Cells - Biloxi Public Schools
... used for storage plant cells usually have one large vacuole that stores water and other substances vacuoles help support the plant animal cells have smaller vacuoles that contain either food or wastes vacuoles in animals cells can be temporary small organelles that break down sugar and r ...
... used for storage plant cells usually have one large vacuole that stores water and other substances vacuoles help support the plant animal cells have smaller vacuoles that contain either food or wastes vacuoles in animals cells can be temporary small organelles that break down sugar and r ...
Document
... he experimented with pea plants. • Dominant traits always are visible, and are represented by capital letters. • Recessive traits are hidden unless both alleles are the recessive one ...
... he experimented with pea plants. • Dominant traits always are visible, and are represented by capital letters. • Recessive traits are hidden unless both alleles are the recessive one ...
Biology EOC review
... by a nuclear membrane; no membranebound organelles; found in bacteria and ...
... by a nuclear membrane; no membranebound organelles; found in bacteria and ...
Life Science Final Review
... 5. For a science project Susie wants to compare the densities of different types of wood. She gets a block of pine and the same size block of oak. She finds two of the same sized nails, (but one is made of steel and the other is made of aluminum). She finds two of the same hammers. Then she recruit ...
... 5. For a science project Susie wants to compare the densities of different types of wood. She gets a block of pine and the same size block of oak. She finds two of the same sized nails, (but one is made of steel and the other is made of aluminum). She finds two of the same hammers. Then she recruit ...
Human physiology is the science of the mechanical
... Living systems are open self-organizing living things that interact with their environment. These systems are maintained by flows of information, energy and matter. ...
... Living systems are open self-organizing living things that interact with their environment. These systems are maintained by flows of information, energy and matter. ...
Levels of Organization-Plants
... Bell Ringer 9/3/13 1. What is the function of a hot plate? 2. Which science tool would you use for accurate volume measurement?(2 possible answers) 3. List something that you organize or need to organize 4. Besides by grade how are schools organized? ...
... Bell Ringer 9/3/13 1. What is the function of a hot plate? 2. Which science tool would you use for accurate volume measurement?(2 possible answers) 3. List something that you organize or need to organize 4. Besides by grade how are schools organized? ...
2015 1st Semester Exam Review Key
... What organic compound does the nucleus contain and what does it have the code for in the cell? It contains the DNA which stores all the information for inheritance and running the cells. It also has a nucleolus that makes parts of the ribosomes 1. Define the job of each organelle in the eukaryotic ...
... What organic compound does the nucleus contain and what does it have the code for in the cell? It contains the DNA which stores all the information for inheritance and running the cells. It also has a nucleolus that makes parts of the ribosomes 1. Define the job of each organelle in the eukaryotic ...
Six Kingdoms of Living Things Teacher Notes
... Until the 20th century, most biologists considered all living things to be classifiable as either a plant or an animal. But in the 1950s and 1960s, most biologists came to the realization that this system failed to accommodate the fungi, protists, and bacteria. By the 1970s, a system of Five Kingdom ...
... Until the 20th century, most biologists considered all living things to be classifiable as either a plant or an animal. But in the 1950s and 1960s, most biologists came to the realization that this system failed to accommodate the fungi, protists, and bacteria. By the 1970s, a system of Five Kingdom ...
What is a cell? - Epiphany Catholic School
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function ...
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function ...
1 - MrMBiology
... 54. Restriction enzymes cut double-stranded DNA at specific base sequence a. Between genes b. Producing fragments of four to eight base pairs in length c. Between bacterial and viral DNAs d. Between purines and pyrimidines e. Between promote and operator DNA sequences 55. The fragments of chromosom ...
... 54. Restriction enzymes cut double-stranded DNA at specific base sequence a. Between genes b. Producing fragments of four to eight base pairs in length c. Between bacterial and viral DNAs d. Between purines and pyrimidines e. Between promote and operator DNA sequences 55. The fragments of chromosom ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... using feedback mechanisms. 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D. While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state c ...
... using feedback mechanisms. 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D. While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state c ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the
... using feedback mechanisms. 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D. While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state c ...
... using feedback mechanisms. 1. Feedback mechanisms are cycles in which the product of one reaction causes another to start or stop. D. While organisms are balanced, they are not unchanging. The term used to describe the balanced state is dynamic equilibrium. 1. Dynamic Equilibrium: A balanced state c ...
Bio Sem I review
... Genetic engineering – method of altering a gene to add change or delete a trait. Ecosystems An ecosystem is made up of all of the biotic (living) and (nonliving) things in an environment Producers- autotrophs- plants- make their own food by photosynthesis Consumers- heterotrophs- rely on pro ...
... Genetic engineering – method of altering a gene to add change or delete a trait. Ecosystems An ecosystem is made up of all of the biotic (living) and (nonliving) things in an environment Producers- autotrophs- plants- make their own food by photosynthesis Consumers- heterotrophs- rely on pro ...
LECTURE OUTLINE 1
... Nervous and Hormonal systems -these 2 organ systems are dedicated to coordinating all other organ systems common design and functions -both systems penetrate the body tissues -tissue level of organization in the body] -both use a network NERVOUS SYSTEM -nervous system unique to Kingdom Anamalia -pri ...
... Nervous and Hormonal systems -these 2 organ systems are dedicated to coordinating all other organ systems common design and functions -both systems penetrate the body tissues -tissue level of organization in the body] -both use a network NERVOUS SYSTEM -nervous system unique to Kingdom Anamalia -pri ...
Biology Cell revision
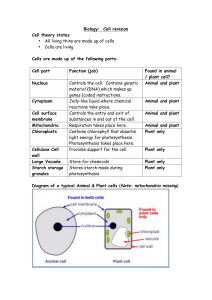
... Biology: Cell revision Cell theory states • All living thins are made up of cells • Cells are living Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell part ...
... Biology: Cell revision Cell theory states • All living thins are made up of cells • Cells are living Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell part ...
CASE STUDY ANALYSIS Biology 6 – Spring 2016
... For those who have already done this assignment in one of my previous classes, you should read the following 2 articles and summarize each in at least 600 words (i.e., 600 words each for a total of 1200 words). “Traces of a Distant Past” by Gary Stix, Scientific American, July 2008, pp. 56-63. “What ...
... For those who have already done this assignment in one of my previous classes, you should read the following 2 articles and summarize each in at least 600 words (i.e., 600 words each for a total of 1200 words). “Traces of a Distant Past” by Gary Stix, Scientific American, July 2008, pp. 56-63. “What ...
Bioinformatics Presentation by Susan Cates, Ph.D.
... Question 1: How many genes are found in the human genome? Question 2: How many DNA base pairs make up the human genome? Question 3: Name 2 project goals that will require the help of ...
... Question 1: How many genes are found in the human genome? Question 2: How many DNA base pairs make up the human genome? Question 3: Name 2 project goals that will require the help of ...
1999 AP Biology Exam - Speedway High School
... 46. A number of different phylogenies (evolutionary trees) have been proposed by scientists. These phylogenies are useful because they can be used to (A) determine when two similar populations of a species evolved into two separate species (B) evaluate which groups of organisms may be most closely r ...
... 46. A number of different phylogenies (evolutionary trees) have been proposed by scientists. These phylogenies are useful because they can be used to (A) determine when two similar populations of a species evolved into two separate species (B) evaluate which groups of organisms may be most closely r ...
Term 2 Exam 2 Study Guide Pt 2 File
... What are 2 types of insects that sometimes spread human diseases? What do termites eat? What is a pollinator? Why is it bad for some plants if the number of bees keeps going down? ...
... What are 2 types of insects that sometimes spread human diseases? What do termites eat? What is a pollinator? Why is it bad for some plants if the number of bees keeps going down? ...
Honors Biology Final Exam Review Mrs. Speirs Directions: In no
... tRNA (anticodon) (amino acid) sequence of amino acids protein the mRNA codon decoder box showing corresponding amino acids a frame shift mutation a deletion (one nucleotide) a point mutation (one nucleotide) a substitution (one nucleotide for another nucleotide) Given a sequence of amino acids, dete ...
... tRNA (anticodon) (amino acid) sequence of amino acids protein the mRNA codon decoder box showing corresponding amino acids a frame shift mutation a deletion (one nucleotide) a point mutation (one nucleotide) a substitution (one nucleotide for another nucleotide) Given a sequence of amino acids, dete ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.