
... organs as a collection of tissues with the same function, and organ systems as various organs that work together to perform the same function, and finally the organism as a whole system comprised of many parts that work together to keep the body stable through the process of homeostasis. Students wi ...
... organs as a collection of tissues with the same function, and organ systems as various organs that work together to perform the same function, and finally the organism as a whole system comprised of many parts that work together to keep the body stable through the process of homeostasis. Students wi ...
Nutrition: How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... Bulk feeders - humans, lions, buffalo. Eat large pieces of food. Some animals, like corals might be hard to put into one of these categories. Corals are mostly suspension feeders, but they also photosynthesize (with the help of algae living in their tissues) What kind of food does an animal eat? Her ...
... Bulk feeders - humans, lions, buffalo. Eat large pieces of food. Some animals, like corals might be hard to put into one of these categories. Corals are mostly suspension feeders, but they also photosynthesize (with the help of algae living in their tissues) What kind of food does an animal eat? Her ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.