Chapter 7 - Diversity - NCERT Ques Ans
... much over a period of time.As per the body design, the primitve organisms which hav simple structures are different from those so-called advanced organisms which have complex body structure and organization. 2. Will advanced organisms be the same as complex organisms? Why? Yes, because the advanced ...
... much over a period of time.As per the body design, the primitve organisms which hav simple structures are different from those so-called advanced organisms which have complex body structure and organization. 2. Will advanced organisms be the same as complex organisms? Why? Yes, because the advanced ...
Biology of Cancer
... 1. If retroviruses could activate c-src proto-oncogene into a potent oncogene, perhaps other carcinogens might operate in a similar way. 2. All of the transforming powers of RSV derived from the presence of a single gene – v-src. Thus, a single oncogene can change the shape, metabolism, and growth b ...
... 1. If retroviruses could activate c-src proto-oncogene into a potent oncogene, perhaps other carcinogens might operate in a similar way. 2. All of the transforming powers of RSV derived from the presence of a single gene – v-src. Thus, a single oncogene can change the shape, metabolism, and growth b ...
Biology EOC Review Packet
... http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology ...
... http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology ...
Biology EOC Review Packet
... http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology ...
... http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology ...
File
... • investigate and describe example scientific studies of the characteristics of living things (e.g., investigate and describe an ongoing scientific study of a locally-found organism) • apply the concept of system in describing familiar organisms and analyzing their general structure and function • i ...
... • investigate and describe example scientific studies of the characteristics of living things (e.g., investigate and describe an ongoing scientific study of a locally-found organism) • apply the concept of system in describing familiar organisms and analyzing their general structure and function • i ...
Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Everything on your digestion work package including structures, organs and their functions etc. Homeostasis Explain, using all the systems studies (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, how different animal systems, help maintain homeostasis (317-1) Circulatory Systems (general) Define circulatio ...
... Everything on your digestion work package including structures, organs and their functions etc. Homeostasis Explain, using all the systems studies (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, how different animal systems, help maintain homeostasis (317-1) Circulatory Systems (general) Define circulatio ...
Study guide packet part 1
... C. Ribosomes- these make the proteins in the cell D. Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy by Cellular respiration. E. Cell wall- this is not in animals. Provides protection and support for the cell F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis h ...
... C. Ribosomes- these make the proteins in the cell D. Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy by Cellular respiration. E. Cell wall- this is not in animals. Provides protection and support for the cell F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis h ...
Human Body Systems Unit Plan
... 1. How do organ systems interact with one another? 2. How do organ systems interact with their environment to meet basic needs? CURRICULAR COMPETENCIES ...
... 1. How do organ systems interact with one another? 2. How do organ systems interact with their environment to meet basic needs? CURRICULAR COMPETENCIES ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
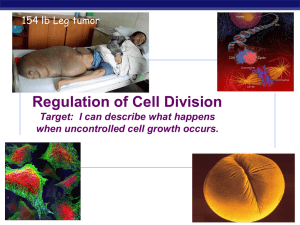
... chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
... chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
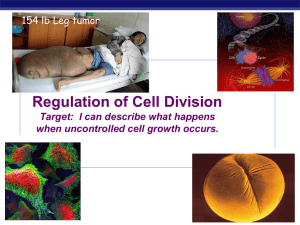
... chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
... chemical signals at critical points signals indicate if key cellular processes have been completed correctly ...
CELL
... • Cell theory was not formulated for nearly 200 years after the introduction of microscopy. ...
... • Cell theory was not formulated for nearly 200 years after the introduction of microscopy. ...
Sea Page 66
... Colonial Animal Animal in which many small individuals grow together, making one large body. Detritus Small bits of matter, such as decaying plant and animal parts, and animal waste. Provides food for some animals living in the deep, lightless regions of the ocean. Dichotomous Dividing or branching ...
... Colonial Animal Animal in which many small individuals grow together, making one large body. Detritus Small bits of matter, such as decaying plant and animal parts, and animal waste. Provides food for some animals living in the deep, lightless regions of the ocean. Dichotomous Dividing or branching ...
Biology Review
... bacteria in the mouth, a Swedish study suggests. The work challenges earlier suggestions that a diet rich in nitrates could pose a health risk. Joel Petersson was awarded his PhD by the University of Uppsala on May 9 for the study, which shows that rats fed on a nitrate-rich diet had a thicker layer ...
... bacteria in the mouth, a Swedish study suggests. The work challenges earlier suggestions that a diet rich in nitrates could pose a health risk. Joel Petersson was awarded his PhD by the University of Uppsala on May 9 for the study, which shows that rats fed on a nitrate-rich diet had a thicker layer ...
Document
... 26. Arrow A shows molecules going from an area of less concentration to an area of greater concentration, which is active transport because energy is needed to go against the concentration gradient. Passive transport is different in that it doesn’t need energy. 27. Receptor molecules, proteins on t ...
... 26. Arrow A shows molecules going from an area of less concentration to an area of greater concentration, which is active transport because energy is needed to go against the concentration gradient. Passive transport is different in that it doesn’t need energy. 27. Receptor molecules, proteins on t ...
Biology EOC Review - Lyman High School
... P. I created the system of binomial nomenclature using Latin. Q. I worked with Darwin on my own studies of populations. R. I supported the idea of biogenesis by my curved flask experiment. My name is a process to keep milk fresh. S. We found that methane, ammonia, hydrogen gases from early earth cha ...
... P. I created the system of binomial nomenclature using Latin. Q. I worked with Darwin on my own studies of populations. R. I supported the idea of biogenesis by my curved flask experiment. My name is a process to keep milk fresh. S. We found that methane, ammonia, hydrogen gases from early earth cha ...
Genus species
... species that have evolved from one common ancestral species. For natural classification, it is assumed that all members of that group shared a common ancestor at some point in their history. This can be seen in their structure. Unnatural or artificial classification for example would be birds and fl ...
... species that have evolved from one common ancestral species. For natural classification, it is assumed that all members of that group shared a common ancestor at some point in their history. This can be seen in their structure. Unnatural or artificial classification for example would be birds and fl ...
Honors Anatomy and Physiology
... and lipids are primary sources of energy, while ATP provides a reservoir of energy for cellular metabolism. Explain the processes of respiration (intracellular, extracellular) by which energy is released. Scale & Structure: Describe the hierarchy of molecular organization from biomolecules to co ...
... and lipids are primary sources of energy, while ATP provides a reservoir of energy for cellular metabolism. Explain the processes of respiration (intracellular, extracellular) by which energy is released. Scale & Structure: Describe the hierarchy of molecular organization from biomolecules to co ...
Cell - centralmountainbiology
... • “All organisms are made of one or more cells. • All the life functions of organisms occur within cells. • All cells come from already existing cells.” • Pgs. 56 – 58 ...
... • “All organisms are made of one or more cells. • All the life functions of organisms occur within cells. • All cells come from already existing cells.” • Pgs. 56 – 58 ...
Chapter 30: Comparing Invertebrates
... mollusks, arthropods, and the members of most of the minor ____________________________________________ ...
... mollusks, arthropods, and the members of most of the minor ____________________________________________ ...
Review Facts for the Biology SOL
... Information about relationships among present organisms and those that inhabited Earth in the past is gained by comparing developmental stages of organisms and by examining and interpreting the fossil record. This information is continually being gathered and used to modify and clarify existing cl ...
... Information about relationships among present organisms and those that inhabited Earth in the past is gained by comparing developmental stages of organisms and by examining and interpreting the fossil record. This information is continually being gathered and used to modify and clarify existing cl ...
Unit 1 Cellular Biology Test Review
... o Which type is the most powerful? o What is the earliest microscope? o What is the benefit of using a SEM vs. a TEM? o How is magnification calculated? (occipital lens x objective lens) Calculations – know how to calculate the magnification of a biological drawing! Cell Organelles o Know function ...
... o Which type is the most powerful? o What is the earliest microscope? o What is the benefit of using a SEM vs. a TEM? o How is magnification calculated? (occipital lens x objective lens) Calculations – know how to calculate the magnification of a biological drawing! Cell Organelles o Know function ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.