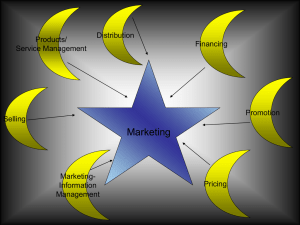
Relationship Marketing
... Promotional and selling activities aimed at developing and managing trusting and longterm relationships with larger customers. Customer profile, buying patterns, and history of contacts is maintained in a sales database, and a service representative (also called account executive) is assigned to one ...
... Promotional and selling activities aimed at developing and managing trusting and longterm relationships with larger customers. Customer profile, buying patterns, and history of contacts is maintained in a sales database, and a service representative (also called account executive) is assigned to one ...
Marketing Foundations
... are Not Satisfied • When businesses do not consider customer needs, it results in extra expenses of marketing products o They have to convince the customers to buy the product ...
... are Not Satisfied • When businesses do not consider customer needs, it results in extra expenses of marketing products o They have to convince the customers to buy the product ...
E-commerce marketing
... E-marketing requires a business to understand how and when their customers want to be contacted, and information they want to receive Plus they need to know how long customers are willing to gather information, order products, and work with customer service personnel. Not all on-line customers ...
... E-marketing requires a business to understand how and when their customers want to be contacted, and information they want to receive Plus they need to know how long customers are willing to gather information, order products, and work with customer service personnel. Not all on-line customers ...
case 6
... good service exists, and where giving good service to internal as well as ultimate, external customers is considered a natural way of life and one of the most important norms by everyone” Christian Gronroos “Managing Internal Marketing-a Prerequisite for Successful External Marketing” ...
... good service exists, and where giving good service to internal as well as ultimate, external customers is considered a natural way of life and one of the most important norms by everyone” Christian Gronroos “Managing Internal Marketing-a Prerequisite for Successful External Marketing” ...
7 P*s of Marketing
... right staff is required to create a competitive advantage. Customers make judgments about service provision and delivery based on the people representing your organization. This is because people are one of the few elements of the service that customers can see and interact with. Customers are likel ...
... right staff is required to create a competitive advantage. Customers make judgments about service provision and delivery based on the people representing your organization. This is because people are one of the few elements of the service that customers can see and interact with. Customers are likel ...
10x AS MUCH - Orange Element
... THE FIRST YEAR THAT MARKETING IS FULLY DRIVEN BY THE WANTS AND NEEDS OF THE CUSTOMER. ...
... THE FIRST YEAR THAT MARKETING IS FULLY DRIVEN BY THE WANTS AND NEEDS OF THE CUSTOMER. ...
Marketing of Services Course Outline Sept 2011
... The course is intended to augment the coverage of traditional marketing courses, which are based primarily on tangible goods, instead of intangible services. Intangible services include transportation services such as air, rail and bus; accommodations; tourism; entertainment; education; consulting; ...
... The course is intended to augment the coverage of traditional marketing courses, which are based primarily on tangible goods, instead of intangible services. Intangible services include transportation services such as air, rail and bus; accommodations; tourism; entertainment; education; consulting; ...
Marketing Mix
... The marketing mix is the combination of marketing activities that an organisation engages in so as to best meet the needs of its targeted market. Traditionally the marketing mix consisted of just 4 Ps. Getting the mix of these elements right enables the organisation to meet its marketing objectives ...
... The marketing mix is the combination of marketing activities that an organisation engages in so as to best meet the needs of its targeted market. Traditionally the marketing mix consisted of just 4 Ps. Getting the mix of these elements right enables the organisation to meet its marketing objectives ...
Experiential Marketing
... Chain of Phenomenon Alexandra Richardson Marketing, Media, and Communication II ...
... Chain of Phenomenon Alexandra Richardson Marketing, Media, and Communication II ...
Example #1 - West Salem High School
... of the item, then you design a way to promote the product. Next decided how you are going to sell it and then make decisions on how to market the product. Next you finance the product and price it. Now you promote it and get people to ...
... of the item, then you design a way to promote the product. Next decided how you are going to sell it and then make decisions on how to market the product. Next you finance the product and price it. Now you promote it and get people to ...
Service products
... ‘A service is an activity which benefits recipients even though they own nothing extra as a result.’ (Masterson and Pickton, 2010: 241) ...
... ‘A service is an activity which benefits recipients even though they own nothing extra as a result.’ (Masterson and Pickton, 2010: 241) ...
A VALUE-DELIVERY CONCEPT OF MARKETING Marketing is the
... A VALUE-DELIVERY CONCEPT OF MARKETING Marketing is the process of defining, developing, and delivering value to customers ...
... A VALUE-DELIVERY CONCEPT OF MARKETING Marketing is the process of defining, developing, and delivering value to customers ...
7 Key Marketing Functions
... Example: General Motors offers loans to customers through its GMAC division. ...
... Example: General Motors offers loans to customers through its GMAC division. ...
DOWNLOAD - Midterm Jeopardy - 2nd Game
... _____ are low-growth, high share businesses or products. They generate a lot of cash that the firm uses to pay its bills and support other SBUs that need investment. ...
... _____ are low-growth, high share businesses or products. They generate a lot of cash that the firm uses to pay its bills and support other SBUs that need investment. ...
Marketing Functions Defined
... customer satisfaction. For example, at The Limited, Taylor searches for a birthday present for her sister, when Gwen (a sales associate) asks if she could help her find the ...
... customer satisfaction. For example, at The Limited, Taylor searches for a birthday present for her sister, when Gwen (a sales associate) asks if she could help her find the ...
SEM Basics PPT 1
... The marketing concept is… • A business approach that directs all marketing efforts towards satisfying customer’s needs and wants. • Understanding that everything a business does revolves around the customer. • The customer is # 1. • The customer is always right. ...
... The marketing concept is… • A business approach that directs all marketing efforts towards satisfying customer’s needs and wants. • Understanding that everything a business does revolves around the customer. • The customer is # 1. • The customer is always right. ...
KotlerMM_ch13 - UMM Directory
... • What are the characteristics of products and how can they be classified? • How can companies differentiate products? • How can a company build and manage its product mix and product lines? • How can companies combine products to create strong co-brands or ingredient brands? • How can companies use ...
... • What are the characteristics of products and how can they be classified? • How can companies differentiate products? • How can a company build and manage its product mix and product lines? • How can companies combine products to create strong co-brands or ingredient brands? • How can companies use ...
Understand Opportunity
... • Sole Proprietorship – One individual (or married couple) in business alone. – Most common form of entrepreneurship ...
... • Sole Proprietorship – One individual (or married couple) in business alone. – Most common form of entrepreneurship ...
2.01 Recognize the importance of marketing.
... • List five products your family uses that now have lowered or reduced prices • List five stores which have lowered their prices ...
... • List five products your family uses that now have lowered or reduced prices • List five stores which have lowered their prices ...
Abstract - Florida Atlantic University
... advanced economy like the U.S., which is mainly service-based, services marketing forms an essential ingredient of the offerings mix of any organization. Better serviceproviding capability leads to smoother business functions for all parties involved in the exchange processes. Reduced transaction co ...
... advanced economy like the U.S., which is mainly service-based, services marketing forms an essential ingredient of the offerings mix of any organization. Better serviceproviding capability leads to smoother business functions for all parties involved in the exchange processes. Reduced transaction co ...
Chapter8-McKinsey`s Eight Technology Trends to Watch for 2008
... marketing (such as viral marketing), and the after-sales process get better insights into customer needs and behavior and may be able to cut the cost of acquiring customers, engender greater loyalty, and speed up development cycles”. ...
... marketing (such as viral marketing), and the after-sales process get better insights into customer needs and behavior and may be able to cut the cost of acquiring customers, engender greater loyalty, and speed up development cycles”. ...
What is marketing questions 12
... The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives. What are the two main areas of socially responsible marketing? The two main areas of socially responsibl ...
... The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives. What are the two main areas of socially responsible marketing? The two main areas of socially responsibl ...
Customer markets
... – Increase in intensity of competition coupled with higher market uncertainty ...
... – Increase in intensity of competition coupled with higher market uncertainty ...