CRIME PREVENTION THROUGH ENVIRONMENTAL DESIGN
... 1) Very Efficient - 20-28,000 hrs. life 2) Can cut through fog and allow the eyes to see detail at greater distance ( used on streets & parking lots ) 3) In some cases it can be used with CCTV ...
... 1) Very Efficient - 20-28,000 hrs. life 2) Can cut through fog and allow the eyes to see detail at greater distance ( used on streets & parking lots ) 3) In some cases it can be used with CCTV ...
Ch25 lecture 2 Refraction S2017
... A diverging lens has a focal length of –32 cm. An object is placed 19 cm in front of this lens. Calculate (a) the image distance and (b) the magnification (c) Is the image real or virtual? (d) Is the image upright or inverted? (e) Is the image enlarged or reduced in size? (f) Draw a ray diagram. ...
... A diverging lens has a focal length of –32 cm. An object is placed 19 cm in front of this lens. Calculate (a) the image distance and (b) the magnification (c) Is the image real or virtual? (d) Is the image upright or inverted? (e) Is the image enlarged or reduced in size? (f) Draw a ray diagram. ...
Lighting For Security
... 1) Very Efficient - 20-28,000 hrs. life 2) Can cut through fog and allow the eyes to see detail at greater distance ( used on streets & parking lots ) 3) In some cases it can be used with CCTV ...
... 1) Very Efficient - 20-28,000 hrs. life 2) Can cut through fog and allow the eyes to see detail at greater distance ( used on streets & parking lots ) 3) In some cases it can be used with CCTV ...
Notes on Light Ch 13-14 - Oakland Schools Moodle
... vibrating up-down, or east west, or any diagonal combination of those. Take a minute to actually point north, and oscillate your hand in these directions. Light which is polarized, due to being emitted, reflected, or transmitted in a special way, only has its efield oscillating in one direction. If ...
... vibrating up-down, or east west, or any diagonal combination of those. Take a minute to actually point north, and oscillate your hand in these directions. Light which is polarized, due to being emitted, reflected, or transmitted in a special way, only has its efield oscillating in one direction. If ...
A Model for Light
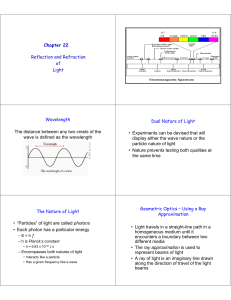
... In this chapter we will examine some experimental evidences in favor of the wave properties of light ...
... In this chapter we will examine some experimental evidences in favor of the wave properties of light ...
Properties of Light
... The bending occurs because the speed in which light travels through a substance depends on the substance's density. In air light travels at about 186,000 miles per second but in water light travels only about 140,000 miles per second (see chart below). Since light travels slower in water than in a ...
... The bending occurs because the speed in which light travels through a substance depends on the substance's density. In air light travels at about 186,000 miles per second but in water light travels only about 140,000 miles per second (see chart below). Since light travels slower in water than in a ...
Light Slides
... relative sensitivity of the human eye to light of various wavelengths. The center of the visible region is about 555 nm, which produces the sensation that we call yellow-green The limits of this visible spectrum are not well defined because the eye-sensitivity curve approaches the zero-sensitivity l ...
... relative sensitivity of the human eye to light of various wavelengths. The center of the visible region is about 555 nm, which produces the sensation that we call yellow-green The limits of this visible spectrum are not well defined because the eye-sensitivity curve approaches the zero-sensitivity l ...
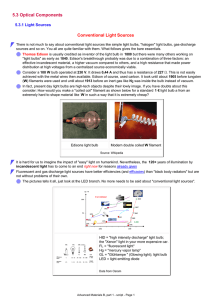
5.3 Optical Components Conventional Light Sources 5.3.1 Light Sources
... Light emitting diodes or LED's nowadays come in two variants: "Standard" LED's made from inorganic crystalline semiconductors based on, e.g., GAAlAs, GaP or GaN and "organic" LED's or OLED's. OLED devices are coming into their own right now (2011). They are not yet mass products for general lightnin ...
... Light emitting diodes or LED's nowadays come in two variants: "Standard" LED's made from inorganic crystalline semiconductors based on, e.g., GAAlAs, GaP or GaN and "organic" LED's or OLED's. OLED devices are coming into their own right now (2011). They are not yet mass products for general lightnin ...
Bioluminescence

Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria and terrestrial invertebrates such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is produced by symbiotic organisms such as Vibrio bacteria.The principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves the light-emitting pigment luciferin and the enzyme luciferase, assisted by other proteins such as aequorin in some species. The enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin. In some species, the type of luciferin requires cofactors such as calcium or magnesium ions, and sometimes also the energy-carrying molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In evolution, luciferins vary little: one in particular, coelenterazine, is found in nine different animal (phyla), though in some of these, the animals obtain it through their diet. Conversely, luciferases vary widely in different species. Bioluminescence has arisen over forty times in evolutionary history.Both Aristotle and Pliny the Elder mentioned that damp wood sometimes gives off a glow and many centuries later Robert Boyle showed that oxygen was involved in the process, both in wood and in glow-worms. It was not until the late nineteenth century that bioluminescence was properly investigated. The phenomenon is widely distributed among animal groups, especially in marine environments where dinoflagellates cause phosphorescence in the surface layers of water. On land it occurs in fungi, bacteria and some groups of invertebrates, including insects.The uses of bioluminescence by animals include counter-illumination camouflage, mimicry of other animals, for example to lure prey, and signalling to other individuals of the same species, such as to attract mates. In the laboratory, luciferase-based systems are used in genetic engineering and for biomedical research. Other researchers are investigating the possibility of using bioluminescent systems for street and decorative lighting, and a bioluminescent plant has been created.