Important Evolutionary Advancement
... 1. Organisms are grouped together based on similarities and differences amongst their: a. Physical traits - structure (anatomy) and function (physiology) b. Biochemical composition - DNA (genes) and proteins 2. The taxa (groups) used to categorize organisms from general characteristics to more speci ...
... 1. Organisms are grouped together based on similarities and differences amongst their: a. Physical traits - structure (anatomy) and function (physiology) b. Biochemical composition - DNA (genes) and proteins 2. The taxa (groups) used to categorize organisms from general characteristics to more speci ...
Keystone Biology Practice Questions copy.pages
... C. The offspring plants have half the amount of genetic material.! D. The offspring plants contain genetic material from multiple plants.! 36. Under favorable conditions, the bacterium, E. coli, can divide to form two genetically-identical daughter cells in less than an hour. Which characteristic b ...
... C. The offspring plants have half the amount of genetic material.! D. The offspring plants contain genetic material from multiple plants.! 36. Under favorable conditions, the bacterium, E. coli, can divide to form two genetically-identical daughter cells in less than an hour. Which characteristic b ...
EOC Review Answer Key- Friday
... Fish might die at some point – living systems cannot handle too much increase in T. 6. Why would it be a bad idea to do this? Death of fish 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and pred ...
... Fish might die at some point – living systems cannot handle too much increase in T. 6. Why would it be a bad idea to do this? Death of fish 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and pred ...
Evolutionary Principles - Bremen High School District 228
... live on Earth today are related to each other by descent from common ancestors and that biological classifications are based on how organisms are related. Understand how to analyze fossil evidence with regard to mass extinction, episodic speciation, and biological diversity. Understand how scientifi ...
... live on Earth today are related to each other by descent from common ancestors and that biological classifications are based on how organisms are related. Understand how to analyze fossil evidence with regard to mass extinction, episodic speciation, and biological diversity. Understand how scientifi ...
GHSGT BIOLOGY REVIEW
... generation. He also said that traits not used would “waste away” This theory has been proven false. Charles Darwin developed the theory of natural selection. This theory states that animals who are better suited to their environments will live longer and reproduce more offspring, thus passing on the ...
... generation. He also said that traits not used would “waste away” This theory has been proven false. Charles Darwin developed the theory of natural selection. This theory states that animals who are better suited to their environments will live longer and reproduce more offspring, thus passing on the ...
Class: - 09 Chapter: - Diversity in Living Organisms
... sides. These are further sub- divided into schizocoelomates or protostomes(coelom formed due to splitting of mesoderm) and enterocoelomates or dueterostomes( coelom formed from pouches pinched off from endoderm) iii) Pseudo coelomate - these are organisms having false coelom. They have pouches of me ...
... sides. These are further sub- divided into schizocoelomates or protostomes(coelom formed due to splitting of mesoderm) and enterocoelomates or dueterostomes( coelom formed from pouches pinched off from endoderm) iii) Pseudo coelomate - these are organisms having false coelom. They have pouches of me ...
Topic 1 - Manhasset Public Schools
... 8. The ability to grow in size is a characteristic of living organisms. Although an icicle may grow in size over time, it is considered nonliving because there is ...
... 8. The ability to grow in size is a characteristic of living organisms. Although an icicle may grow in size over time, it is considered nonliving because there is ...
Background Metabolism shapes the cellular energy budget in
... control circuits for bacterial metabolism. Our primary goal will be to build a theory that links the architecture and parameters of feedback regulation with the resulting metabolic phenotypes. The mathematical work requires a combination of nonlinear ODE analysis, biochemical modeling and parameter ...
... control circuits for bacterial metabolism. Our primary goal will be to build a theory that links the architecture and parameters of feedback regulation with the resulting metabolic phenotypes. The mathematical work requires a combination of nonlinear ODE analysis, biochemical modeling and parameter ...
Chapter 18. - Spokane Public Schools
... for 1 gene, only ~1 mutation in 10 million replications each day, ~2,000 bacteria develop mutation in that gene but consider all 4300 genes, then: 4300 x 2000 = 9 million mutations per day per human host! ...
... for 1 gene, only ~1 mutation in 10 million replications each day, ~2,000 bacteria develop mutation in that gene but consider all 4300 genes, then: 4300 x 2000 = 9 million mutations per day per human host! ...
Course Specifications
... Functions and possibilities of all kinds of organels and cell processes Basic knowledge for plant and animal sciences, of genetics and of biochemistry ...
... Functions and possibilities of all kinds of organels and cell processes Basic knowledge for plant and animal sciences, of genetics and of biochemistry ...
Classification of Organisms
... based on evolutionary relationships. Homologous and analogous relationships are both important. 2. Cladistics: Grouping also based on evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characte ...
... based on evolutionary relationships. Homologous and analogous relationships are both important. 2. Cladistics: Grouping also based on evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characte ...
Classification of Organisms
... based on evolutionary relationships. Homologous and analogous relationships are both important. 2. Cladistics: Grouping also based on evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characte ...
... based on evolutionary relationships. Homologous and analogous relationships are both important. 2. Cladistics: Grouping also based on evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characte ...
Biology Undergraduate Scholarship Application
... stereotypy in male- and female-directed signals between two closely related bird species (Manacus: Aves). Evolution. Prado, F., Billo, T.J., and B. Kerr. 2009. Introgression of sexually-selected traits in lek-mating species. Evolutionary Ecology Research. (11): 1235-1250. http://timbillo.files.wordp ...
... stereotypy in male- and female-directed signals between two closely related bird species (Manacus: Aves). Evolution. Prado, F., Billo, T.J., and B. Kerr. 2009. Introgression of sexually-selected traits in lek-mating species. Evolutionary Ecology Research. (11): 1235-1250. http://timbillo.files.wordp ...
Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion
... Internal fertilization: is a form of animal fertilization of an ovum by spermatozoan within the body of an inseminated animal, whether female or hermaphrodite External fertilization: Those processes involved in the union of male and female sex cells outside the body of the female Compare sexual ...
... Internal fertilization: is a form of animal fertilization of an ovum by spermatozoan within the body of an inseminated animal, whether female or hermaphrodite External fertilization: Those processes involved in the union of male and female sex cells outside the body of the female Compare sexual ...
Classification Booklet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
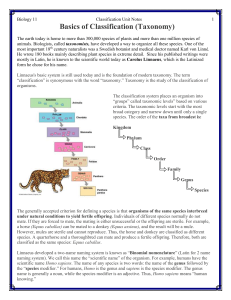
... The earth today is home to more than 300,000 species of plants and more than one million species of animals. Biologists, called taxonomists, have developed a way to organize all these species. One of the most important 18th century naturalists was a Swedish botanist and medical doctor named Karl von ...
... The earth today is home to more than 300,000 species of plants and more than one million species of animals. Biologists, called taxonomists, have developed a way to organize all these species. One of the most important 18th century naturalists was a Swedish botanist and medical doctor named Karl von ...
Epigenetics - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Epigenetics Originally defined as “ the branch of biology which studies the causal interactions between genes and their products, which brings the phenotype into being” Waddington, 1942 “The study of any potentially stable, and ideally, heritable change in gene expression or cellular phenotype that ...
... Epigenetics Originally defined as “ the branch of biology which studies the causal interactions between genes and their products, which brings the phenotype into being” Waddington, 1942 “The study of any potentially stable, and ideally, heritable change in gene expression or cellular phenotype that ...
IBO 1991 Theory_CCL - International Biology Olympiad
... a) transference some food elements from an organism to atmosphere; b) joining the most food elements to food webs through animals; c) increasing of population density in that regions where food elements storage are more than in another; d) number limitation of ecosystem organisms caused by shortage ...
... a) transference some food elements from an organism to atmosphere; b) joining the most food elements to food webs through animals; c) increasing of population density in that regions where food elements storage are more than in another; d) number limitation of ecosystem organisms caused by shortage ...
Overview of Kingdom Animalia
... • Specialized organs and organ systems can develop in coelem • Coelem cushions & protects internal organs, provides room for them to grow, and move independently within an animals body • Example: Earthworm ...
... • Specialized organs and organ systems can develop in coelem • Coelem cushions & protects internal organs, provides room for them to grow, and move independently within an animals body • Example: Earthworm ...
Name
... 1. __________________________ command center of the cell; contains DNA 2. __________________________ small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. __________________________ the site of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. __________________________ transport system of the cel ...
... 1. __________________________ command center of the cell; contains DNA 2. __________________________ small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. __________________________ the site of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. __________________________ transport system of the cel ...
Name: Period: ______ Biology Final Review Worksheet (24 pts
... c. insects trapped in tree sap d. All of the above __D__ 22. Darwin drew ideas for his theory from observations of organisms on a. the Samoan Islands. b. Manhattan Island. c. The Hawaiian Islands. d. The Galapagos Islands. __C__ 23. According to Darwin, evolution occurs a. only through artificial se ...
... c. insects trapped in tree sap d. All of the above __D__ 22. Darwin drew ideas for his theory from observations of organisms on a. the Samoan Islands. b. Manhattan Island. c. The Hawaiian Islands. d. The Galapagos Islands. __C__ 23. According to Darwin, evolution occurs a. only through artificial se ...
evidences of evolution - biology4isc
... of vertebrates can be explained on the basis that all of them have evolved from common ancestors. Thus, homology in structural organisation provides a convincing evidence for the concept of descent with modification. HOMOLOGY IN STRUCTURE OF HEART The heart is two chambered in fishes, with one auric ...
... of vertebrates can be explained on the basis that all of them have evolved from common ancestors. Thus, homology in structural organisation provides a convincing evidence for the concept of descent with modification. HOMOLOGY IN STRUCTURE OF HEART The heart is two chambered in fishes, with one auric ...
6.1.01a - UC CEAS
... Describe a malfunction that can occur in the system chosen. Your answer must include at least: The name of the system and a malfunction that can occur in this system. A description of a possible cause of the malfunction identified. An effect this malfunction may have on any other body systems. ...
... Describe a malfunction that can occur in the system chosen. Your answer must include at least: The name of the system and a malfunction that can occur in this system. A description of a possible cause of the malfunction identified. An effect this malfunction may have on any other body systems. ...
A study reveals how respiratory tubes and capillaries form
... A tube-cell image. In red, the tube; in blue, the cell nuclei; in green, cell shape. (electron microscopy). Credit: Copyright IRB Barcelona. J. Casanova Scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and CSIC report on the formation of the small-diameter respiratory tubes of ...
... A tube-cell image. In red, the tube; in blue, the cell nuclei; in green, cell shape. (electron microscopy). Credit: Copyright IRB Barcelona. J. Casanova Scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and CSIC report on the formation of the small-diameter respiratory tubes of ...
Characteristics of organisms 08
... Fig 8.6 - Blood circulatory system and how it becomes complex from cellular level to system level ...
... Fig 8.6 - Blood circulatory system and how it becomes complex from cellular level to system level ...
StandardB1: INQUIRY, Reflection, And social implications
... B2.5B Explain how major systems and processes work together in animals and plants, including relationships between organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. Relate these to molecular functions. B2.5C Describe how energy is transferred and transformed from the Sun to energy-ri ...
... B2.5B Explain how major systems and processes work together in animals and plants, including relationships between organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. Relate these to molecular functions. B2.5C Describe how energy is transferred and transformed from the Sun to energy-ri ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.